Changes in Nucleus and Cytoplast During Oocyte Maturation: Involvement in Embryo Production
Changes in Nucleus and Cytoplast During Oocyte Maturation: Involvement in Embryo Production
Rashid Al Zeidi1, Haitham Al Masruri2, Aiman Al Mufarji3, Abd El-Nasser Ahmed Mohammed3, Al-Hassan Mohammed4*
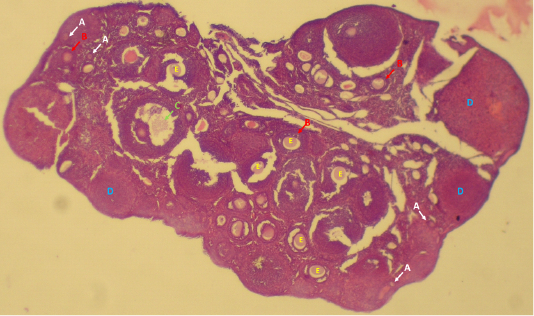
Ovarian follicle structures in mice; pre-antral follicles (A), antral follicles (B), preovulatory follicles (C), corpora lutea (D) and oocytes inside the follicles (E).
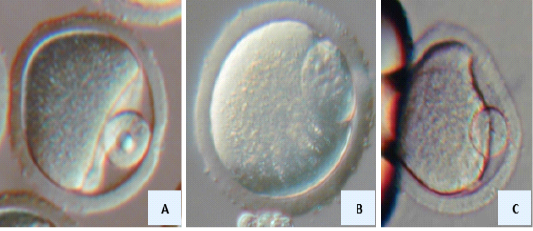
Aspiration of oocytes from follicles (A), antral follicle (B), the collected cumulus-enclosed germinal vesicle oocytes (C) stripped-off cumulus cells from the cumulus-enclosed germinal vesicle oocytes (D) in mice.
Germinal vesicle cytoplast used for germinal vesicle (A) embryonic (B) and somatic (C) nuclear transfer
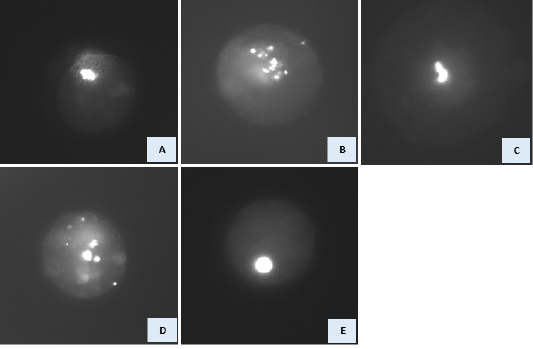
Nuclear morphology at the expected MI stage of GV cytoplasts reconstructed with GV, embryonic and somatic nuclei. DNA was stained with Hoechst 33342. A) GV cytoplast reconstructed with GV nucleus. Various abnormal nuclear morphology was observed in manipulated GV cytoplast reconstructed with embryonic/somatic at the expected MI stage. These include: condensed, scattered chromosomes (B), partially condensed chromosomes (C), formation of micronuclei and «pycnotic» nuclei (D), and interphase-like nuclei (E).
Reconstructed GV oocytes with somatic cells after 17 hr. of maturation. Extruded large-sized PBs (A, B), DNA was stained with Hoechst 33342 where the oocyte had scattered chromosomes (C), DNA was stained haematoxyline where the oocyte had interphase-like nucleus (D), the oocyte had partially condensed chromosomes (E) the oocyte had uneven distribution of chromatin (micronuclei)