Changes in the Intestinal Microbes of Wild Spermophilus dauricus (Rodentia: Sciuridae) in Different Periods of Hibernation (A Model of Gut Ischemic Reperfusion Injury)
Changes in the Intestinal Microbes of Wild Spermophilus dauricus (Rodentia: Sciuridae) in Different Periods of Hibernation (A Model of Gut Ischemic Reperfusion Injury)
Chun Shi, Juanjuan Guo, Meng Li, Qi Yang and Jingang Li*
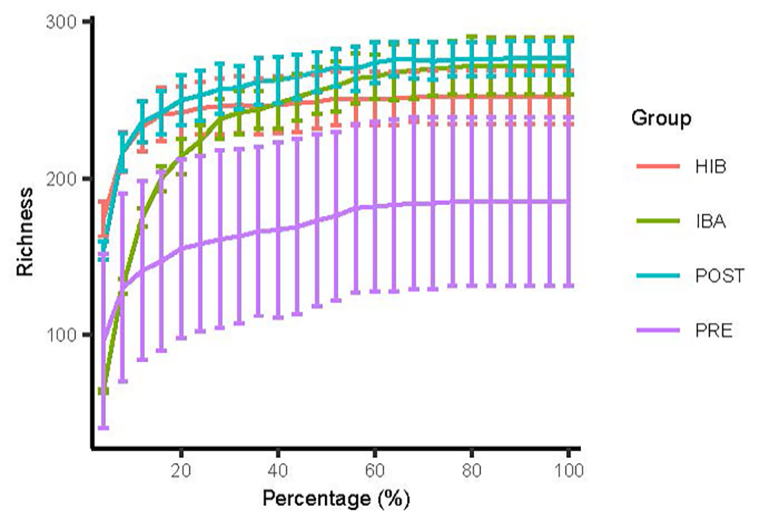
The rarefaction curves of all groups.
Comparison of the alpha diversities in all groups. Note: A-F depict the alpha diversity index of ACE, chao1, invsimpson, richness, Shannon, and simpson, respectively.
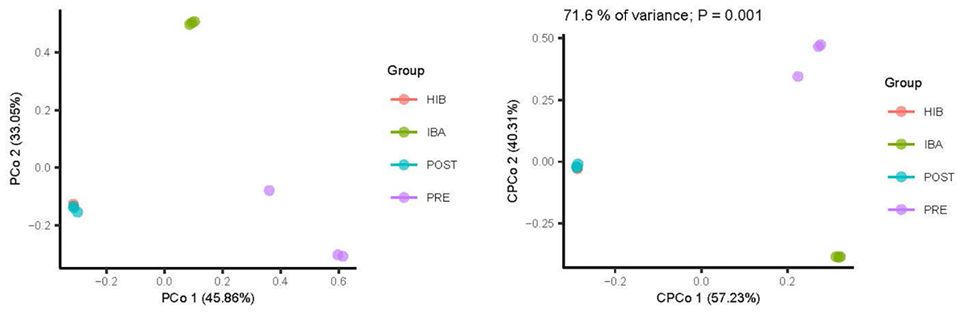
Beta diversity: Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) and constrained (PCoA) analyses of Bray-Curtis distance in all groups.
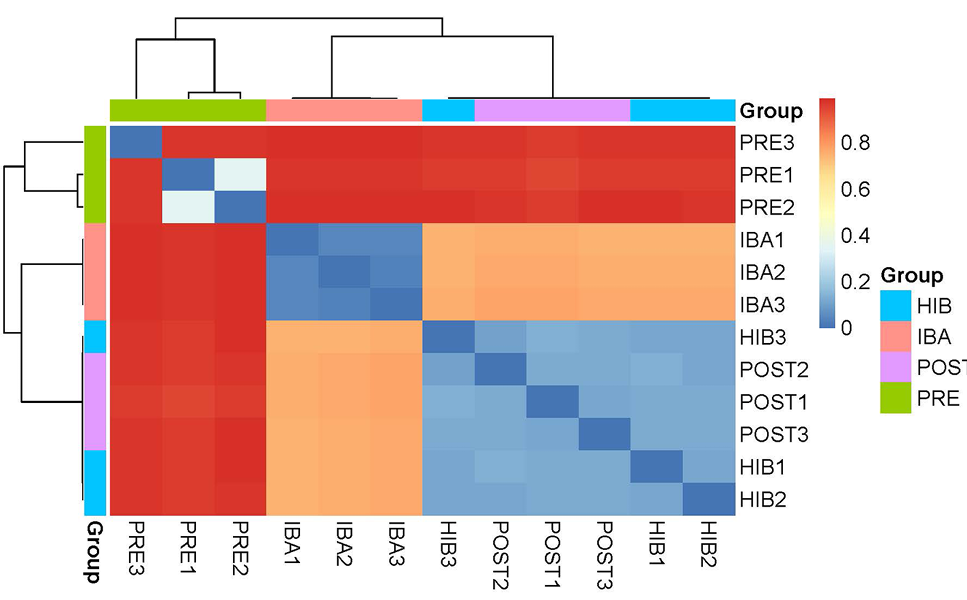
Beta diversity: Heatmap of the Bray-Curtis distance between each sample.
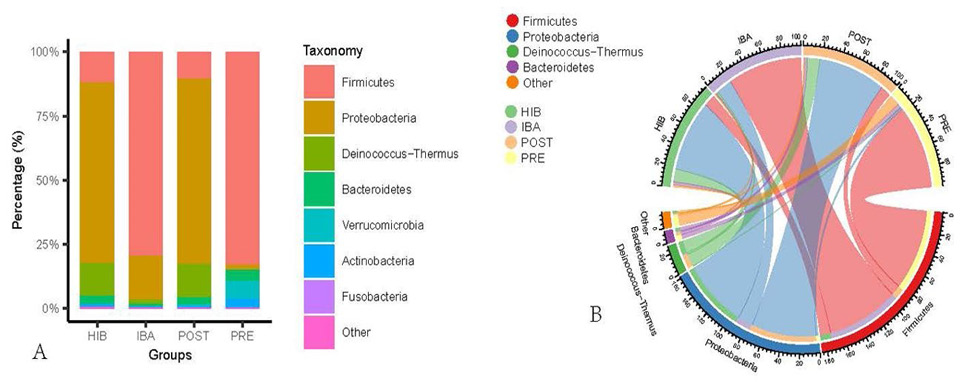
Bacterial community distribution at the phylum level. A, Stacked histogram of the intestinal bacterial abundance in each group at the phylum level (top 7). B, Chord diagram of intestinal bacterial abundance in each group at the phylum level (top 4).
Biomarkers predicted in LEfSe. A, LEfSe result in bar; B, LEfSe result in Cladogram.
Significant differences in bacterial abundance at the phylum level.
Significant differences in bacterial abundance at the genus level.
Venn figure of the OTUs in all groups.
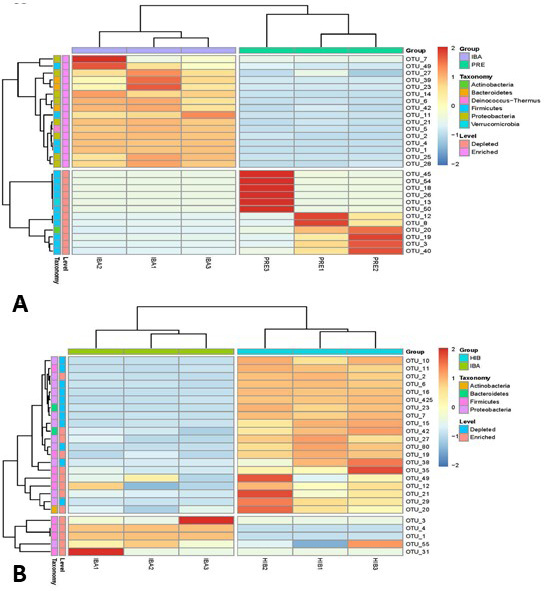
Manhattan chart of significant bacterial abundance at the phylum level in IBA, PRE, and HIB groups.
Manhattan chart of significant bacterial abundance at the genus level in IBA, PRE, and HIB groups.