Comparative Assessment of Hydroponic and Geoponic Cultivation Systems for Sustainable Spinach Cultivation
Comparative Assessment of Hydroponic and Geoponic Cultivation Systems for Sustainable Spinach Cultivation
Ain-ul-Abad Syed1*, Zaheer Ahmed Khan1, Shakeel Hussain Chattha1, Irfan Ahmed Shaikh2, Mian Noor Hussain Asghar Ali1, Zohaib ur Rehman Bughio3, Shahzad Hussain Dahri2 and Ghous Bakhsh Buriro4
Deep water culture reservoir system (used hydroponic model).
Net pots used in the study.
Air pump used in deep water culture model.
Full-spectrum light-emitting diode and PVC pipes light stand.
Schematic (a) top view and (b) side view of the hydroponic model (Dimensional view).
Graphical (a) top view and (b) side view of the hydroponic model (Functional view).
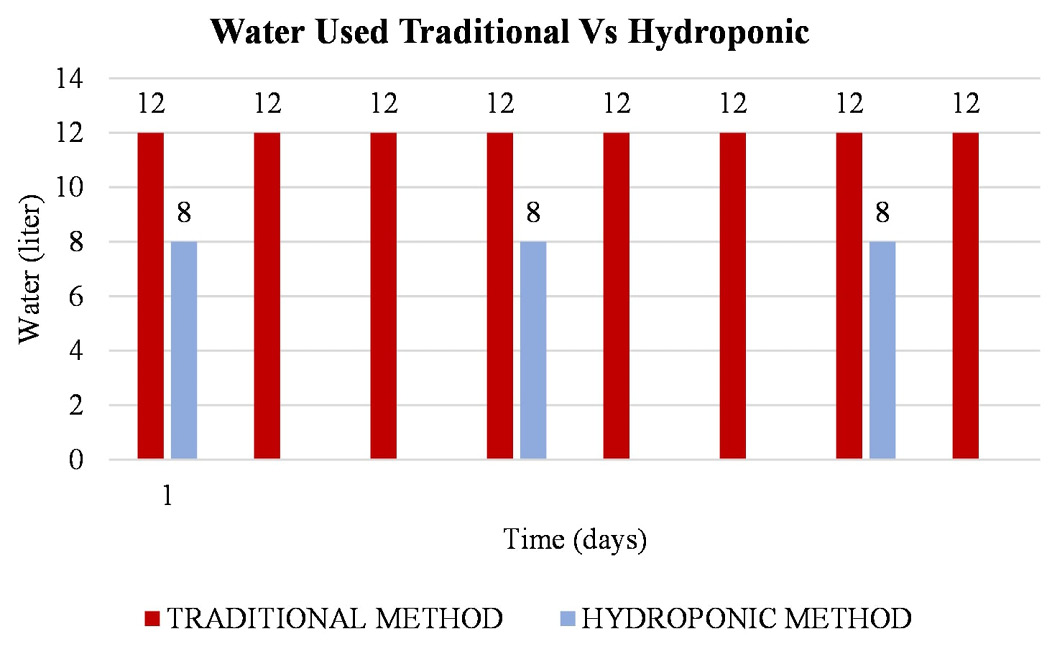
Water used hydroponic vs traditional.
Average (a) Height (b) stem size and (c) Leaf area.
Plant (a) Height (b) stem size and (c) Leaf area.