Complete Mitochondrial DNA Genome Sequences for Two Lineages in Coilia mystus (Clupeiformes: Engraulididae): Mitogenomic Perspective on the Phylogenetic Relationships of Genus Coilia
Complete Mitochondrial DNA Genome Sequences for Two Lineages in Coilia mystus (Clupeiformes: Engraulididae): Mitogenomic Perspective on the Phylogenetic Relationships of Genus Coilia
Ai Guo1,2,3, Jiaguang Xiao4, Binbin Shan4, Tianxiang Gao5 and Yongdong Zhou3,*
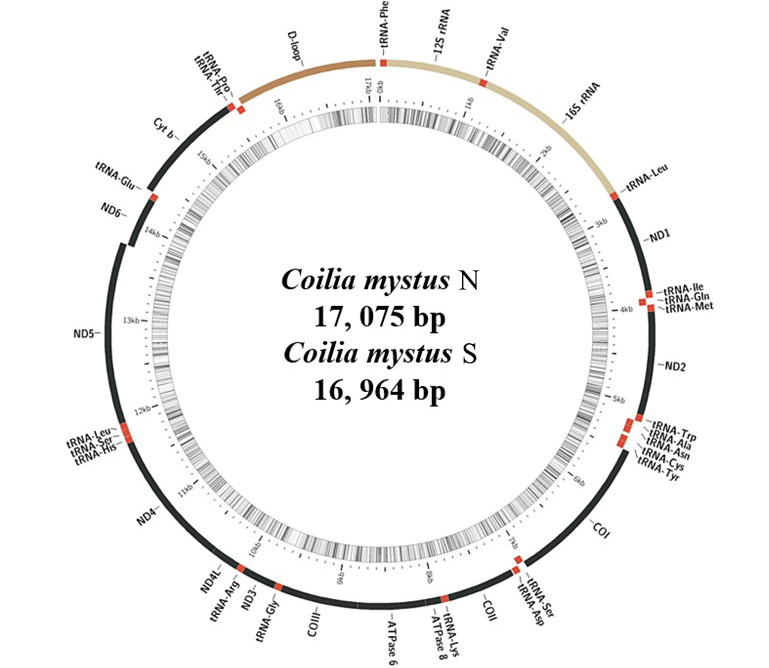
Gene organization for the mitochondrial genomes of the Coilia mystus N and Coilia mystus S. (C. mystus N and C. mystus S shared the same structural organization and gene arrangement, so only gene organization of C. mystus N were shown).
H-strand comparison of frequencies of codons ending with the same nucleotide. Values on the y-axis represent the sum of relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) values of codons ending with the same nucleotide across all codon families (x-axis).
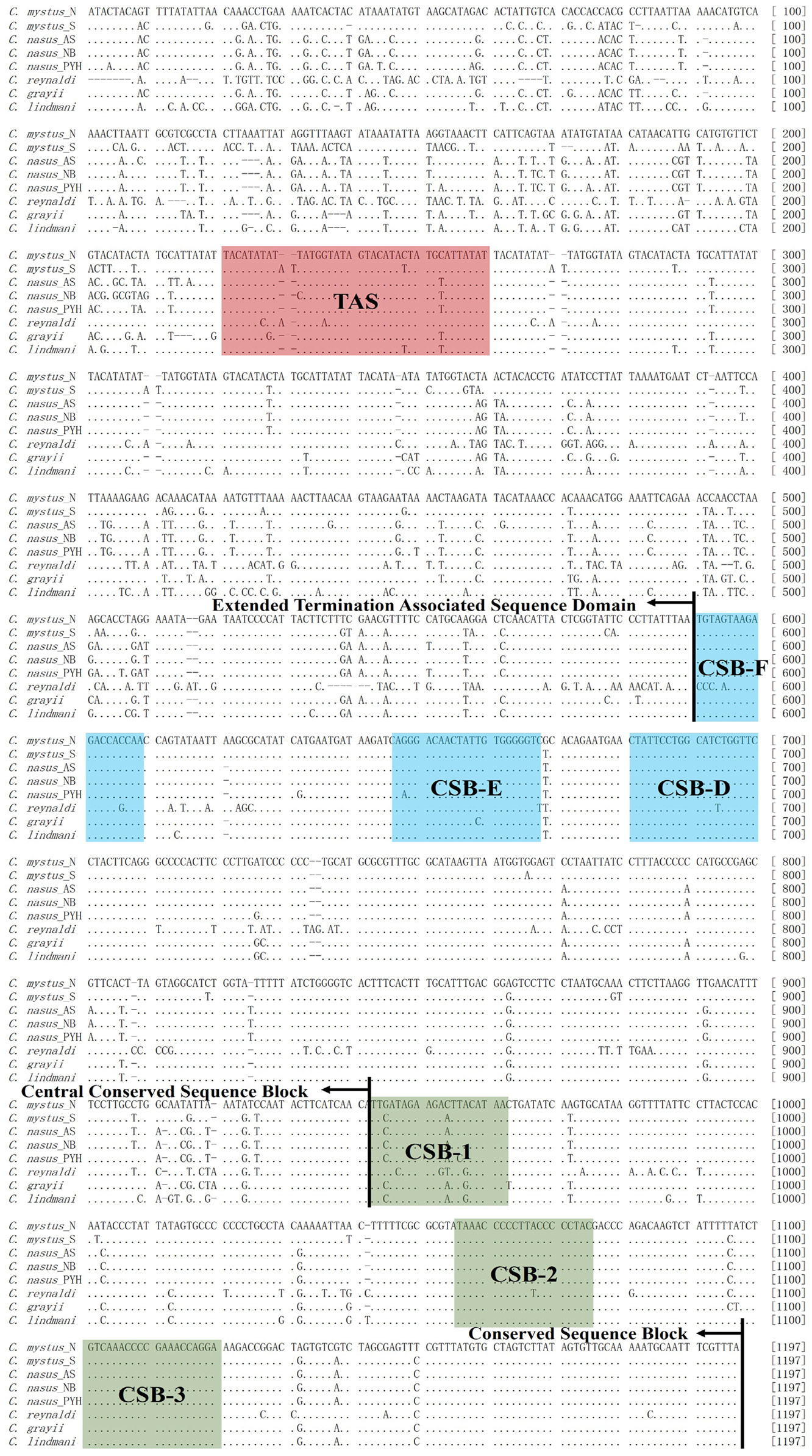
Complete nucleotide sequences of mitochondrial control region of Coilia. Termination associated sequence (TAS), central conserved sequences (CSB-F, -E, -D) and sequence blocks (CSB-1, -2, -3). VNTRs were embellished in the same times for sequences alignment.
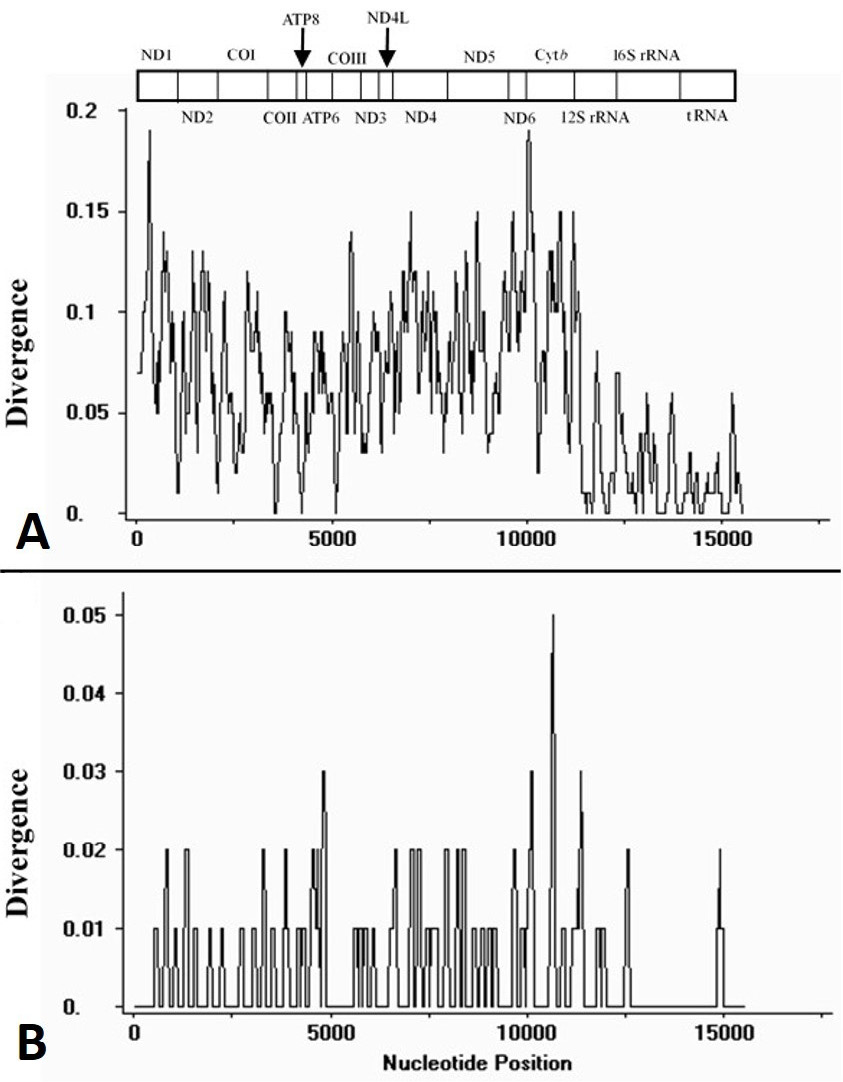
Plot of divergences among mtDNA sequences excluding non-coding regions. The sliding window analysis calculates the divergence of C. mystus N and C. mystus S (A), C. mystus N and C. mystus (KJ710625) (B), respectively. The bar at the top illustrates the position of protein-coding genes, rRNAs and tRNAs are represented as black boxes.
Inferred phylogenetic relationships among Coilia based on the concatenated nucleotide sequences of 13 mitochondrial protein-coding genes using maximum likelihood (ML) and Bayesian Inference (BI). Numbers on branches are bootstrap percentages and Bayesian posterior probabilities. Engraulis japonicas (NC_003097) and Engraulis encrasicolus (NC_009581) are used as outgroups.