Drivers of Electric Pylon Used as Nesting Sites by Birds in Baicheng City, China
Drivers of Electric Pylon Used as Nesting Sites by Birds in Baicheng City, China
Zheng Han1, Junbo Liu2, Jingyao Luan2, Changlong Gao2, Yufeng Tai2, He Liu2, Saipeng Zhang2, Guanqiang Zhai2, Xi Yang1,3, Haitao Wang1,4*
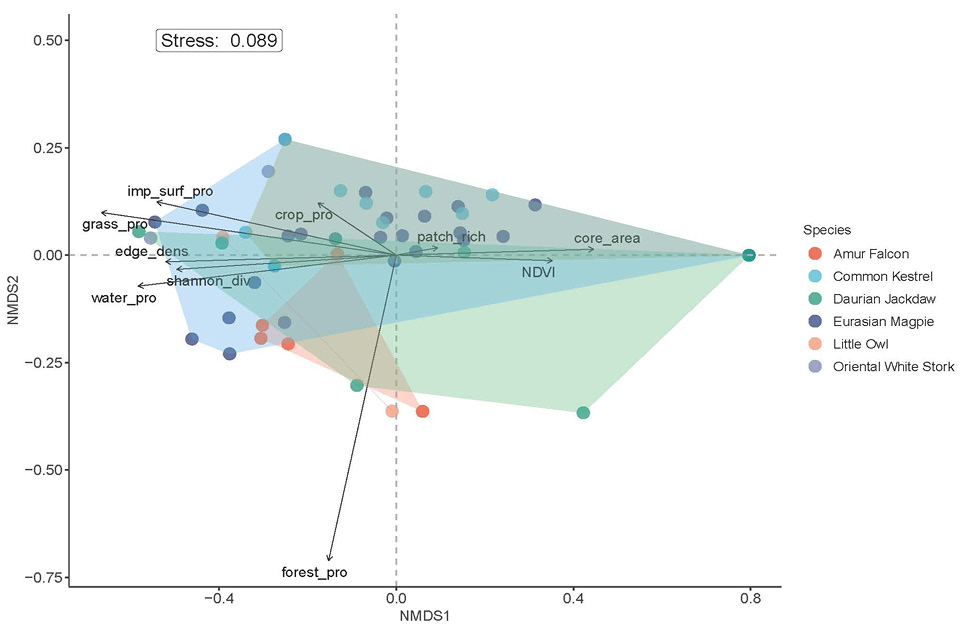
Non-metric multidimensional scaling plot based on the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity matrix for surrounding habitat features of occupied pylons by nesting birds. The proximity of species to arrows and their perpendicular distance along an arrow are measures of the relative influence of explanatory variables. Convex hulls connecting the vertices of the points showed how species cluster based on their occupied pylons’ habitat features.
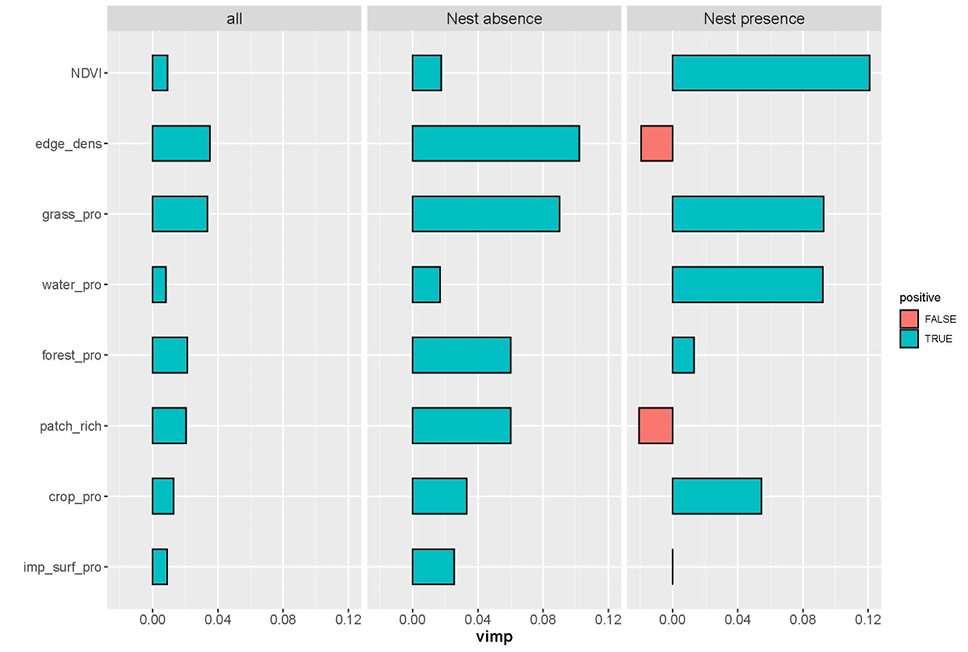
The variable importance (VIMP) plot for each habitat variable when predicting the presence and absence of nesting birds on electric pylons using random forest models.
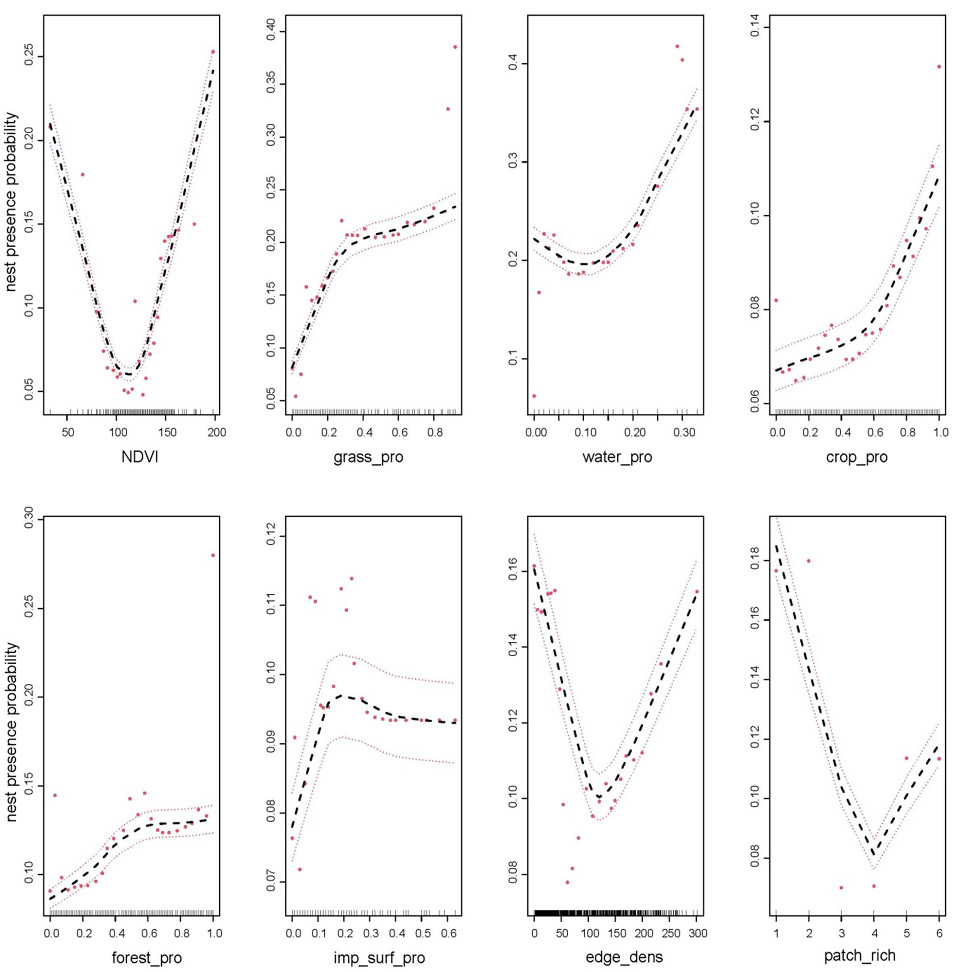
Partial dependence plots (representing estimated marginal effects when the remaining variables are held at their average) for eight environmental variables used in the Random Forest model. Variables are sorted by their relative importance in predicting nest presence on electric pylons.