FliI Role in Flagellar Assembly of Salmonella ΔfliI Mutant Strain Determines Motility and Biofilm Formation
FliI Role in Flagellar Assembly of Salmonella ΔfliI Mutant Strain Determines Motility and Biofilm Formation
Iram Liaqat1,*, Safdar Ali Mirza2, Sumera Sajjad3, Shaukat Ali1,*, Muhammad Faiz Qamar4 and Ikram Ul Haq5
Agarose gel electropherograms of the fliI from wild type and fliI complemented Salmonella using phusion PCR. 1st Lane, 1kb DNA ladder plus PageRulerTM Prestained Protein Ladder; 2nd Lane, fliI (wild type); 3rd – 5th Lane, fliI from fliI complemented Salmonella at different annealing temperatures of 60, 62 and 65°C.
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide electrophoresis pattern of FliI in whole-cell extracts from SJW2702, SWJ1102 (wild type Salmonella), and fliI complemented Salmonella strains induced with IPTG. 1st Lane, PageRuler™ Prestained protein ladder; 2nd Lane, without plasmid; 3rd Lane, with plasmid and in the absence of IPTG; 4th and 5th Lanes, with plasmid and in the presence of 2mM IPTG.
A, S. typhimurium growth curves. Three strains of Salmonella including wild type, S. typhimurium complemented fliI and SJW2702 (ΔfliI) were grown in Luria-Bertani broth at 37°C with aeration. Bacterial growth was determined by OD600. Data were obtained from the average of three independent experiments; B, specific growth rate of three strains.
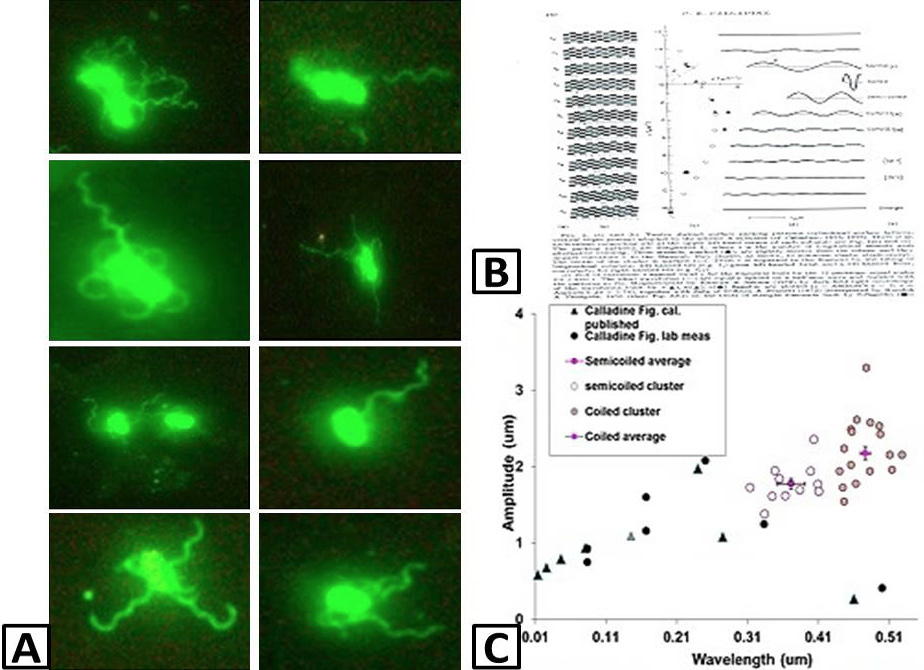
A, phased contrast microscopy of Alexa flour-488 labeled flagellar strains of fliI complemented Salmonella; B, Calladine (1975) model; C, polymorphic transitions were calculated in flagella following Calladine (1975) model and placed in semi-coiled category.
A, Time kinetics for Biofilm formation. Bacteria were grown for 16 hours and diluted in fresh Luria Bertani medium supplemented with antibiotic. Data was obtained from the average of three independent experiments. B, biofilm formation assays by wild type and fliI complemented Salmonella strains by liquid-interface coverslip assay. C, biofilm formation assays by wild type and fliI complemented Salmonella strains by test tube method. All three strains were grown in LB medium for 96 h. O.D was measured at 595 nm. fliI complemented Salmonella showed best biofilm formation compared to both wild type and fliI deleted SWJ2702. Experiment was performed in duplicate.