Foot-and-Mouth Disease Serotype SAT2 Outbreak in Iraqi Buffaloes: Molecular and Epidemiological Analysis
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Serotype SAT2 Outbreak in Iraqi Buffaloes: Molecular and Epidemiological Analysis
Thaer W. Enad*, Khalefa A. Mansour
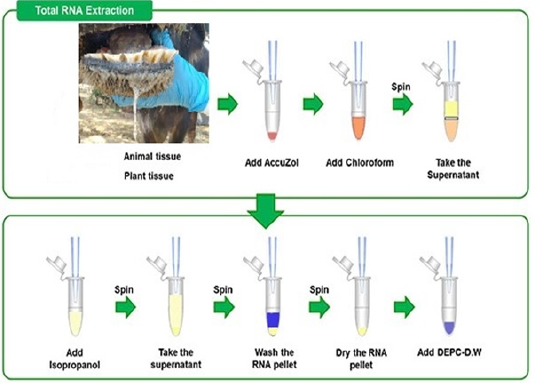
Steps of viral RNA extraction.
Shows clinical signs of FMD; A: Saliva hanging in long ropy strings; B: Nostril lesion.
Clinical signs of FMD; A: lesion of the oral cavity; B: lesion of coronary band.
Clinical signs of FMD in buffalo results.
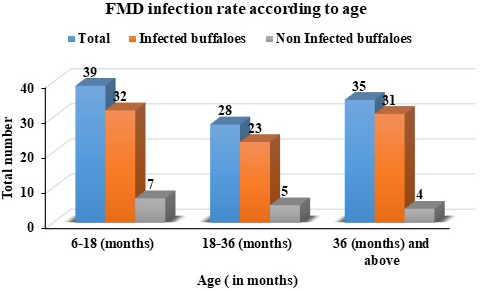
FMD infection rate according to age.
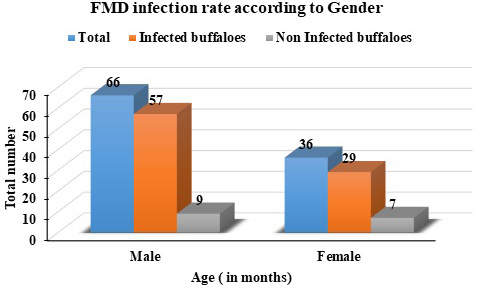
FMD infection rate according to gender.
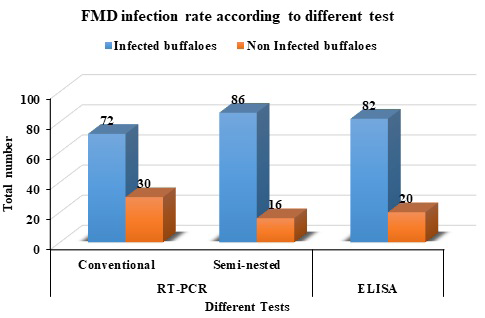
FMD infection rate in buffaloes based on the Different test.
The agarose electrophoresis for FMD SAT 2 (VP1) gene amplicon; lane 1-10 positive samples, the marker M (2000-100 bp). The amplicon size is 715 bp. Revers transcripts PCR.
The agarose electrophoresis of FMD (VP1) gene amplicon; lane 1-10 positive samples, the marker M (2000-100 bp); the amplicon size is 506 bp.