Genetic Transformation of Tobacco Serine Acetyltransferase 4 (NtSAT4) gene in Brassica napus L.
Genetic Transformation of Tobacco Serine Acetyltransferase 4 (NtSAT4) gene in Brassica napus L.
Hala Rajab1, Muhammad Sayyar Khan1*, Safdar Hussain Shah1 and Syed Mehar Ali Shah2
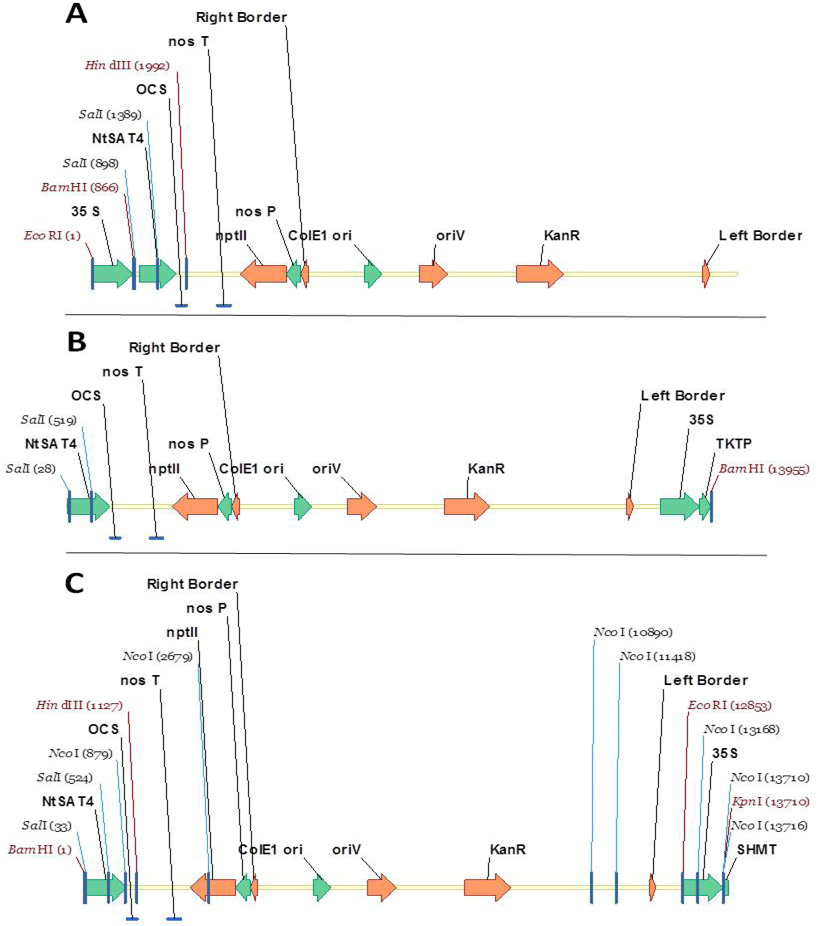
Overexpression construct of NtSAT4 targeting the three compartments; Expression vectors of the NtSAT4 gene is put under the 35S promoter in each of (A) Cytosolic targeted pBin-AR-NtSAT4 13717 bp; (B) Plastid targeted pBin-AR-TKTP-NtSAT4 13959 bp; (C) Mitochondrial targeted pBin-AR-SHMT-NtSAT4 13818 bp.
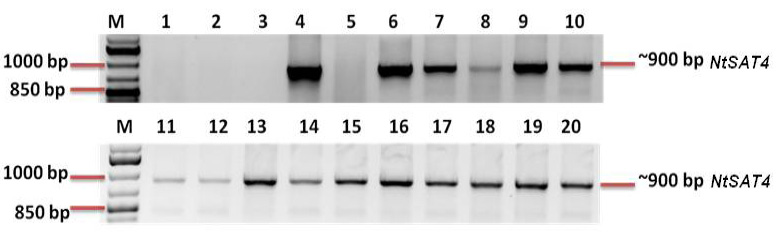
Genomic PCR characterization of the putative transformed NtSAT4 overexpression lines; PCR result (0.9 Kb) using genomic DNA against NtSAT4 gene specific primers. Lane M: DNA ladder 1kb plus; Lanes 1,2,3: wild-type B. napus as negative control; Lane 4: positive control; Lanes 5-20: examples of putatively transformed plants with the cytosolic; plastidic and mitochondrial NtSAT4 constructs.
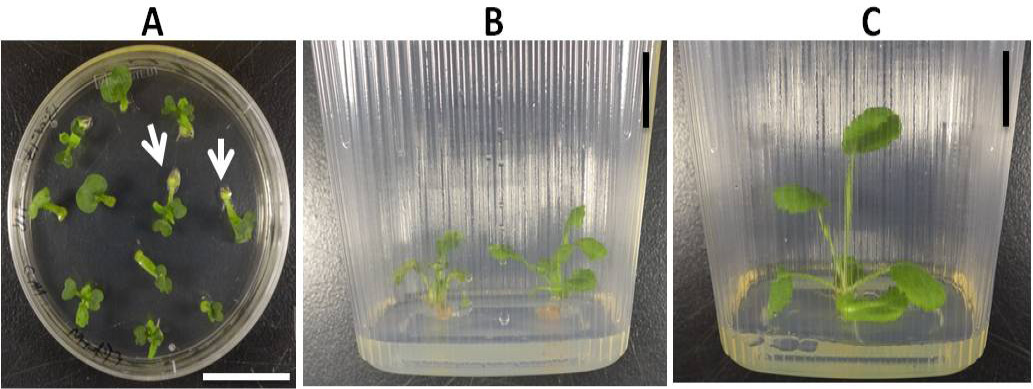
Development of transgenics through tissue culturing using hypocotyls explants; (A) Hypocotyls after infection growing on callus induction medium; (B) Shoot developed from the green callus outgrowth into small shoot and leaf; (C) The shoots turning brown and plants don’t develop roots; (D) Bleaching and purple coloration of shoots outgrowth in the presence of Kanamycin as a selective marker. Scale bar= 3cm.
Callus and shoot formation from cotyledon explants following infection with Agrobacterium AGl1 strain harboring NtSAT4 gene; (A) Callus induction of cotyledons after infection with Agrobacterium harboring NtSAT4 gene, growing in MS medium containing BAP 0.75 mgL-1, NAA 0.2 mgL-1 and GA3 0.1 mgL-1 grown at 25 oC under long day conditions. White arrows indicate the callus formation in the cotyledons; (B) Side-view of emerging shoots on shoot initiation medium (MS medium, BAP 3 mgL-1, NAA 0.2 mgL-1 and GA3 0.1 mgL-1 and kanamycin 25 mgL-1); (C) Plants surviving selection in MS media, BAP 0.0125 mgL-1 and kanamycin 50 mgL-1. Scale bar= 3cm.
Top view of supposedly non-transgenic plants on selection media; Non-transformed plants showed anthocyanin production and ultimate bleaching on long term exposure to kanamycin on MS media. Scale bar= 3cm.
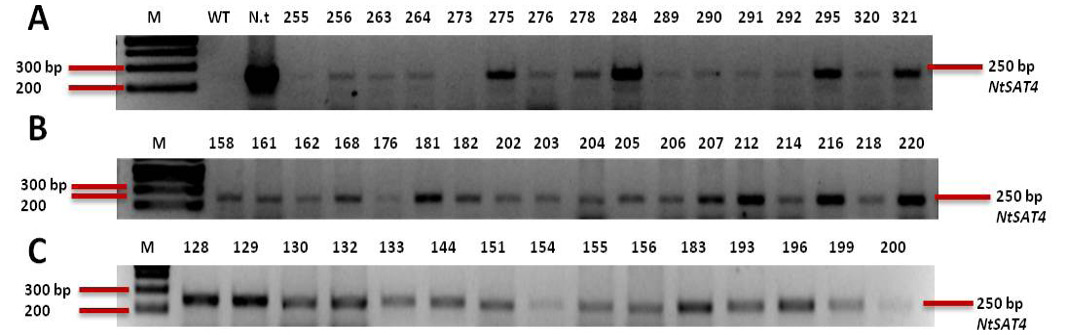
Analysis of gDNA PCR for the F1 transgenic samples run on 1.5 % agarose; Lanes; M: 1kb plus ladder; WT: B. napus wild-type (negative control); N.t: Nicotiana tabacum wild-type (positive control); The gels show the samples corresponding to different compartments; A: cytosolic lines gDNA samples; B: Plastidic lines; C: Mitochondrial lines.
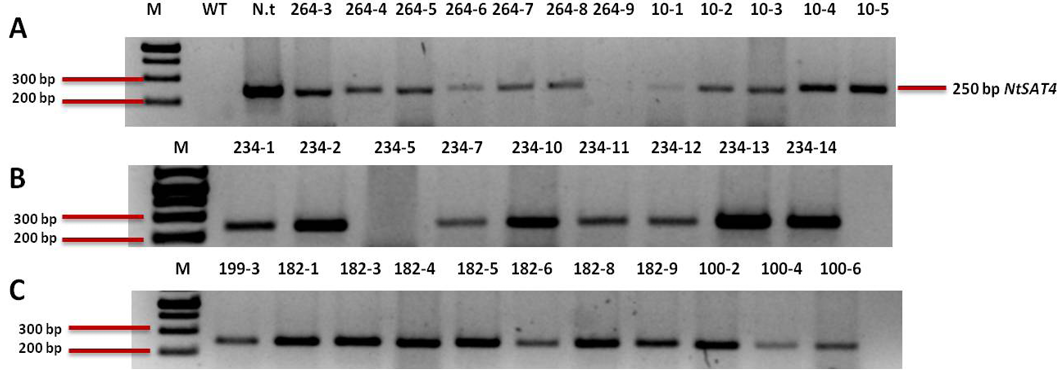
Analysis of gDNA PCR for the F2 transgenic samples run on 1.5 % agarose; Lanes; M: 1kb plus ladder; WT: B. napus wild-type (negative control); N.t: Nicotiana tabacum wild-type (positive control); Agarose gels result show the ands for samples corresponding to different compartments; A: cytosolic lines gDNA samples; B: Plastidic lines; C: Mitochondrial lines.
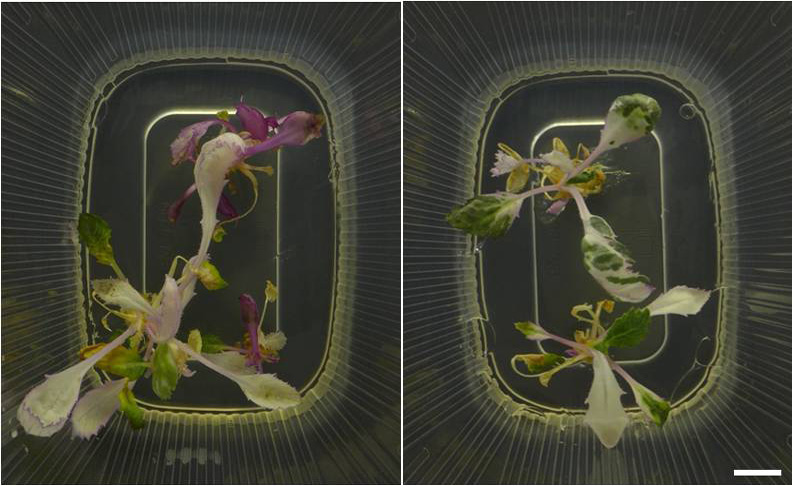
Root induction and acclimatization of plants in soil under controlled conditions; (A) Plantlets developed roots on half-MS media with IBA 3 mgL-1 (bottom view); (B) Plants transferred to soil to acclimatize under controlled long day conditions at 25 oC and kept covered to ensure high humidity. Scale bar = 3cm; B) Positive expressing NtSAT4 transgenic plantlets transferred to soil to acclimatize under controlled long day conditions at 25 oC and high humidity. Scale bar = 3cm; (C) Developed transgenic plant with early floral buds covered with perforated plastic bags to ensure self fertilization and seed setting.