Growth and Yield Response of Wheat to Organic Manures (Farm Yard Manure, Phospho-Compost (PROM) and Press Mud) Alone and in Combination with Mineral Fertilizer
Growth and Yield Response of Wheat to Organic Manures (Farm Yard Manure, Phospho-Compost (PROM) and Press Mud) Alone and in Combination with Mineral Fertilizer
Rana Aamir Shehzad1, Ghulam Sarwar1*, Sabir Hussain Shah2, Mukkram Ali Tahir1, Noor-us-Sabah1, Sher Muhammad2, Muhammad Aftab3, Muhammad Zeeshan Manzoor1, Imran Shehzad1 and Usman Saleem4
Impact of organic and inorganic sources of nutrients on height of wheat plants.
Impact organic and inorganic sources of nutrients on shoot dry weight of wheat.
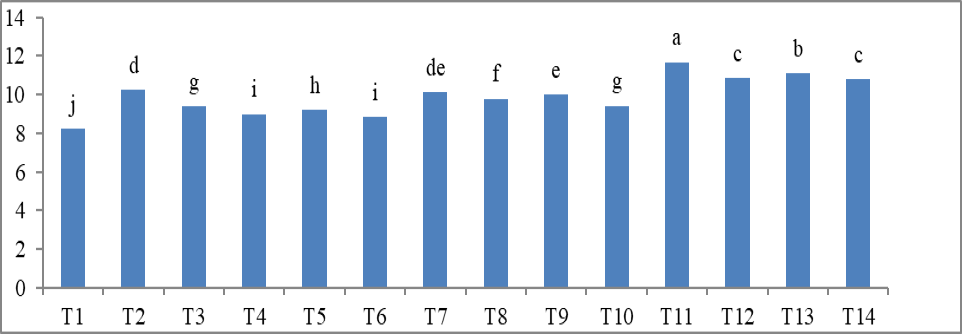
Impact of organic and inorganic sources of nutrients on length of spikes of wheat
Impact of organic and inorganic sources of nutrients on tiller numbers in a plant of wheat.
Impact of organic and inorganic sources of nutrients on weight of dry root (g) of wheat.
Impact of organic and inorganic sources of nutrients on root length (cm) of wheat.
Impact of organic and inorganic sources of nutrients on weight of 1000 grains (g) of wheat.
Impact of organic and inorganic sources of nutrients on biomass of wheat.