Immunomodulatory Effects of Calotropis procera on Human T-lymphocytes In Vitro
Immunomodulatory Effects of Calotropis procera on Human T-lymphocytes In Vitro
Sajida Batool, Iqra Ashraf, Shafaat Yar Khan, Sitara Shameem* and Breha Kazmi
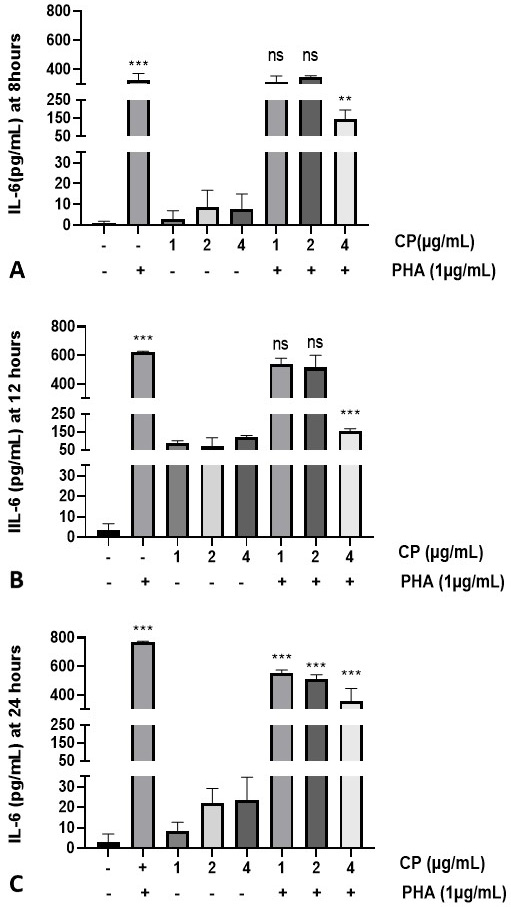
Effect of Calotropis procera on IL-6 production. At 8 (A), 12 (B) and 24 h (C) PHA stimulation of T-cells produced the IL-6 significantly (P<0.001) up to 357.1±47.48 pg/mL, 625.7 ± 8.08 pg/mL, and 772.9 ± 7.07 pg/mL respectively. While different doses of C. procera extract prevent the production of IL-6 by PHA stimulated T-cells. Data represents Mean±SD and analyzed by ANOVA with post-Tukey’s test (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001).
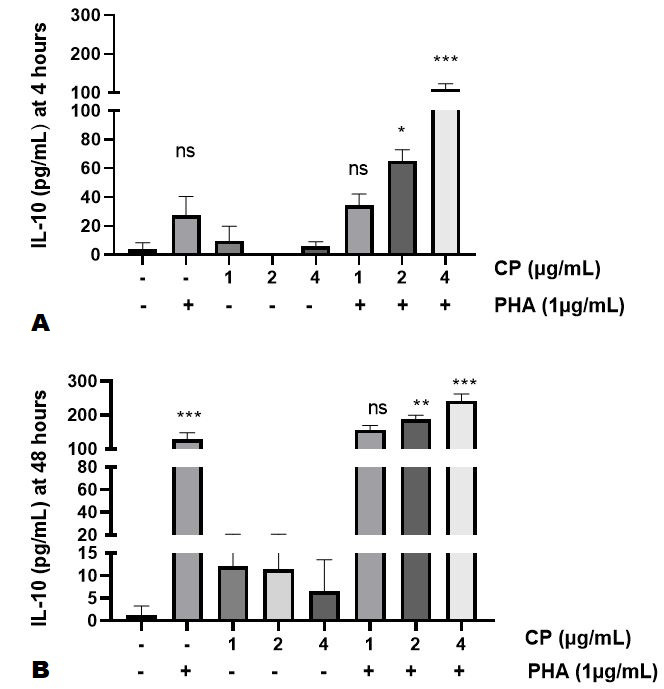
Effects of Calotropis procera on IL-10 production. T-cells stimulated with PHA (1 µg/mL) for 4 h did not a show significant increase in the concentration of IL-10 i.e. 36.55±12.16 pg/mL whereas stimulation for 48 h resulted in a considerable increase (P<0.01) up to 142.9±20.13 pg/mL in time-dependent manner as shown in (B). Methanolic leaf extracts of C. procera stimulates the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10) in dose-dependent manner. Data represent Mean±SD and analyzed by ANOVA followed by post-Tukey’s test (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001). CP, Calotropis procera; PHA, phytohaemagglutinin; IL-10, interleukin 10; pg/mL, pictogram per milliliter; µg/mL, microgram per milliliter; ns, non-significant.