Molecular Characterization of Mercury Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Tannery Wastewater
Molecular Characterization of Mercury Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Tannery Wastewater
Aatif Amin1,*, Zakia Latif2, Arslan Sarwar1, Basit Zeshan1 and Mushtaq A. Saleem1
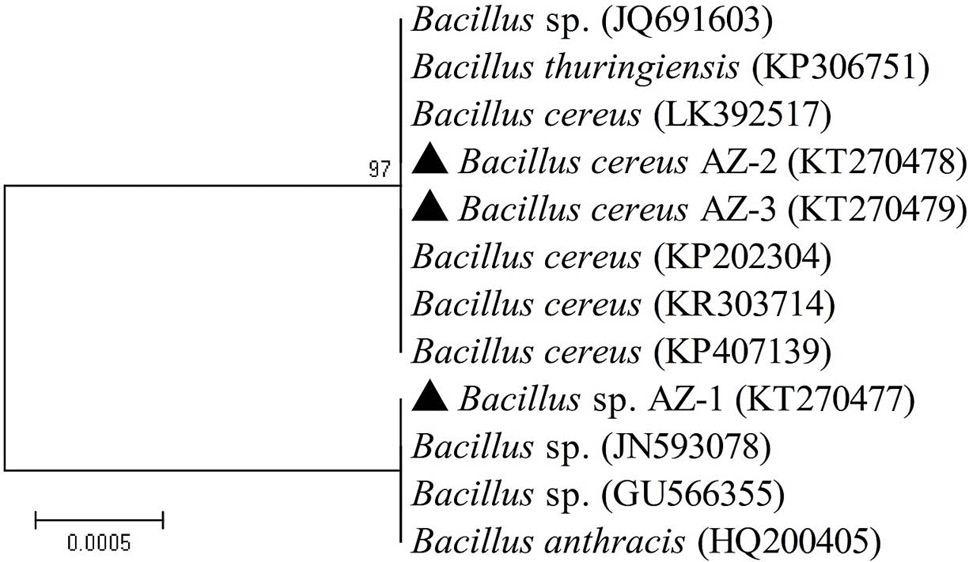
Evolutionary relationships of different Bacillus sp. on the basis of 16S rDNA ribotyping.
Evolutionary relationship of different Bacillus sp. on the basis of merA gene was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method with the sum of branch length 0.53623375. The branch lengths and the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree are in the same units with the bootstrap test value 500. The analysis involved 17 nucleotide sequences and codon positions included were 1st+2nd+3rd+Noncoding. A total of 1279 positions were in the final dataset with no gaps and missing data. Evolutionary analyses were performed by MEGA 5 software (Tamura et al., 2004).
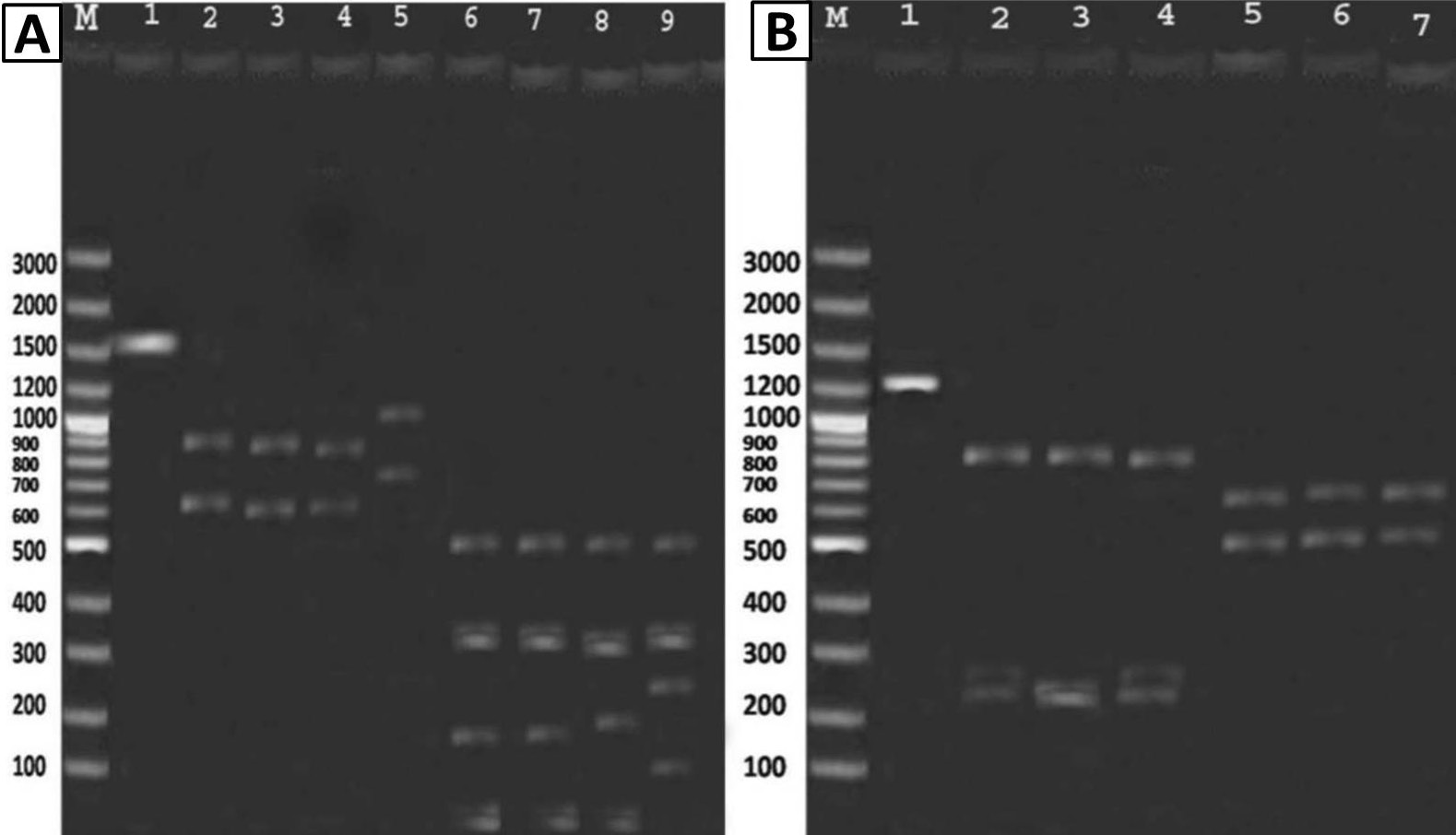
A, digested patterns for the 16S rDNA fragment from bacterial strains (HgR), Bacillus sp. AZ-1, B. cereus AZ-2, B. cereus AZ-3 and E. cloacae ZN-15 (HgS) (Lane M, size markers of 100 bp plus DNA Ladder; Lane 1, 1543bp PCR product of 16S rDNA fragment; Lanes 2-5, digested patterns of the 16S rDNA fragments by EcoR1; Lanes 6-9, digested patterns of the 16S rDNA fragments by Taq1); B, digested patterns for the merA gene from bacterial strains (HgR), Bacillus sp. AZ-1, B. cereus AZ-2 and B. cereus AZ-3 (Lane M, size markers of 100bp plus DNA Ladder; Lane 1, 1289bp PCR products of merA gene; Lanes 2-4, digested patterns of the merA gene by HinF1; Lanes 5-7, digested patterns of the merA gene by HaeIII).
Detoxification of Hg2+ by mercury resistant bacterial strains (p<0.05).