Multi Metal Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae KW is an Efficient Copper Accumulator and Bioremediator of Industrial Waste Water
Multi Metal Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae KW is an Efficient Copper Accumulator and Bioremediator of Industrial Waste Water
Maimoona Imran1,2, Soumble Zulfiqar2, Hafsa Saeed2 and Farah Rauf Shakoori1*
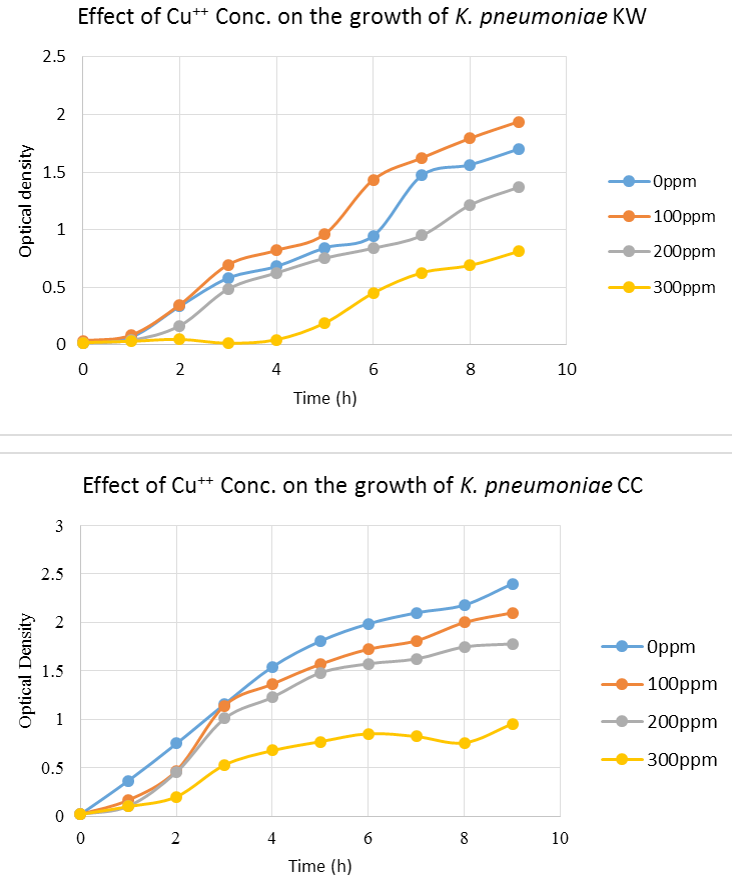
Effect of presence of different concentrations of Cu++ in the medium on the growth pattern of K. pneumoniae KW and CC. 300 ppm proved to be detrimental for the growth of both strains.
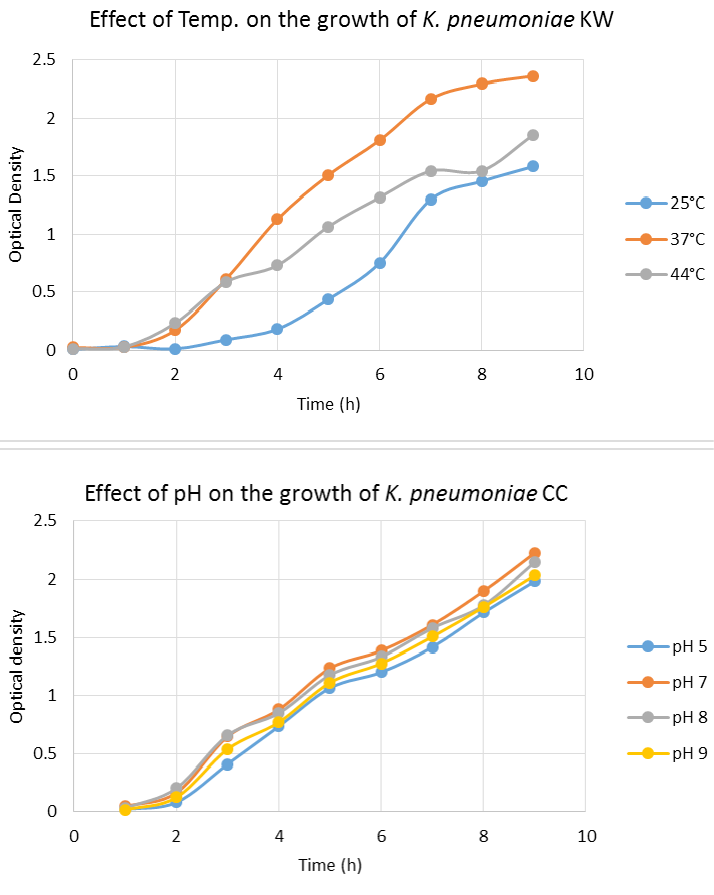
Effect of temperature and pH on growth pattern of K. pneumoniae KW and CC. Optimum temperature for both strains was determined as 37°C. Both strains appeared capable to survive and grow in a wide range of pH.
Cu++ uptake by K. pneumoniae KW and CC was determined in the presence of 100, 200 and 300ppm Cu++ in the medium. For simplicity, only one uptake value (the maximum one) between 3-7h is shown in graphs. CC exhibited more Cu++ accumulation ability as compared to KW. However, KW was found to possess more efficient efflux system.
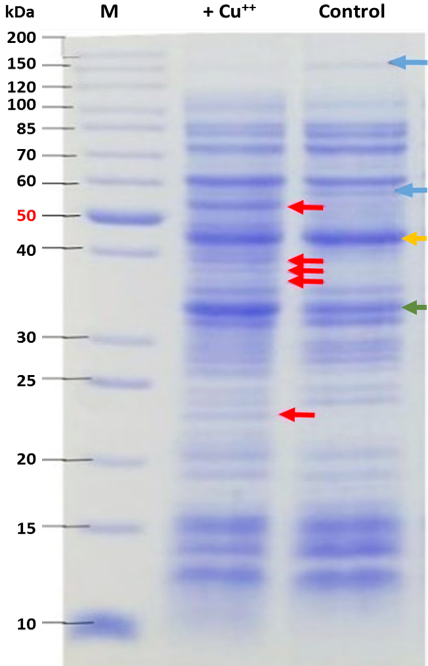
Protein profiles of Klebsiella pneumoniae KW grown in the absence and presence of copper were compared. Overexpression of a 45kDa protein (yellow arrow), low expression of a 33kDa protein (green arrow), disappearance or undetectable expression of proteins at 50, 30-35 and around 23kDa (red arrow) and appearance of 150 and 55kDa proteins (blue arrow) as result of the presence of Cu++ were detected.