Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Pasteurella Species Isolated from Camels in Egypt
Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Pasteurella Species Isolated from Camels in Egypt
M. Hanafy1, Rehab Elhelw2, Soliman M. Soliman3, Sherif Marouf2*
Sampling of suspected diseased camels; A: Nasal swabbing, B: Blood sampling.
Clinical presentation of the suspected diseased camels suffering respiratory distress; A: lethargy with depressed demeanor, B: oral breathing and ocular discharge, C: nasal discharge with difficult breathing, D and E: salivation and paralysis of lower lip, F: semi-closed eye lids with ocular discharge.
A: Growth of P. multocida on BHI agar plate, B: growth of M. haemolytica on blood agar plate with β-zone of hemolysis, C: growth of P. multocida on blood agar plate with no hemolysis, D: growth of P. multocida on MacConkey agar plate with lactose fermentation.
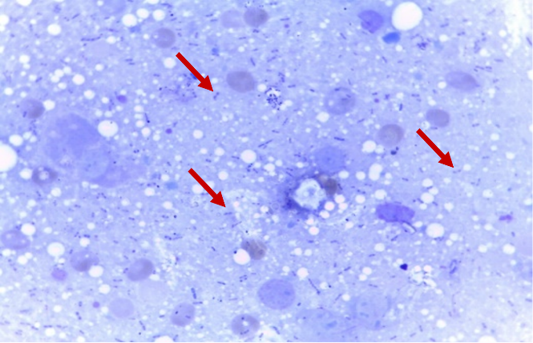
Smears of heart blood from dead mice stained with Leishman’s stain revealed the characteristic bipolarity of Pasteurella spp.
Agarose gel photo-documentation of conventional PCR on genetic material extracted from P. multocida strains as a molecular typing for detection of KMT1 gene. Lane L, Ladder (Molecular weight marker, 100-1000 bp); Lane P: positive control, Lanes 15, 17, 42, 45, 48, 61 positive samples with amplicon size of 460 bp, the rest lanes are negative samples.
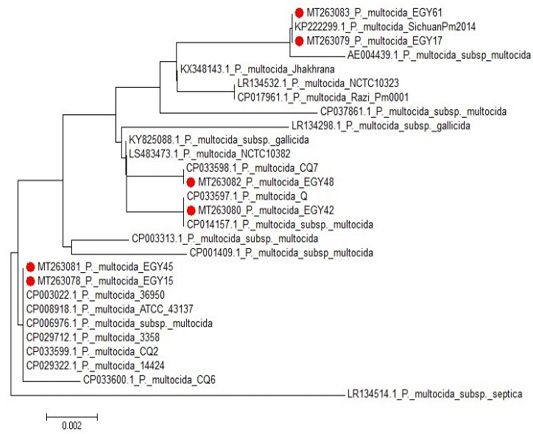
The Phylogenic tree (Neighbor joining tree) of the isolated P. multocida strains versus the ancestors.
The Sequence distance and the identity percentage between the isolated strains (P. multocida) and the common referral ancestors.
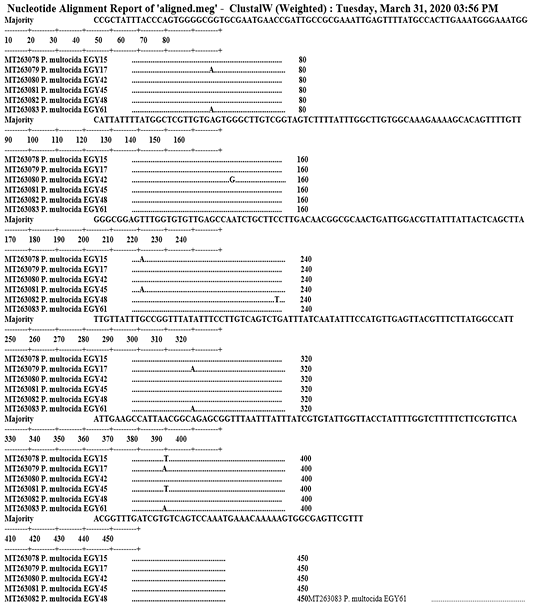
The Nucleotide Alignment Report of the isolated strains (Clustal W).