Prokaryotic Expression of the Toxoplasma gondii SAG2 Gene in Pet Cats and Establishment of an Indirect ELISA Method
Prokaryotic Expression of the Toxoplasma gondii SAG2 Gene in Pet Cats and Establishment of an Indirect ELISA Method
Liyun Chang1, Aiju Liu2, Jianshuang Zhang3, Yingbin Chen1 and Zhiyong Liu4*
Amplification of the SAG2 gene of T. gondii. M, DL1000 DNA marker; 1, SAG2 gene of T. gondii; 2, negative control results.
Restriction enzyme digestion analysis results of pET32a-SAG2. M, DL2000 plus DNA marker, 1, The product of recombinant plasmid double-enzyme digestion.
Expression of SAG2 gene in E. coli BL21. M, Marker; 1, Control plasmid expression; 2, Precipitation of recombinant bacteria; 3, Supernatant recombinant bacteria; 4, Recombinant bacteria.
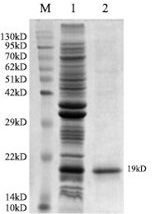
Recombinant SAG2 protein purification. M, Marker: (1) Precipitation of recombinant bacteria induced; (2) Purified recombinant protein.
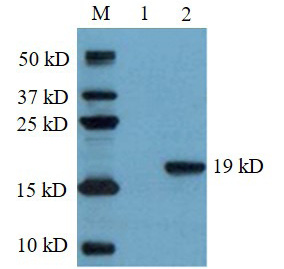
Recombinant protein identification by Western blot. M, Marker; (1) blank control; (2) purified recombinant protein.