The Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus on Alleviating Stress Response and Production Impairment Induced by Escherichia coli Lipopolysaccharide in Laying Hens
The Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus on Alleviating Stress Response and Production Impairment Induced by Escherichia coli Lipopolysaccharide in Laying Hens
Abdulaziz A. Alaqil*
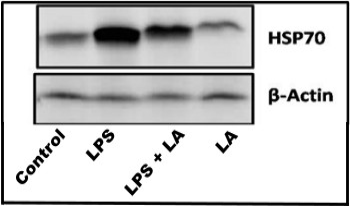
Effect of dietary Lactobacillus acidophilus (LA) supplementation and lipopolysaccharides (LPS) challenge on spleen heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) expression (n=10). Treatment groups: control, layers were fed on a basal diet and injected with 0.5 mL saline; LPS, layers were fed on a basal diet and injected with 0.5 mL LPS at 8 mg/kg body weight; LPS+LA, layers were fed on a basal diet containing 2×109 CFU/kg LA and injected with 0.5 mL LPS at 8 mg/kg body weight; LA, layers were fed on a basal diet containing 2×109 CFU/kg LA and injected with 0.5 mL saline.
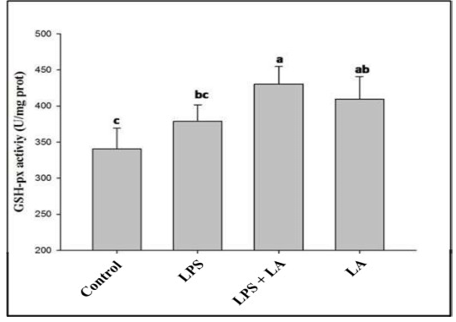
Effect of dietary Lactobacillus acidophilus (LA) supplementation and lipopolysaccharides (LPS) challenge on intestinal glutathione peroxidase (GSH-px) activity (n=10). Treatment groups: control, layers were fed on a basal diet and injected with 0.5 mL saline; LPS, layers were fed on a basal diet and injected with 0.5 mL LPS at 8 mg/kg body weight; LPS+LA, layers were fed on a basal diet containing 2×109 CFU/kg LA and injected with 0.5 mL LPS at 8 mg/kg body weight; LA, layers were fed on a basal diet containing 2×109 CFU/kg LA and injected with 0.5 mL saline.