The Microbial Community in the Feces of Cape Oryx (Oryx gazella) as Determined by High-throughput Illumina Sequencing Technology
The Microbial Community in the Feces of Cape Oryx (Oryx gazella) as Determined by High-throughput Illumina Sequencing Technology
Jun Chen1, Shuai Shang2, Xiaoyang Wu1, Jiakuo Yan1, Huaming Zhong1, Huanxin Zhang2, Weilai Sha1, Wanchao Zhu1 and Honghai Zhang1,*
Rarefaction curves comparing the number of reads with the number of phylotypes found in the rDNA of the three cape oryx.
Fecal bacterial community at the phylum level. Relative abundance of bacterial groups (phylum level) in the feces of three cape oryx.
Fecal bacterial community at the family level. Relative abundance of bacterial groups (family level) in the feces of three cape oryx.
Fecal bacterial community at the genus level. Relative abundances of bacterial groups excepting the unclassified bacteria (genus level) in the feces of three cape oryx.
Bacterial distribution among the three samples. Dendrogram showing the bacterial distribution among the three samples. The bacterial phylogenetic tree was calculated using the neighbor-joining method. The relationship among samples was determined by the Bray distance and the complete clustering method. Total genera were sorted for the analysis after each value (the abundance of total bacteria) was multiplied by ten thousand. The heat map plot depicts the percentage of each bacteria (variables clustering on the Y-axis) within each sample (X-axis clustering). The relative values for bacterial genus are depicted by color intensity with the legend indicated at the right of the figure. Clusters based on the distance of the three samples along the X-axis and the bacterial genera along the Y-axis are indicated in the lower and right parts of the figure, respectively. Black represents the result of no bacteria being found.
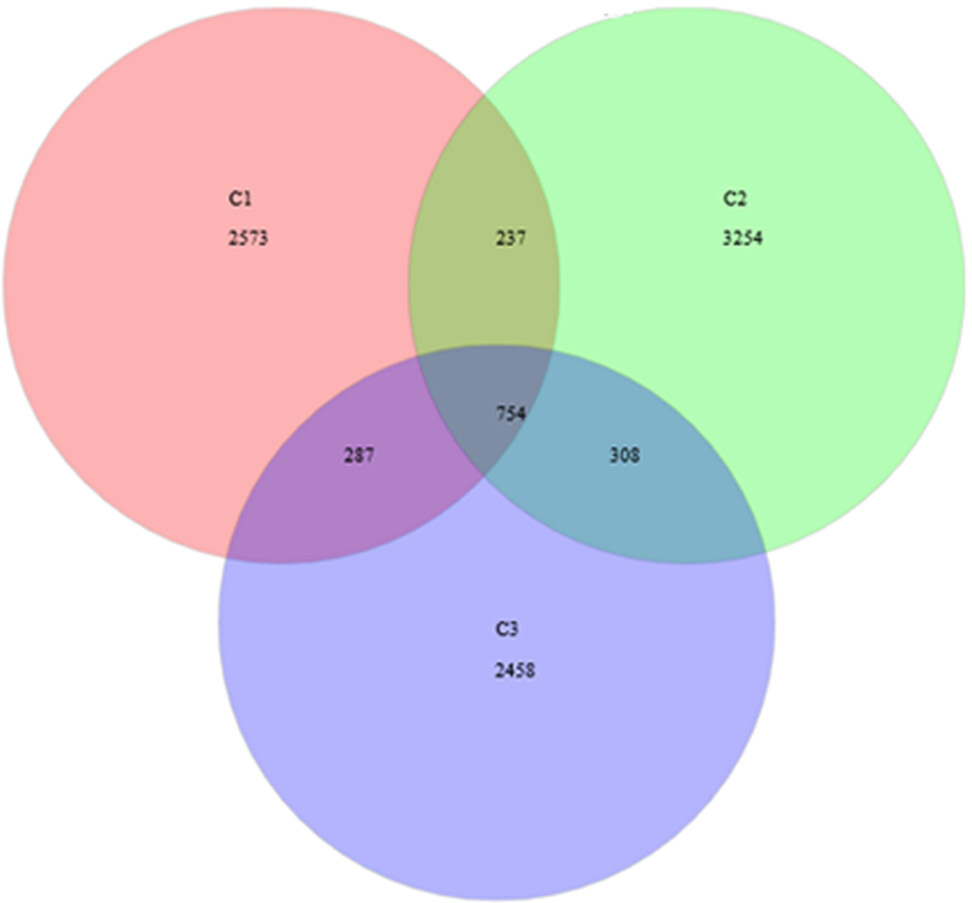
Venn diagram at distance 0.03. The total richness of all groups is 9871. The number of species in group C1 is 3851, group C2 is 4553, and group C3 is 3807. The number of common species between groups C1 and C2 is 991, between groups C1 and C3 is 1041, and between groups C2 and C3 is 1062. The total shared richness is 754.