Ameliorative Effect of GSPE Against AFB1 Induced Immunotoxicity and Hepatotoxicity in Japanese Quail
Ameliorative Effect of GSPE Against AFB1 Induced Immunotoxicity and Hepatotoxicity in Japanese Quail
Maha Khalil1, Gamal Shams2, Hosny Abdel Fadil2, Nagah Edrees2, Mostafa Abonorag1, Nasser El-Sabbagh3, Eman A. Ahmed4*
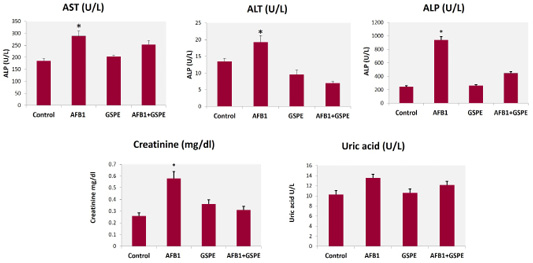
Effect of GSPE on quails’ liver and kidney functions of fed diets contaminated with AFB1. Values are represented as the mean±SE (n=9). Means within the column with different stars are significantly different, p<0.05
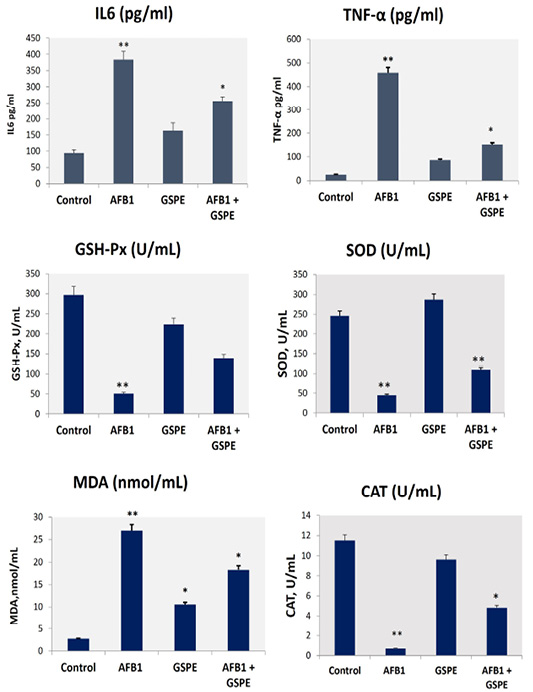
Effects on AFB1-induced liver oxidative stress markers and serum inflammatory cytokines. Values are represented as the mean ± SE (n = 9). *column with different superscript letters were significantly different (p < 0.05). AFB1, aflatoxin B1); GSPE, grape seed proanthocyanidin; SOD, total superoxide dismutase; MDA, malondialdehyde; GSH-Px, glutathione peroxidase; CAT, catalase, IL6, interleukin-6; and TNF-α, Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
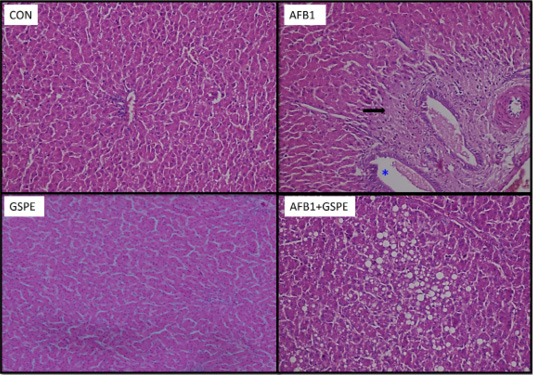
Photomicrographs of liver sections from quails in the different groups: Con, control quails showing normal hepatocytes arranged in plates radiating from the central vein and separated by blood sinusoids; AFB1, quails treated with aflatoxins alone showing marked fibrosis of portal area (→) associated with focal dilation of hepatic sinusoids; GSPE, quails treated with GSPE revealing normal hepatocytes and D, quails treated with (AF+GSPE) showing large intra-hepatic fat droplets.