Ameliorative Effect of Almond Oil Against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Mice Via Downregulation of TLR4 Gene Expression, Lowering NF-κB and TNF-α Levels
Ameliorative Effect of Almond Oil Against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Mice Via Downregulation of TLR4 Gene Expression, Lowering NF-κB and TNF-α Levels
Doaa Sh. Mohamed1, Nema S. Shaban2 , Mai M. Labib3, Olfat Shehata4
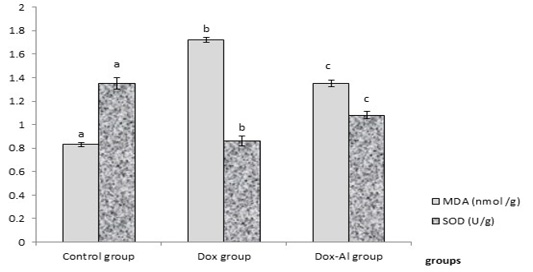
Changes in MDA levels and SOD activity in the heart of mice in different studied groups. The different superscript letters mean a significant difference at (P > 0.05) between different groups. Legend higand
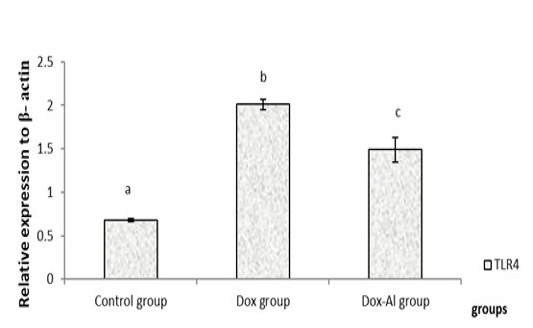
The relative expression levels of TLR4 gene in the various studied groups. The different superscript letters mean a significant difference at (P value less than 0.05) between different groups.
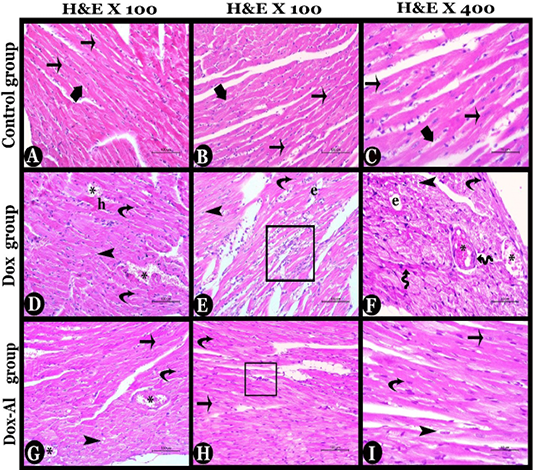
Photomicrographs of histolopathological sections of the heart tissues of all studied mice stained with H&E stain, 1st, and 2nd columns X100, and 3rd column X400: A, B & C) Control group showing normal cardiac architecture, normal arrangement of cylindrical branched myocytes (thin arrows) contained acidophilic cytoplasm and oval central vesicular nuclei. Note, narrow slits (thick arrows) between the myocytes contained fine connective tissue and normal blood vessels. D, E & F) Doxorubicin group showing degenerated condensed myocytes with pyknotic nuclei (curved arrows), deteriorated myocytes with vacuolated cytoplasm infiltrated by inflammatory cells (square), interfibrillar vacuolations (arrowheads), Hyalinosis (h), in addition to damaged blood vessels with congestion (*), proliferating fibroblast (zigzagged arrows) and interstitial edema (e). G, H & I) Almond oil-treated group showing mild degenerative changes appeared in form of few degenerated myocytes with pyknotic nuclei (curved arrows), interfibrillar vacuolations (arrowheads), few inflammatory cells infiltration (square) and vascular degeneration with congestion (*), while most of myocytes appeared as normal (thin arrows).
Explain the in silico computational protein-ligand docking for SOD induced by doxorubicin. The in silico docking analysis showed: a) The 2D chemical interaction of SOD- doxorubicin complex with four conventional hydrogen bonds, b): The PKS (PT domain) - interaction of SOD-doxorubicin complex, c): Hydrogen bond interaction of SOD- doxorubicin complex, d): The predicted charges of the SOD- doxorubicin complex, e): Hydrophobic interaction of SOD- doxorubicin complex, f): The ionizability of the SOD- doxorubicin complex and g): The SAS area in of the SOD- doxorubicin complex.