Anti-angiogenic Effect of Ginsenoside Rh2 by Downregulation of VEGF in a Zebrafish Model
Anti-angiogenic Effect of Ginsenoside Rh2 by Downregulation of VEGF in a Zebrafish Model
MA Liman1, QI Yongxiao1, Wang Wenji2* and Zhong Qianyi3*
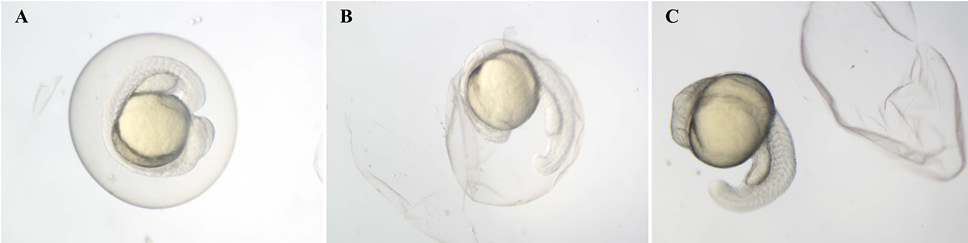
Dechorionation of zebrafish embryos by protease (1 mg/ml) at 24 hpf. Embryos in the chorion. B. Embryos separating from chorion. C. Embryos out of the chorion. hpf: hours post-fertilization.
Morphological changes of zebrafish embryos after G-Rh2 treatment. Zebrafish embryos at 24 hpf were treated with 0.1% DMSO and various concentrations of G-Rh2 (30, 42.43, 60, 84.85, 120 μmol) for 48 h. The arrow denotes pericardial edema after treatment with high concentration of G-Rh2 at 120 μmol. hpt: hours post-treatment.
Anti-angiogenic effect of G-Rh2 on Tg (Fli1-EGFP) zebrafish embryos. 24 hpf embryos were treated for 12 h with (A) 0.1% DMSO (vehicle control); (B) 5 μM SU5416 (positive control); (C) 30 μM G-Rh2; (D) 42.43 μM G-Rh2; (E) 60 μM G-Rh2; or (F) 84.85 μM G-Rh2. Magnified views of A–F are shown in A′–F′. Morphological observation of zebrafish embryos is shown in G–L. The dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel (DLAV), dorsal aorta (DA) and intersegmental vessels (ISVs) of zebrafish embryos are indicated by the yellow arrows. Defects in ISV formation are indicated by the white asterisk.
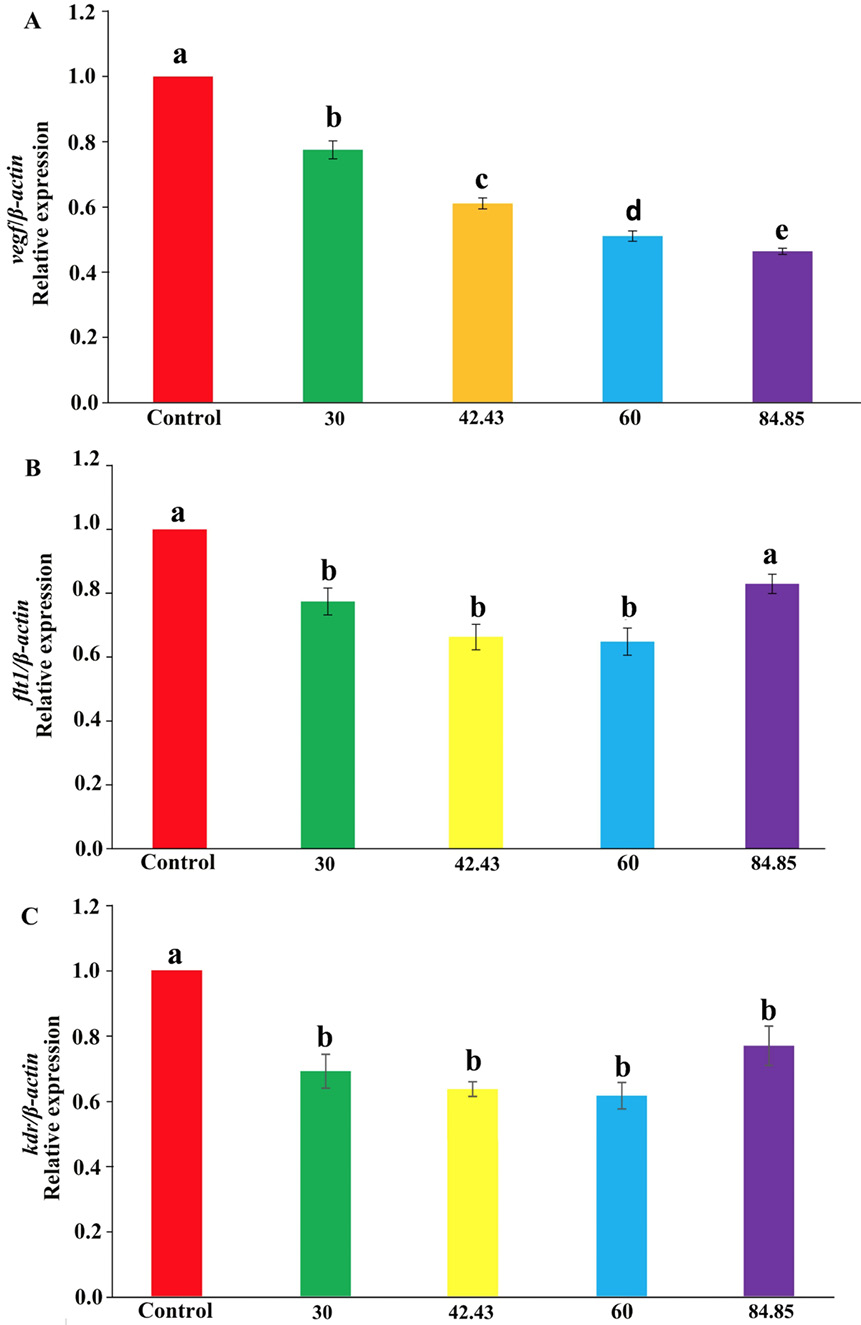
qPCR analysis of VEGF signaling pathway genes in zebrafish embryos treated with G-Rh2. qPCR analysis of vegf (A), flt1 (B) and kdr (C) mRNA expression in 72 hpf zebrafish embryos treated with different concentrations of G-Rh2 or 0.1% DMSO (vehicle control). Data are shown as mean ± SEM of triplicate experiments. Different letters (a–e) above the columns indicate significant differences (P < 0.05).
Western blot analysis of VEGF protein expression in G-Rh2 treated embryos. Western blot of Vegf expression in 72 hpf zebrafish embryos treated with different concentrations of G-Rh2 or 0.1% DMSO (vehicle control). β-Actin was used as loading control. Different letters (a–d) above the columns indicate significant differences (P < 0.05).