Antioxidants Affect Heat Stress Proteins Reactivity on Dermal Fibroblast Cells of Buffalo In Vitro
Antioxidants Affect Heat Stress Proteins Reactivity on Dermal Fibroblast Cells of Buffalo In Vitro
Bipasha Mazumder1, Khadija-Tut-Tahira2, Khondoker Moazzem Hossain1, Gautam Kumar Deb2,3*, Md. Ashadul Alam3, S. M. Jahangir Hossain4
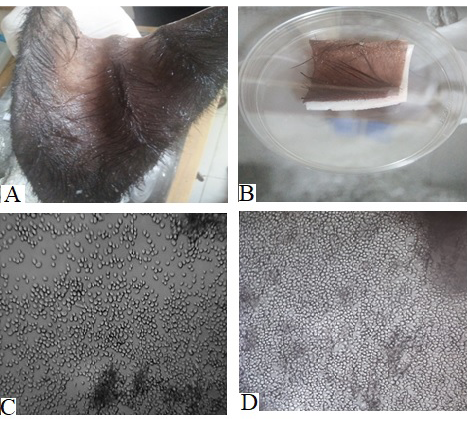
Dermal fibroblast cell culture of buffalo. (A) and (B) Sample for skin biopsy; (C) Growth of cells after 7 days (10x); (D) Growth of fibroblast cells with 70–80% confluence (10x).
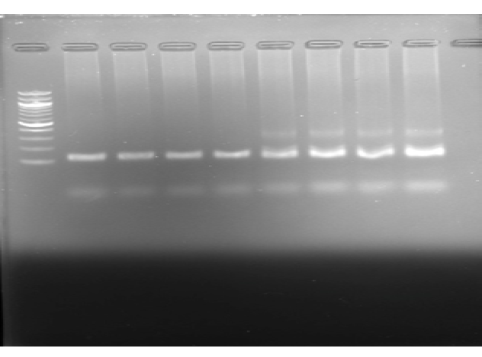
Fibroblast cell confirmation using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Here, from the DNA ladder, the first four are DNA samples from tissue with FN_1 and FSP1 primers, and the other four are DNA samples from cultured cells with FN_1 and FSP1 primers.
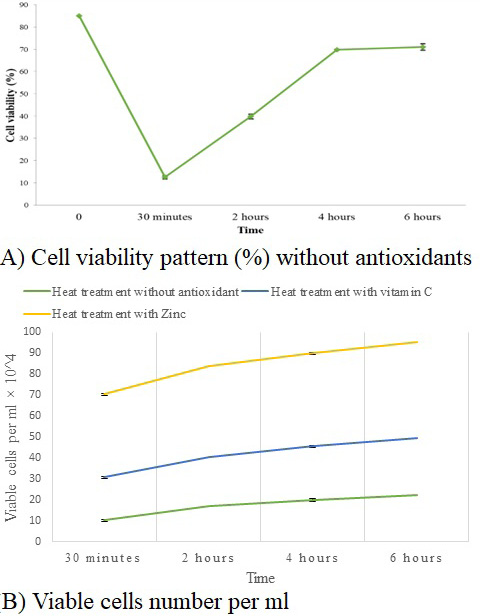
Viable cell growth pattern in heat-stressed buffalo fibroblast cells with and without antioxidant treatment across post-heat stress using the trypan blue dye exclusion method. All data are presented as mean ± SD. All experimental data represent means at P < 0.05. Cell viability after 30 min P< 0.001; after 2h P< 0.001; after 4h P< 0.005; after 6h P <0.006. Live cell numbers after 30 min P< 0.0001; live cells after 2h P< 0.0001; live cells after 4h P< 0.0001; live cells after 6h P <0.0001.