Coexistence Patterns of Sympatric Black-and-white Snub-nosed Monkeys and Rhesus Monkeys in Baimaxueshan National Nature Reserve, Yunnan, China
Coexistence Patterns of Sympatric Black-and-white Snub-nosed Monkeys and Rhesus Monkeys in Baimaxueshan National Nature Reserve, Yunnan, China
Xin Niu1, Xuelan Fang2, Sang Ba3, Yihao Fang1,4, Davide Fornacca1,7, Kun Tan1,4, Yanpeng Li1,4,5*, Zhipang Huang1,4,5* and Wen Xiao1,4,5,6,7
Research area and camera trap layout in Baimaxueshan National Nature Reserve, Yunnan.
Time interval frequency of the sympatric appearance of Rhinopithecus bieti and Macaca mulatta in Baimaxueshan National Nature Reserve, Yunnan, China.
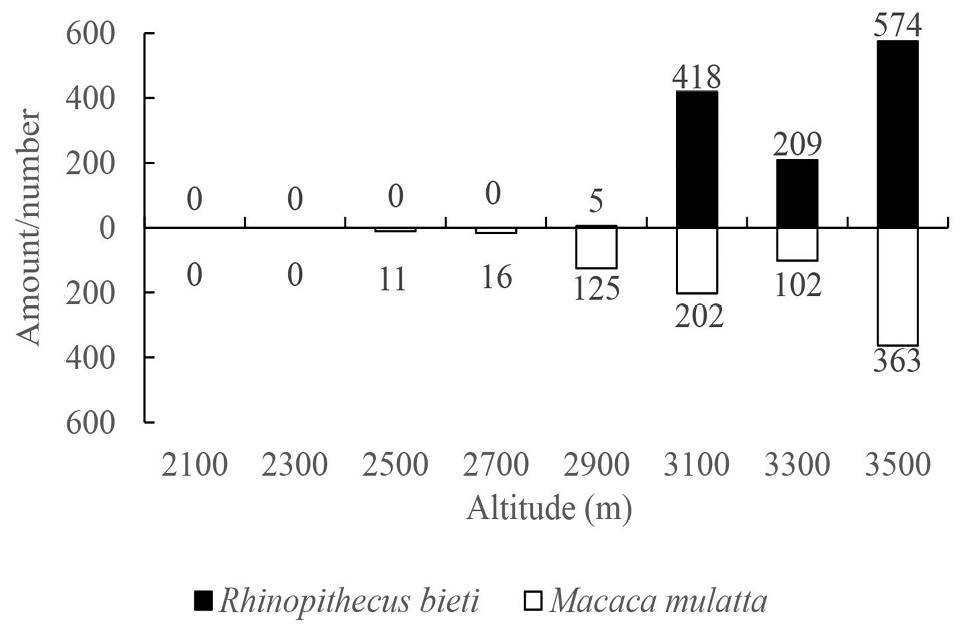
The altitudinal spectrum in which Rhinopithecus bieti and Macaca mulatta were captured in Baimaxueshan Mountain National Nature Reserve, Yunnan.
Spatial-temporal niche utilization by Rhinopithecus bieti and Macaca mulatta in Baimaxueshan National Nature Reserve, Yunnan, China.
Group size differentiation of two sympatric primate species recorded by camera traps installed in Baimaxueshan National Nature Reserve, Yunnan, China A, the whole altitudinal spectrum; B, C and D, 3100m, 3300 and 3500m, respectively.