Comparative Study on Detection of Mycobacterium bovis Infection in Bovine Tuberculous Lesions
Asad Ullah1*, Faizan Hafeez2, Raheela Taj3, Shumaila Gul4, Imad Khan1, Brekhna Faheem5, Mansoor Ahmad5, Rafiq Ullah5, Ashfaq Ahmad5, Muhammad Hanif5, Aziz Ullah Khan5, Muhammad Owais Khan5, Abdul Basit5, Muhammad Idrees Khan6, Shakirullah Khan7 and Muneeb Islam8
1College of Veterinary Science and Animal Husbandry, Abdul Wali Khan University Mardan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan; 2Legend Institute of Management and Sciences, Legend College Multan. Pakistan; 3Institute of Chemical Sciences, University of Peshawar, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan; 4Department of Botany, Shaheed Benazir Bhutto Women University, Peshawar, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan; 5Department of Zoology, Abdul Wali Khan University Mardan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan; 6University of Strathclyde Glasgow, G1 1XQ, 16 Richmond St, Glasgow, United Kingdom; 7Veterinary Research and Disease Investigation Center, Balogram Swat, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan; 8Department of Microbiology, Abdul Wali Khan University Mardan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.
*Correspondence | Asad Ullah, College of Veterinary Science and Animal Husbandry (CVS and AH), Abdul Wali Khan University Mardan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan; Email: asadullah@awkum.edu.pk
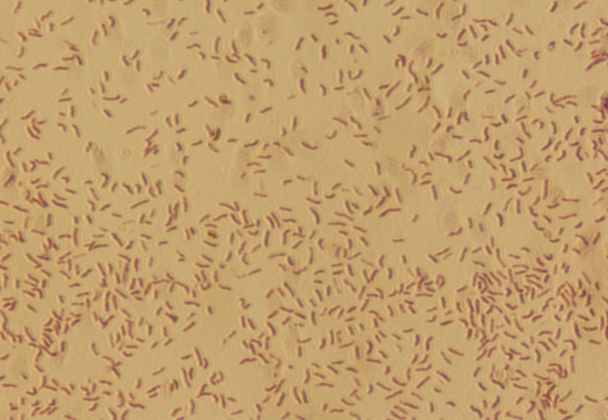
Figure 1:
Ziehl-Neelsen staining of sputum samples of abattoir workers showing acid-fast.
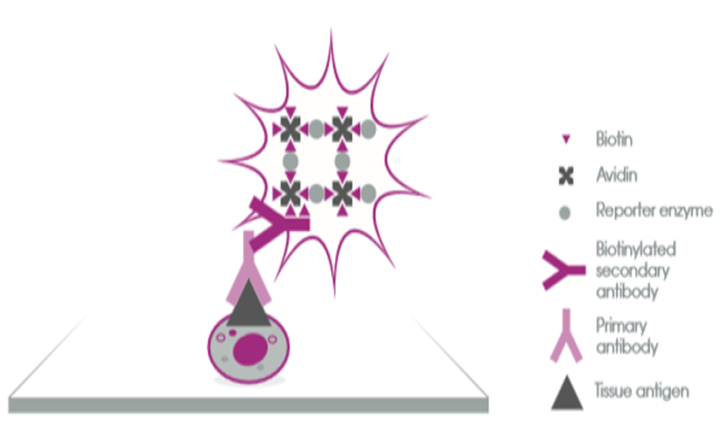
Figure 2:
Avidin-Biotin Complex (ABC) method (https://vectorlabs.com/browse/abc-avidin-biotin-complex-kits).