Cytotoxic Effect of MTH1 Gene Silencing in Gemcitabine Resistant Breast Cancer Cells
Cytotoxic Effect of MTH1 Gene Silencing in Gemcitabine Resistant Breast Cancer Cells
Mahak Fatima1, Memoona Syed1, Rabia Zeeshan2, Farah Rauf Shakoori3, Naveed Shahzad4, Moazzam Ali1 and Zeeshan Mutahir1*
a) MTH1 gene expression was analysed by qRT-PCR after MTH1 specific siRNA transfection. Student’s t-test analysis provided highly significant results for the comparison of +ve and –ve transfected samples (p-value <0.0001). b) Western blot analysis for MTH1 protein expression after MTH1 specific siRNA transfection. Percentage of MTH1 protein expression was quantified by ImageJ software and data was normalised with respect to MTH1 protein expression in –ve transfection group. β-actin expression was used as an experimental control. siRNA +ve and siRNA –ve indicate the expression of MTH1 in +ve and –ve transfected groups of MCF7-R cells respectively.
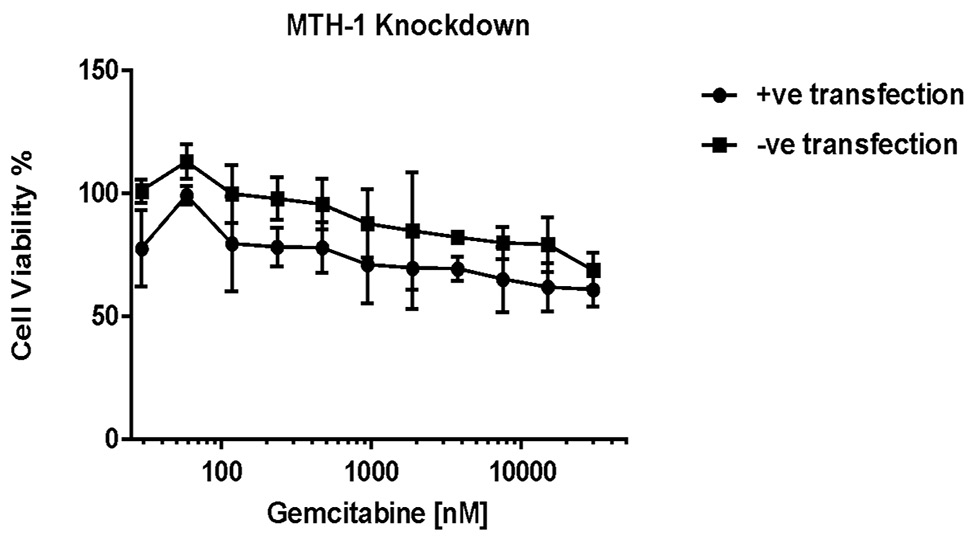
Cell viability of MCF7-R cell line after transfection of MTH1 specific siRNA and subsequent treatment with gemcitabine. Y-axis represents the percentage (%) of viable cells and X-axis represent drug concentration in nM at a log 10 scale. Error bars represent standard error of the mean, while Paired t-test provided extremely significant p-value when siRNA +ve and –ve transfected groups were compared.
MTH1 gene silencing in MCF7-R cells and subsequent treatment with 3µM gemcitabine concentration for 72-h led to apoptosis and remarkably high expression of the p21 protein in the transfected sample. The expression of β-actin was used as an experimental control.