Edible Bird’s Nest Mitigates Histological Alterations in the Cortexes of Rats’ Brains Subjected to Lead Toxicity
Edible Bird’s Nest Mitigates Histological Alterations in the Cortexes of Rats’ Brains Subjected to Lead Toxicity
Abdulla A. Albishtue1,3, Nurhusien Yimer1,5*, Md Zuki A. Zakaria2, Abd Wahid Haron1, Abdul Salam Babji4
Histological changes in the cerebral cortex of rats exposed to LA and treated with EBN. Note: The control group displayed a typical. The T0 group displayed haemorrhage and pyknotic nuclei, that considered signs of degenerative changes in neural cells. T1 and T2 groups demonstrated neuronal cell protection. T3 showed the regeneration, resemble in the histo-architecture for control.
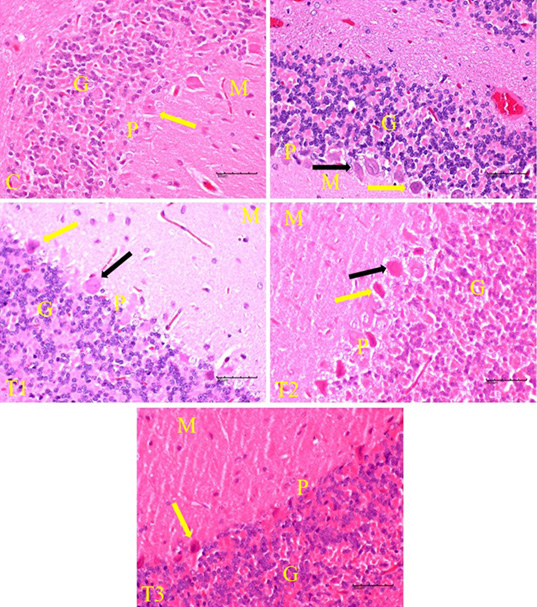
Histological changes in the cerebellar cortex of rats exposed to LA and treated with EBN. Note that darkly stained degenerating pyramidal cells (black arrow) among the healthy pyramidal neurons (yellow arrow) in T0, T1 and T2. Cerebellar layers include molecular(M),purkinje(P) and granular (G).
Histological changes in the cerebellar cortex of rats exposed to LA and treated with EBN. Note that the granule layer in T3 group consists of huge numbers of small granule neurons. Cerebellar layers include molecular(M),purkinje(P) and granular (G).
Impact of EBN on the activities of total antioxidant capacity (TAC) and oxidative stress in the plasma of rats exposed to LA. Reactive substance thiobarbituric acid (TBARS). Informations are expressed as means ± S.E.M.