Effect-of-Bacteriophages-on-Intestinal-Colonization-of-Escherichia-coli-Cecal-Microbiota-Composition-Intestinal-Morphology-and-Growth-Performance-in-Nursery-Pigs-from-Commercial-Pig-Farms
Effect-of-Bacteriophages-on-Intestinal-Colonization-of-Escherichia-coli-Cecal-Microbiota-Composition-Intestinal-Morphology-and-Growth-Performance-in-Nursery-Pigs-from-Commercial-Pig-Farms
Pawinee Kingkan1, Thanathip Supcharoenkul1, Chaowit Rakangthong1, Chaiyapoom Bunchasak1, Komwit Surachat2,3, Wiriya Loongyai1*
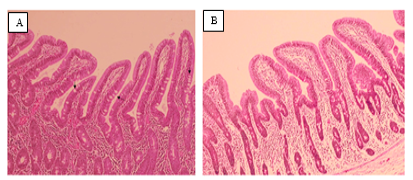
This study was conducted to determine the effects of a bacteriophage cocktail on growth performance, intestinal morphology, E coli detection, cecal bacterial composition, and the incidence of diarrhea in nursery pigs for 6 weeks. A total of 800 pigs (Large White × Landrace × Duroc) were randomly allocated to two treatments: a basal diet supplemented with a mixture of amoxicillin and colistin (Amox-Co) and a basal diet supplemented with amoxicillin and 1 g/kg of a bacteriophage cocktail (Amox-Phage). Each treatment consisted of eight replicate pens, with 50 pigs per replicate. Average daily gain (ADG) and the FCR did not differ between the groups. The Amox-Phage group showed greater resistance to diarrhoea compared with the Amox-Co group during week 6 (p < 0.05). The Amox-Co group showed greater (p < 0.05) villus height at the jejunum and ileum compared with the Amox-Phage group and deeper crypts in the jejunum. Moreover, the goblet cell density in the duodenum was greater in the Amox-Phage group. The total intestinal population of E. coli did not differ between the groups (p > 0.05), ETEC (F18) and EHEC were not detected. Amox-Phage supplementation did not affect cecal bacterial diversity. Firmicutes was the core phylum in the gut microbiota of nursery pigs, and there was a significantly increased relative abundance of Proteobacteria in the Amox-Phage group. Concurrently, the Amox-Phage group showed an increase in the relative abundance of Lactobacillaceae in the caecum. The results of this study indicate that the bacteriophage cocktail has the potential to alter the abundance of intestinal microbiota without increasing the incidence of diarrhea or negatively affecting growth. Hence, a bacteriophage cocktail could be added to the feed of nursery pigs.
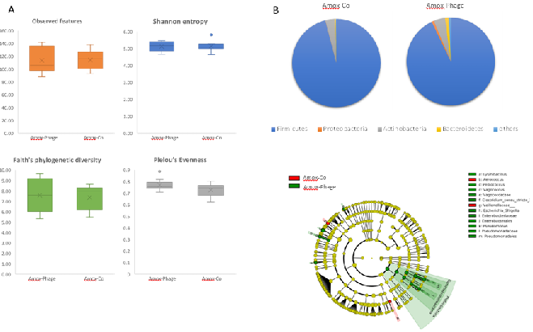
(A) Diversity parameters. Parameters
including index of Observed features, Shannon entropy,
Faith’s phylogenetic diversity and Pielou’s Evenness.
(B) Relative abundant phyla. (C) The histogram of the
linear discriminant analysis (LDA) score illustrating the
differential abundant. Amox-Co: Amoxicillin + Colistin,
Amox-Phage: Amoxicillin + Bacteriophage.