Effects of Quorum Sensing AHL Signaling on the Biological Characteristics of Porcine Derived F4ac+ Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
Effects of Quorum Sensing AHL Signaling on the Biological Characteristics of Porcine Derived F4ac+ Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
Yang Yang1,2, Ji Shao1,2, Mingxu Zhou3,4, Qiangde Duan1,2, Xinyi Zhang1,2 and Guoqiang Zhu1,2*
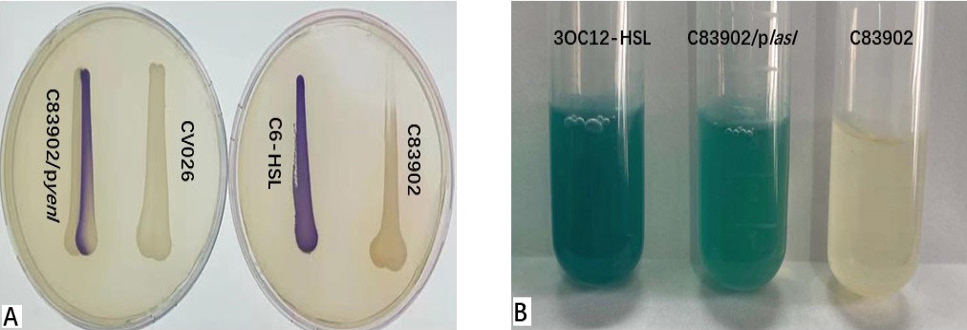
The signal molecule detection of AHL. A, Detection the ability of C83902/pyenI to synthesize short side chain AHL by reporter strain CV026. B, Detection the ability of C83902/plasI to synthesize long side chain AHL by reporter strain JZA1. C6-HSL and 3OC12-HSL were used as positive controls.
The growth curves of C83902 and its recombinant strains under endogenous (A), and exogenous AHLs influence (B).
Quantitative test of biofilm formation of C83902 and its recombinant strains under endogenous (A) and exogenous AHLs influence (B).
The adherence ability of IPEC-J2 cells of C83902 and its recombinant strain under endogenous (A), and exogenous addition of AHL (B). **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001.
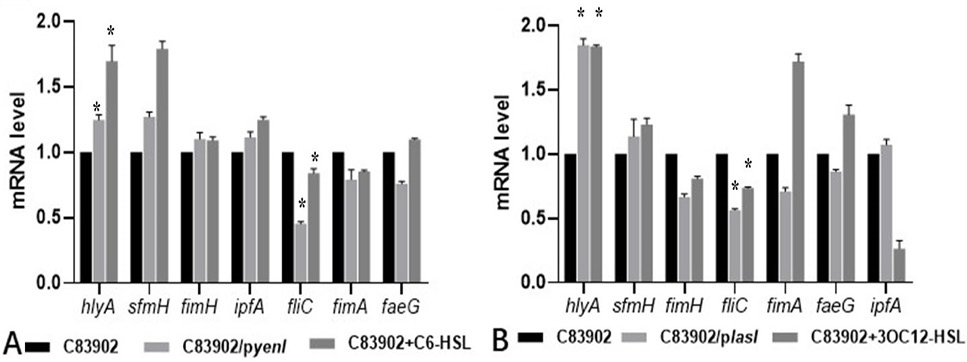
Transcriptional levels of virulence related genes of C83902 and its recombinant strains endogenous and exogenous C6-HSL (A) and OC12-HSL (B). * P<0.05