Epidemiologic and Genetic Assessment of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in Egypt: A Study of Strain Diversity and Evolution
Epidemiologic and Genetic Assessment of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in Egypt: A Study of Strain Diversity and Evolution
Khalid Nabieh1, Wael K. Elfeil2*, Ahmed Ali1, Ali Zanaty3, Magdy F. Elkady1
Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree with 1000 bootstrap repeats tests phylogeny method and Tamura 3-parameter model of the nucleotide’s sequences of 620bp IBDV-VP2 gene hypervariable region. The IBDV –VP2 isolates in the study marked as red rhombus.
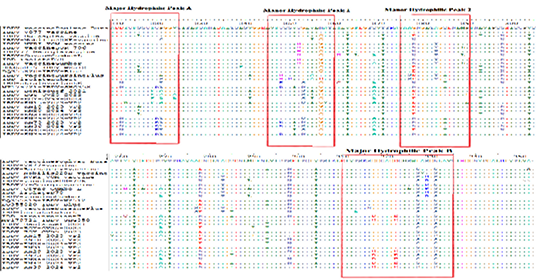
Amino acids alignment report of partial sequence of VP2 gene of IBDV and other Egyptian and representative vaccinal strains.
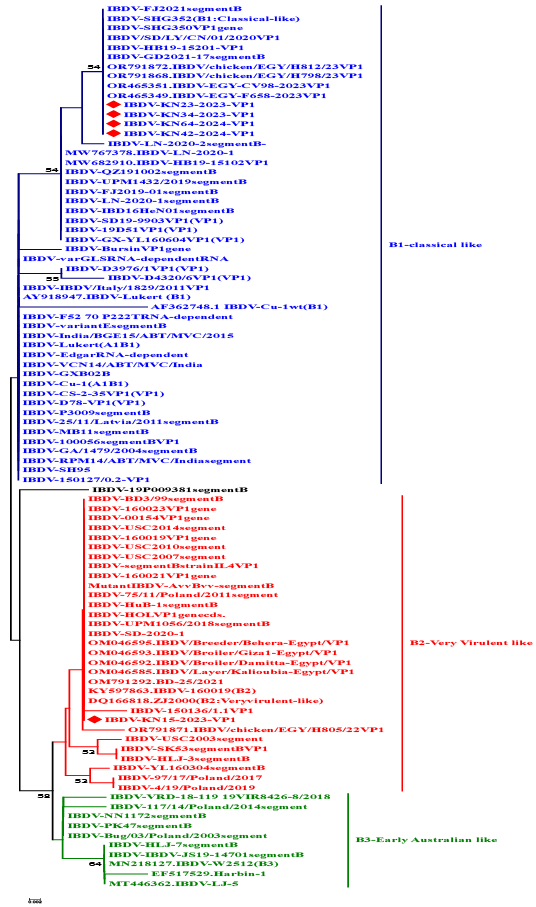
Neighb.or-joining phylogenetic tree with 1000 bootstrap repeats tests phylogeny method and Tamura 3-parameter model of the nucleotide’s sequences of 420bp IBDV-VP1 gene hypervariable region. The five IBDV –VP1 isolates in the study marked as red rhombus.