Evaluation of Arabian Camels Milk’s Ability in Ameliorating Glucose Homeostasis in STZ-induced Diabetes in Adult Male Rats
Evaluation of Arabian Camels Milk’s Ability in Ameliorating Glucose Homeostasis in STZ-induced Diabetes in Adult Male Rats
Ali Mosa Rashid Al-Yasari1, Zahid I. Mohammed2, Haider S. Almnehlawi3,4, Ali F Bargooth5, Nawar Jasim Alsalih1, Huda F. Hasan6*, Mohenned A Alsaadawi1
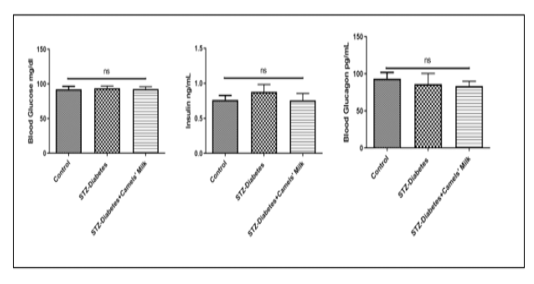
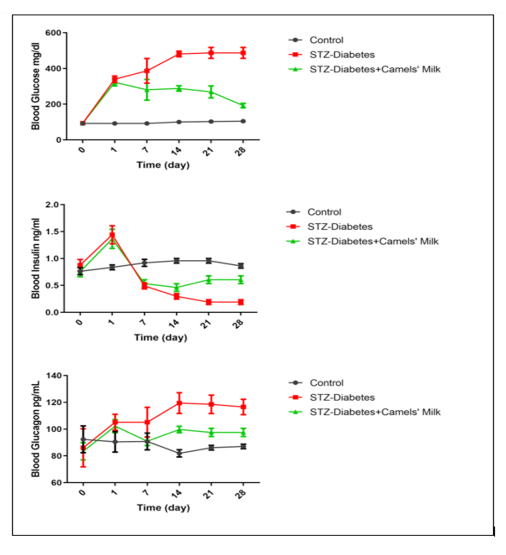
Day 0 shows no change (P>0.05) among groups regarding blood (glucose, Insulin, and Glucagon): Control: Chow and water (ad libitum), STZ-Diabetes: STZ (40mg/kg) on day0, STZ-Diabetes+Camels’ Milk: STZ (40mg/kg) on day0 followed by administration of camels’ milk. Ordinary one-wayANOVA and Newman-Keuls post hoc. N=10.
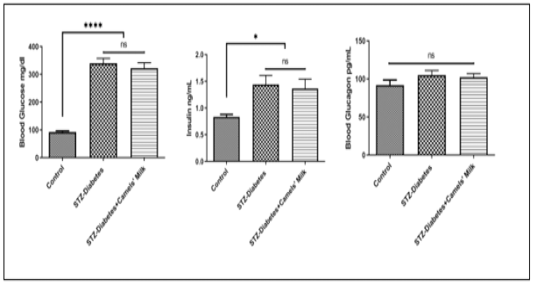
Day 1 shows the effect of STZ injection on blood (glucose, Insulin, and Glucagon): Control: Chow and water (ad libitum), STZ-Diabetes: STZ (40mg/kg) on day0, STZ-Diabetes+Camels’ Milk: STZ (40mg/kg) on day0 followed by administration of camels’ milk. Ordinary one-wayANOVA and Newman-Keuls post hoc. N=10.
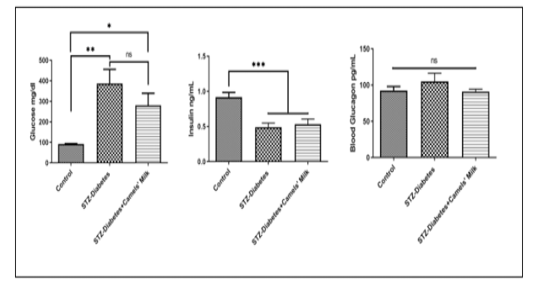
Day 7 shows the effect of STZ injection and Camels milk on blood (glucose, Insulin, and Glucagon): Control: Chow and water (ad libitum), STZ-Diabetes: STZ (40mg/kg) on day0, STZ-Diabetes+Camels’ Milk: STZ (40mg/kg) on day0 followed by administration of camels’ milk. Ordinary one-wayANOVA and Newman-Keuls post hoc. N=10.
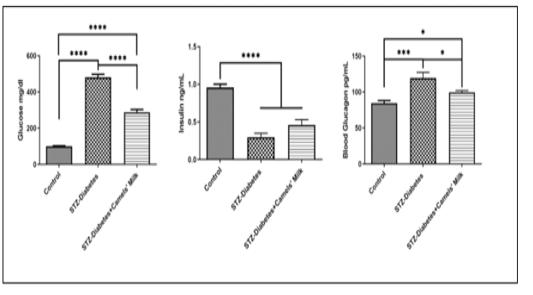
Day 14 shows the effect of STZ injection and Camels milk on blood (glucose, Insulin, and Glucagon): Control: Chow and water (ad libitum), STZ-Diabetes: STZ (40mg/kg) on day0, STZ-Diabetes+Camels’ Milk: STZ (40mg/kg) on day0 followed by administration of camels’ milk. Ordinary one-wayANOVA and Newman-Keuls post hoc. N=10.
Day 21 shows the effect of STZ injection and Camels milk on blood (glucose, Insulin, and Glucagon): Control: Chow and water (ad libitum), STZ-Diabetes: STZ (40mg/kg) on day0, STZ-Diabetes+Camels’ Milk: STZ (40mg/kg) on day0 followed by administration of camels’ milk. Ordinary one-wayANOVA and Newman-Keuls post hoc. N=10.
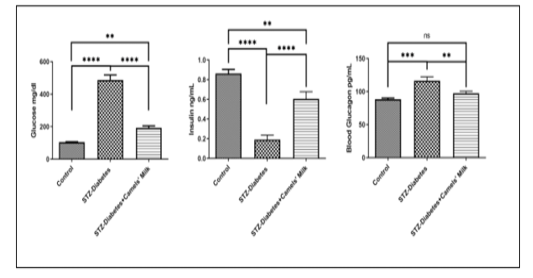
Day 28 shows the effect of STZ injection and Camels milk on blood (glucose, Insulin, and Glucagon): Control: Chow and water (ad libitum), STZ-Diabetes: STZ (40mg/kg) on day0, STZ-Diabetes+Camels’ Milk: STZ (40mg/kg) on day0 followed by administration of camels’ milk. Ordinary one-wayANOVA and Newman-Keuls post hoc. N=10.
Curves represent blood glucose, insulin, and glucagon levels during the experiment. Glucose;Interaction:F(10,60)=9.97,P<0.0001,Time:F(5,60)=22.65,P<0.0001,andTreatment:F(2,12)=187.49,P<0.0001,Insulin;Interaction:F(10,75)=16.27,P<0.0001,Time:F(5,75)=38.25, P<0.0001, and Treatmentent:F(2,15)=7.96,P=0.0044,andGlucagon,Interaction:F(10,60)=3.52,P=0.0011,Time:F(5,60)=4.08,P=0.0030,andTreatment:F(2,12)=3.71,P=0.0558, respectively (two-way ANOVA) and Bonferroni posttests. N=10.
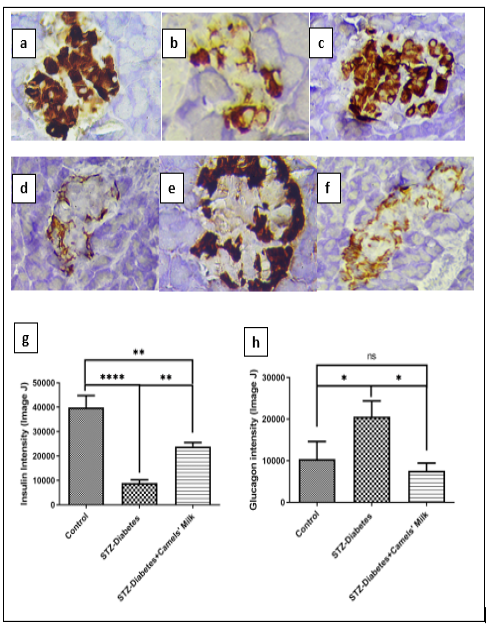
IHC of pancreatic tissues showed that the intensity of insulin and glucagon staining in Control: Chow and water (ad libitum), STZ-Diabetes: injected with single dose of STZ 40mg/kg) on day0, STZ-Diabetes+Camels’ Milk: STZ )40mg/kg) on day0 followed by administration of camels’ milk. . a. Control-insulin, b. STZ-Diabetes-insulin, c. STZ-Diabetes+Camels’ Milk-insulin, d. Control-glucagon, e. STZ-Diabetes-glucagon, f. STZ-Diabetes+Camels’ Milk-glucagon, g and h: Histograms showing means and SEM of insulin and glucagon, respectively. One way ANOVA and Newman-Keuls Multiple Comparison Test, N=10 *P<0.05 and **P<0.01. (20X magnification)