Exploring Helicobacter pylori’s Impact on Clinical Manifestations and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Spectrum
Exploring Helicobacter pylori’s Impact on Clinical Manifestations and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Spectrum
Syed Rafiq Hussain Shah1, Atta Ullah1, Dhafer Hazip Gaber Alwayli1,
Jiaxu Liang1, Tayyab Saeed Akhter2, Faisal Rasheed3, Nimra Zafar Siddiqui4, Bibi Nazia Murtaza5* and Wen Shu1*
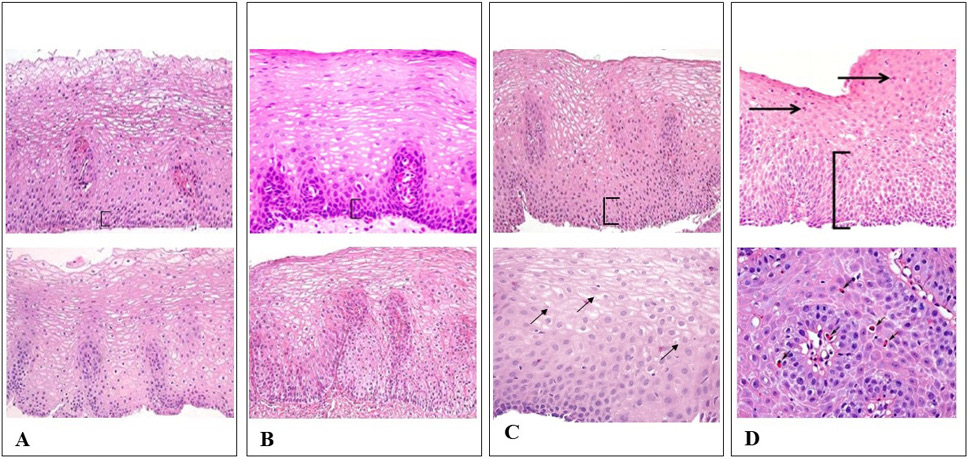
Routine histological examination: (A) Control: normal esophageal mucosa, no inflammatory cells, epithelium basal layer thickness is often less than 15% of the total thickness. (B) Non-erosive reflux diseases: no inflammatory cells in squamous mucosa, mild basal cell hyperplasia, mild papillae elongation (C) NERD + Gastritis: few neutrophils or eosinophils in squamous mucosa. (D) Reflux esophagitis: numerous neutrophils or eosinophils (5-15/HPF) in squamous mucosa, elongated papillae, more than 30% of epithelial thickness is basal cells. (Magnification: 40x,20x) with hematoxylin-eosin staining.