Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes between White and Black Skin Tissues by RNA-Seq in the Tibetan Sheep (Ovis aries)
Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes between White and Black Skin Tissues by RNA-Seq in the Tibetan Sheep (Ovis aries)
Zhen-Yang Wu1, Li Li1, Yu-Hua Fu2, Sheng Wang3, Qing-Ming An1, Xiao-Hui Tang4, Xiao-Yong Du3,5,* and Fei Zhou6,*
The hierarchical clustering based on differentially expressed genes in Tibetan sheep skin between white and black coat color (top 30). 1W, 2W and 3W are the white skin samples from three Tibetan sheep; 1B, 2B and 3B are the black skin samples from three Tibetan sheep.
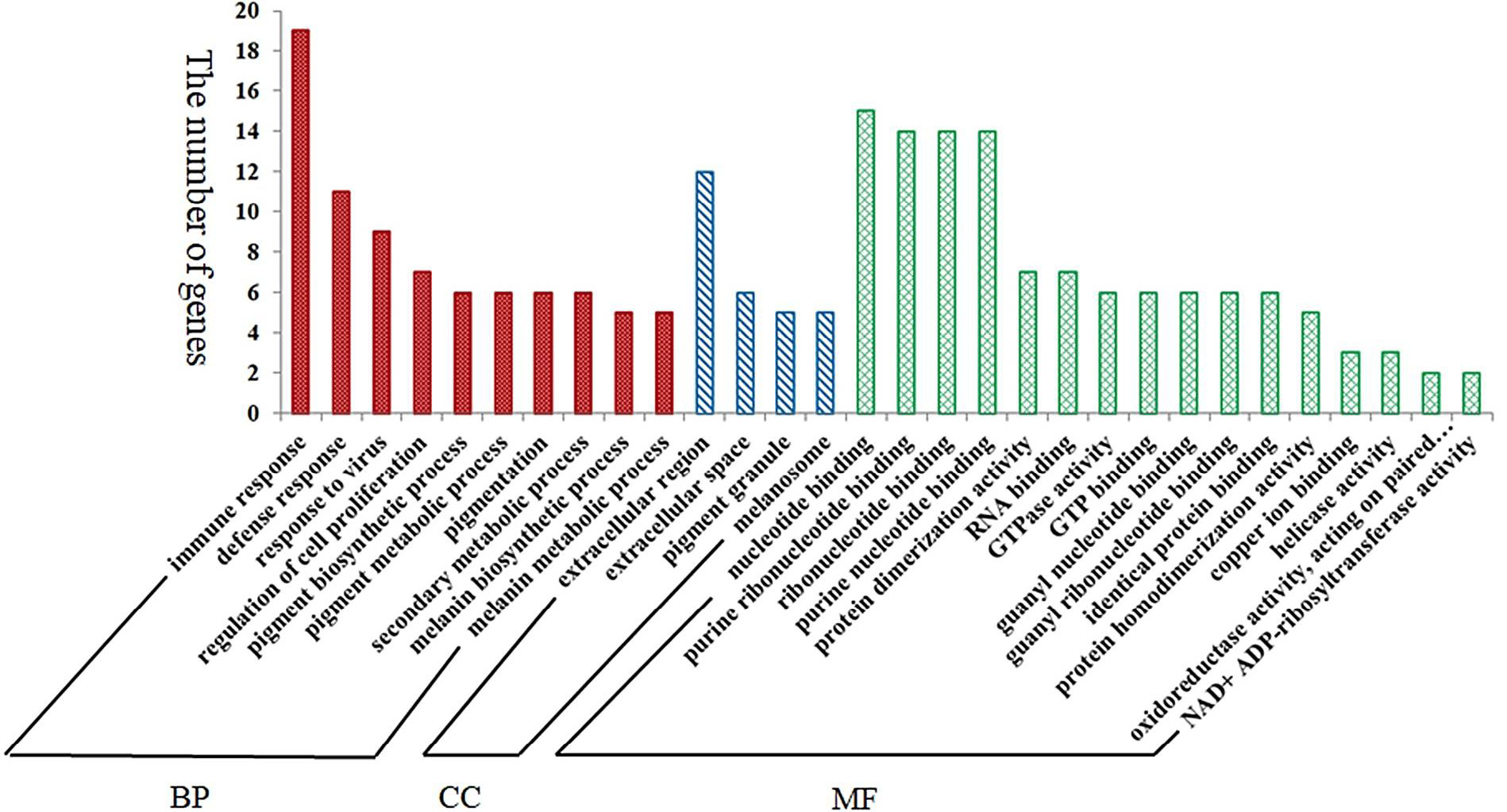
GO analysis of differentially expressed genes in Tibetan sheep with white skin vs. black skin samples.
Relative expression of three differentially expressed genes. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01.
Relative expression of six differentially expressed genes. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01.
Relative expression of four differentially expressed genes. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01.