Impact of Empagliflozin on the Kidneys of Male Albino Rats
Impact of Empagliflozin on the Kidneys of Male Albino Rats
Amal Mahmood Alwan1*, Thekra Atta Ibrahim1, Ghalib Idrees Atiya Ali2
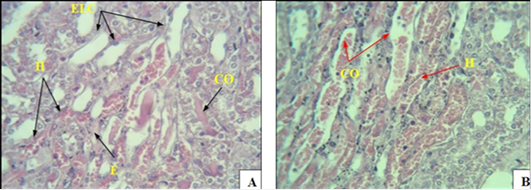
(A) Histopathological section of the kidneys of male rats with alloxan-induced diabetes for 30 days, showing congestion of the urinary tubules CO, hemorrhage H, loss of tubule lining epithelial cells ELC, and edema E. (B) showing congestion of the urinary tubules CO, hemorrhage H (H & E 40x).
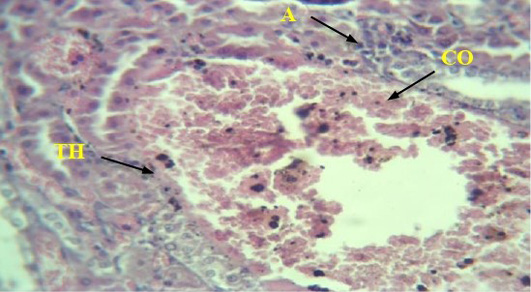
Histological section of the kidneys of male rats in the group suffering from induced diabetes shows vascular congestion. Blood CO, inflammatory cell infiltration A, increased vessel wall thickness in the cortical area TH (H & E 40x).
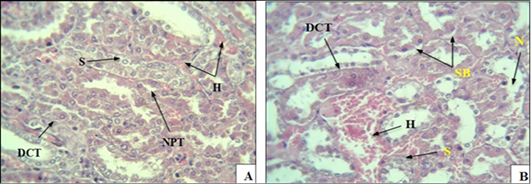
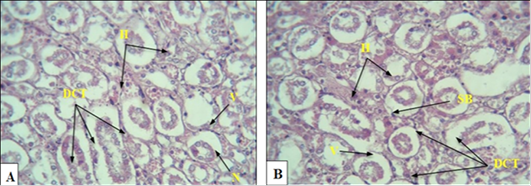
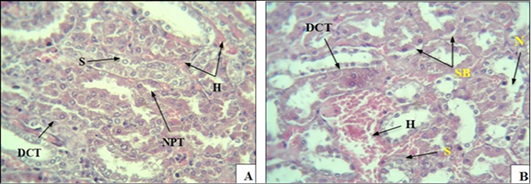
(A): A cross-section of kidney tissue in rats with induced diabetes, showing severe bleeding between the urinary tubules (H), , especially the proximal tubule (NPT), swelling (S). (B): Section showing necrosis (N) of the cells of some urinary tubules, swelling (S), separation of cells from the basement membrane (SB), narrowing of the lumen of some tubules collection of separated epithelial cells in the middle DCT tubule, swelling (S), H bleeding (H & E 40x).
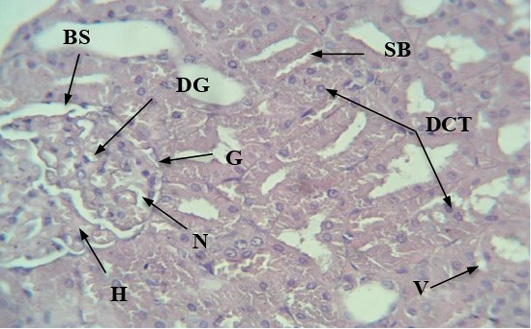
A section of the kidneys of male rats of the experimental group with induced diabetes showing the appearance of histological changes such as glomerular enlargement, intraglomerular haemorrhage (H), narrowing of Bowman’s space (NBS), detachment of some epithelial cells (SB), necrosis (intra-glomerulus) (N), death of some glomerular cells (DGC), and accumulation of detached epithelial cells Middle tubule DCT (H & E 40x).
(A): A section showing the changes in the urinary tubules in the cortex area of male rats with induced diabetes and treated with empagliflozin, which are represented by the accumulation of epithelial cells separated from the basement membrane in most of the urinary tubules in the middle of the DCT, N necrosis, H bleeding, V vacule. (B) showing separation of the epithelial cells lining the tubules from the basement membrane SB, H bleeding, V vacule, (H & E 40x).
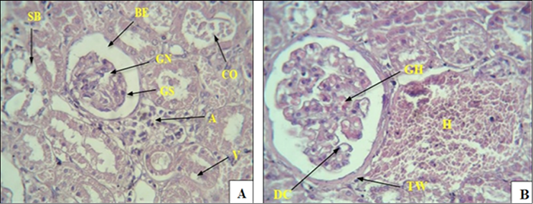
(A): A section of the kidneys of diabetic rats treated with Empagliflozin showing the occurrence of pathological changes in the cortex area, including shrinkage of the glomerulus (GS), widening of Bowman’s space (BE). While (B) showing increased capsular wall thickness (TW), glomerular necrosis (GN), intraglomerular hemorrhage (GH), death of some glomerular cells (DC), and infiltration. Inflammatory cells A, rupture V, epithelial cell detachment SB, severe bleeding H, congestion of some renal tubules CO (H & E 40x).
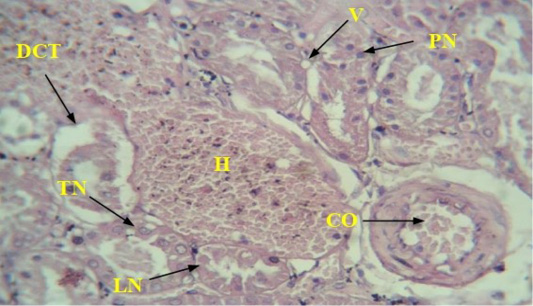
A section showing the kidneys of diabetic rats treated with empagliflozin: CO congestion, severe bleeding (H), loss of nuclei of some cells of the urinary tubules (LN), while thickening of the nuclei occurs in other tubules (PN), in addition to the thickness of the nuclei of some of the epithelial cells lining the urinary tubules (TN), swelling V, Collection of epithelial cells separated from the basement membrane in the tubule lumen DCT (H & E 40x).
(A): A cross-section of kidney tissue in rats with induced diabetes, showing severe bleeding between the urinary tubules (H), , especially the proximal tubule (NPT), swelling (S). (B): Section showing necrosis (N) of the cells of some urinary tubules, swelling (S), separation of cells from the basement membrane (SB), narrowing of the lumen of some tubules collection of separated epithelial cells in the middle DCT tubule, swelling (S), H bleeding (H & E 40x).