Investigating the Impact of Dietary Supplementation on mRNA Expression of Growth-Related Peptides and Gut Health in Broilers
Investigating the Impact of Dietary Supplementation on mRNA Expression of Growth-Related Peptides and Gut Health in Broilers
Hakeem J. Kadhim1*, Iman J. Hasan2
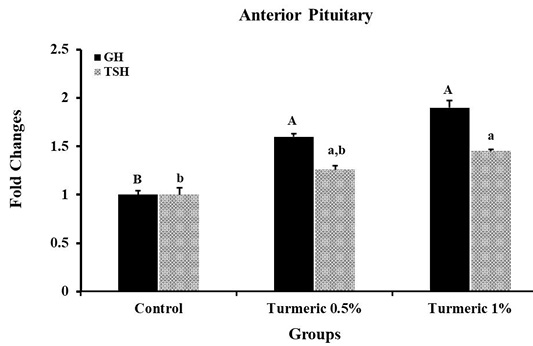
Growth hormone (GH) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) mRNA expression in the anterior pituitary (APit). Fold changes in the mRNA expression were calculated by normalizing the results with the housekeeping gene (18S) using the 2−ΔΔCt equation. Means ± SEM were reported for each gene in each group. A P-value less than 0.05 reflects the significant differences across groups and is indicated by a distinct letter above each histogram.
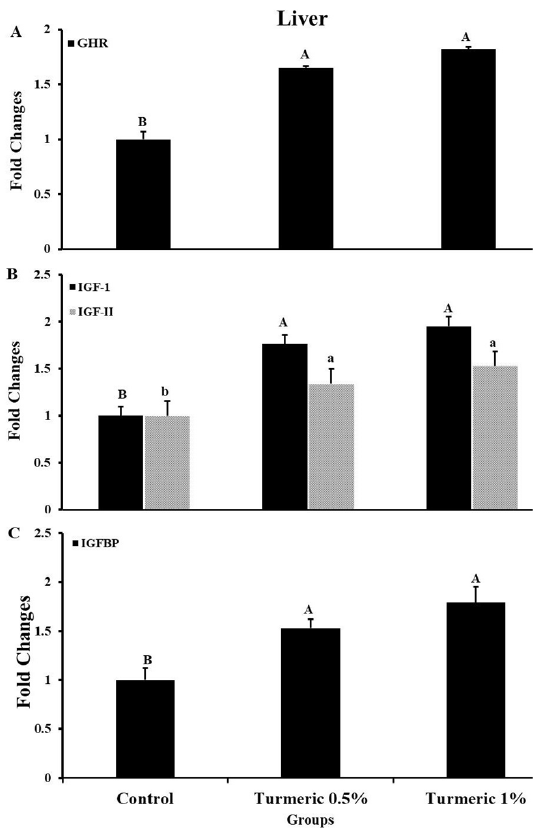
Growth hormone receptor (GHR): insulin-like growth factors I and II (IGF-F and IGF-II): and insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP) mRNA expression in liver tissue. Fold changes in the mRNA expression were calculated by normalizing the results with the housekeeping gene (18S) using the 2−ΔΔCt equation. Means ± SEM were reported for each gene in each group. A P-value less than 0.05 reflects the significant differences across groups and is indicated by a distinct letter above each histogram.
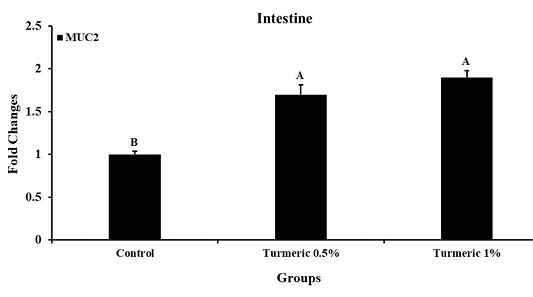
Mucin 2 (MUC2) mRNA expression in the intestinal tissue. Fold changes in the mRNA expression were calculated by normalizing the results with a housekeeping gene (18S) using the 2−ΔΔCt equation. Means ± SEM were reported for each gene in each group. A P-value less than 0.05 states the significant differences across groups and is indicated by a distinct letter above each histogram.