LncRNA BMF-AS1 Exerts Anti-Apoptosis Function in COPD by Regulating BMF Expression
LncRNA BMF-AS1 Exerts Anti-Apoptosis Function in COPD by Regulating BMF Expression
Chuntao Li1, Hua Liu2, Jianqing Zhang1*, Jiaqiang Zhang1, Luming Dai1, Zhihuan Zhao1,Lizhou Fang1, Ling Liu1, Jingkui Shu1 and Jiagang Feng1
Scatter plot of COPD and control group. (A) Scatter Plot shows lncRNAs are differentially expressed between COPD and control group; (B) Scatter Plot shows mRNAs are differentially expressed between COPD and control group.
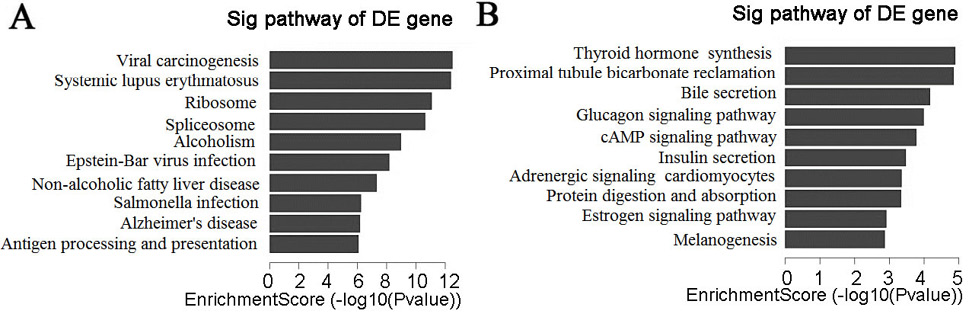
KEGG pathway analysis of the DEmRNAs. (A) The pathways of significantly up-regulated mRNAs in COPD compared with control group; (B) The pathways of significantly down-regulated mRNAs in COPD compared with control group.
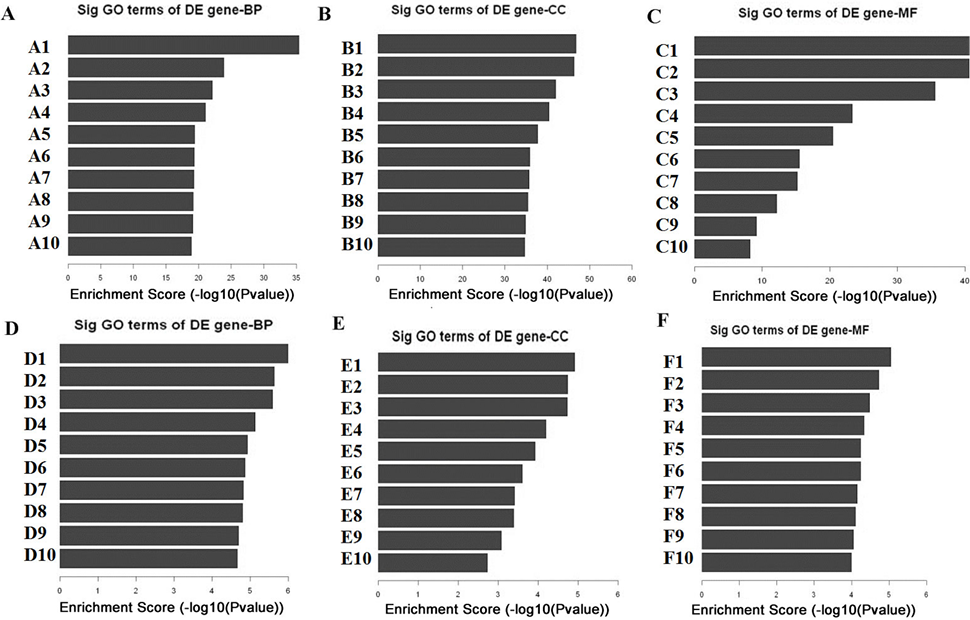
Gene ontology enrichment analysis of DEmRNAs. (A) GO biological process classification of up-regulated mRNAs. A1: mRNA metabolic process, A2: gene expression, A3: immune system process, A4: cellular macromolecule metabolic process, A5: establishment of protein localization to membrane, A6: protein targeting to ER, A7: response to stress, A8: SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, A9: establishment of protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum, A10: cellular component organization or biogenesis; (B) GO cellular component classification of up-regulated mRNAs. B1: intracellular part, B2: intracellular, B3: membrane-bounded organelle, B4: intracellular membrane-bounded organelle, B5: intracellular organelle part, B6: intracellular organelle, B7: organelle part, B8: nucleus, B9: macromolecular complex, B10: nuclear part; (C) GO molecular function classification of up-regulated mRNAs; C1: poly(A)RNA binding, C2: RNA binding, C3: protein binding, C4: binding ,C5: nucleic acid binding, C6: organic cyclic compound binding, C7: heterocyclic compound binding, C8: structural constituent of ribosome, C9: enzyme binding, C10: protein complex binding; (D) GO biological process classification of down-regulated mRNAs; D1: regulation of multicellular organismal process, D2: regulation of cell morphogenesis involved, D3: regulation of multicellular organismal development, D4: system development, D5: nervous system development, D6: regulation of development process, D7: multicellular organismal development, D8: forebrain development, D9: positive regulation of potassium ion, D10: regulation of cell differentiation; (E) GO cellular component classification of down-regulated mRNAs; E1: intrinsic component of plasma membrane, E2: integral component of plasma membrane, E3: plasma membrane part, E4: apical part of cell, E5: apical plasma membrane, E6: cell periphery, E7: plasma membrane, E8: sodium potassium-exchanging ATPase complex, E9: cation-transporting ATPase complex, E10: plasma membrane region; (F) GO molecular function classification of down-regulated mRNAs; F1: cation transmembrane transporter activity, F2: ion transmembrane transporter activity, F3: anion cation symporter activity, F4: transmembrane transporter activity, F5: substrate-specific transporter activity, F6: substrate-specific transmembrane transporter activity, F7: RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory, F8: monovalent inorganic cation transmembrane transporter, F9: sequence-specific DNA binding RNA polymerase, F10: metal ion transmembrane transporter activity.
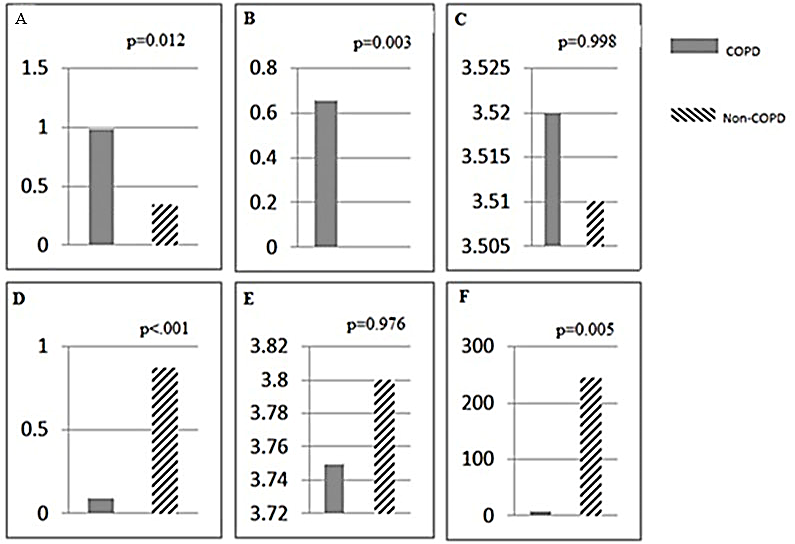
Quantitative reverse transcription PCR validation of differentially expressed mRNAs and lncRNAs. Data are presented as 2 (-ΔCt) relative to actin. (A) BMF mRNA expression (B) CYLD mRNA expression (C) EP300 mRNA expression (D) RP11-521C20.3 expression (E) RP11-327F22.4 expression (F) RP1-85F18.5 expression.