New Approach for Ultrasound-Guided Regional Analgesia of Brachial Plexus in Egyptian Donkeys
New Approach for Ultrasound-Guided Regional Analgesia of Brachial Plexus in Egyptian Donkeys
Adel Sobhy1, Ahmed El-khamary1, Ahmed M. Rashwan2,3, Ashraf Shamaa4, Mostafa Kassem5, Mohamed M. A. Abumandour6*, Ahmed El-Mansi7, 8 and Ahmed G. Nomir2
Gross anatomical image to determine the site of brachial plexus and anatomical landmarks. First-line from the greater tuberosity of the humerus to the jugular vein, the second line is perpendicular to the first line parallel to the first rib and scapula which determines two sites P1 and P2.
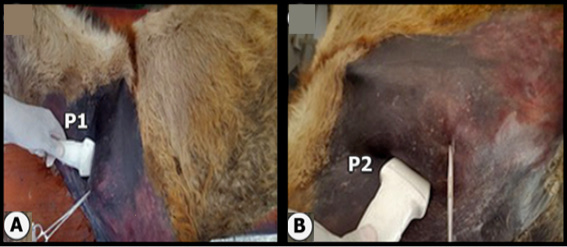
Gross anatomical image in which the A determines the position of probe at p1 of brachial plexus while the B determines the position of probe at p2 of brachial plexus.
Gross anatomical (A) and ultrasound view to determine the US-guided cadaver study at sites p1 (B) and p2 (C).
Ultrasonogram of the brachial plexus region in longitudinal transducer in life beneath the muscle demonstrating the brachial blood vessels.
The donkey showed scapula-humeral angle and was unable to bear weight after the injected forelimb with lidocaine 2%.