Physiological and Agronomic Implications of Foliar Potassium Application on Sunflower Productivity in Calcareous Soils
Physiological and Agronomic Implications of Foliar Potassium Application on Sunflower Productivity in Calcareous Soils
Abdul Aleem Memon1*, Inayatullah Rajpar2, Ghulam Murtaza Jamro2, Javaid Ahmed Shah3 and Saima Kalsoom Babar2
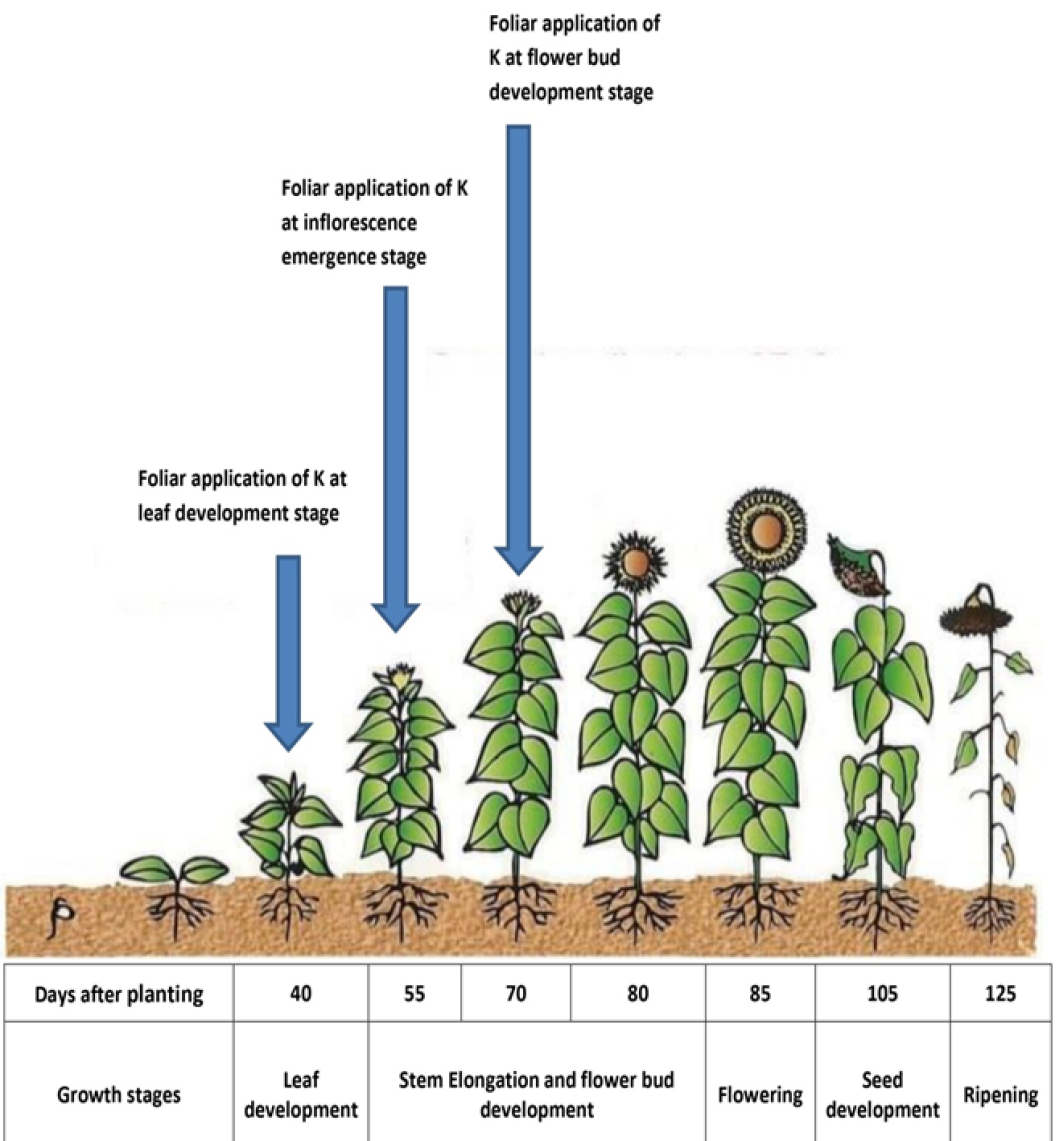
Different stages of sunflower plant where K was applied through foliar.
Effect of K foliar sources and timing on sunflower grown on calcareous (a) plant height (b) head diameter (c) seeds per head.
Effect of K foliar sources and timing on sunflower grown on calcareous (a) Seed weight per head (b) 100-seed weight.
Effect of K foliar sources and timing on (a) Oil Content (b) Seed yield of sunflower grown on calcareous soil.
Effect of K foliar sources and timing on (a) chlorophyll a (b) chlorophyll b (c) Total chlorophyll concentration of sunflower grown on calcareous soil.
Relationship of leaf K concentration (a) with oil content (b) with seed yield of sunflower grown on calcareous soil as affected by K foliar sources and timing.