Polyhydroxyalkanoates Biopolymer Production by Moderately Halophilic Paracoccus onubensis Strain E3: Extraction, Characterization and Synergistic Activity with Sorafenib Drug against Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Molecular Docking Approach
Polyhydroxyalkanoates Biopolymer Production by Moderately Halophilic Paracoccus onubensis Strain E3: Extraction, Characterization and Synergistic Activity with Sorafenib Drug against Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Molecular Docking Approach
Hend A. Hamedo, Ahmed E.M. Shokr, Omnia T. Abd-Elsalam and Naglaa Elshafey*
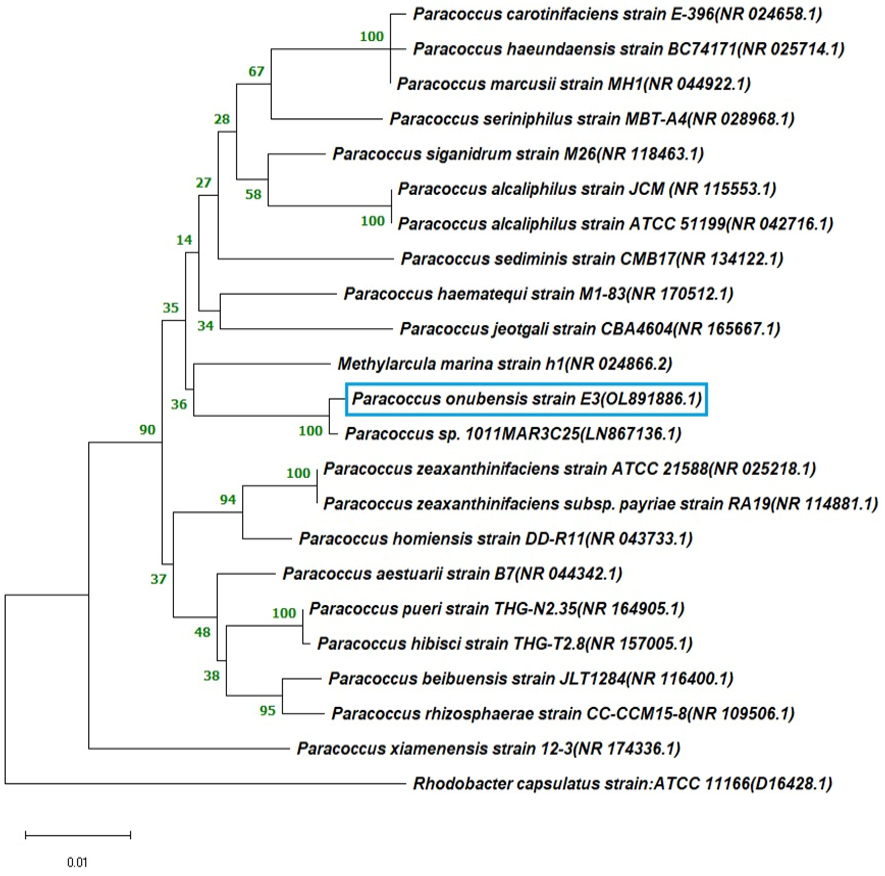
Phylogenetic relationships of bacterial 16S rRNA gene sequences of Paracoccus onubensis strain E closely related to sequences of several strain retrieved from the GenBank database (Similarity > 90%).
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) of Paracoccus onubensis strain E3.
The Factors affecting polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) production (a): Incubation period, (b): pH value, at constant carbon and nitrogen source on growth rate and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) production by Paracoccus onubensis strain E. on the same line the values set by one-self letter(s) were not significantly different. Error bars represent the standard deviation (±SD).
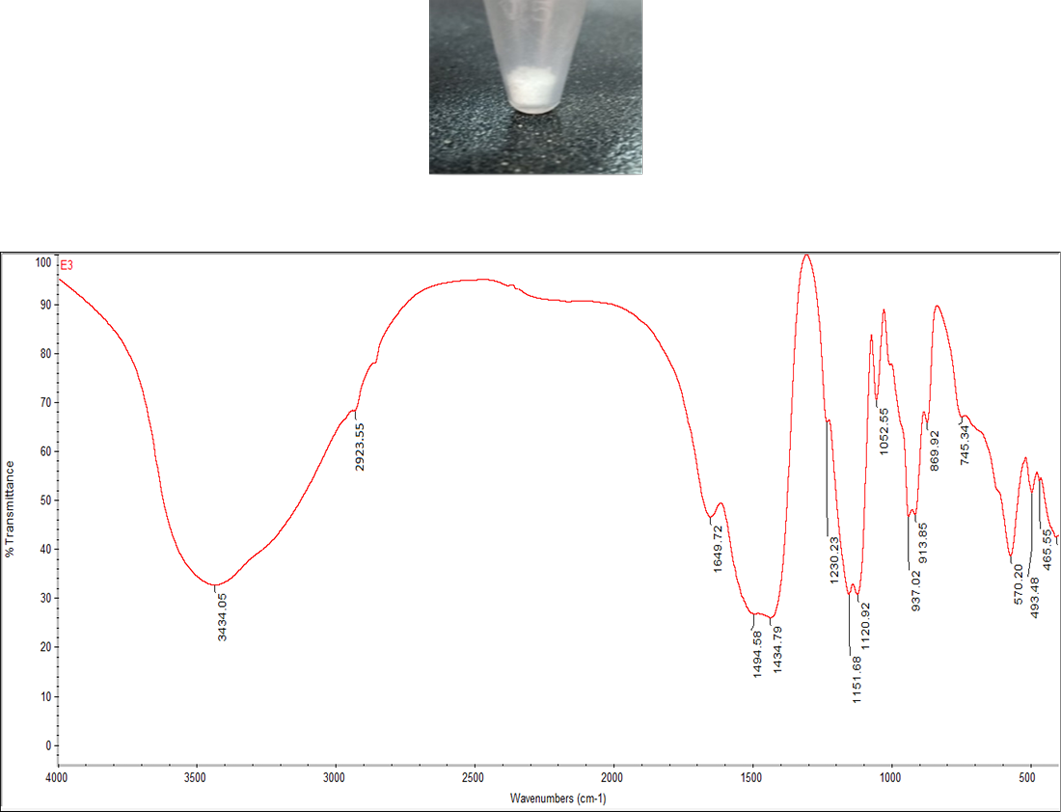
(a): Extracted polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), (b): Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectrum of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) extracted from moderate halophilic Paracoccus onubensis strain E3.
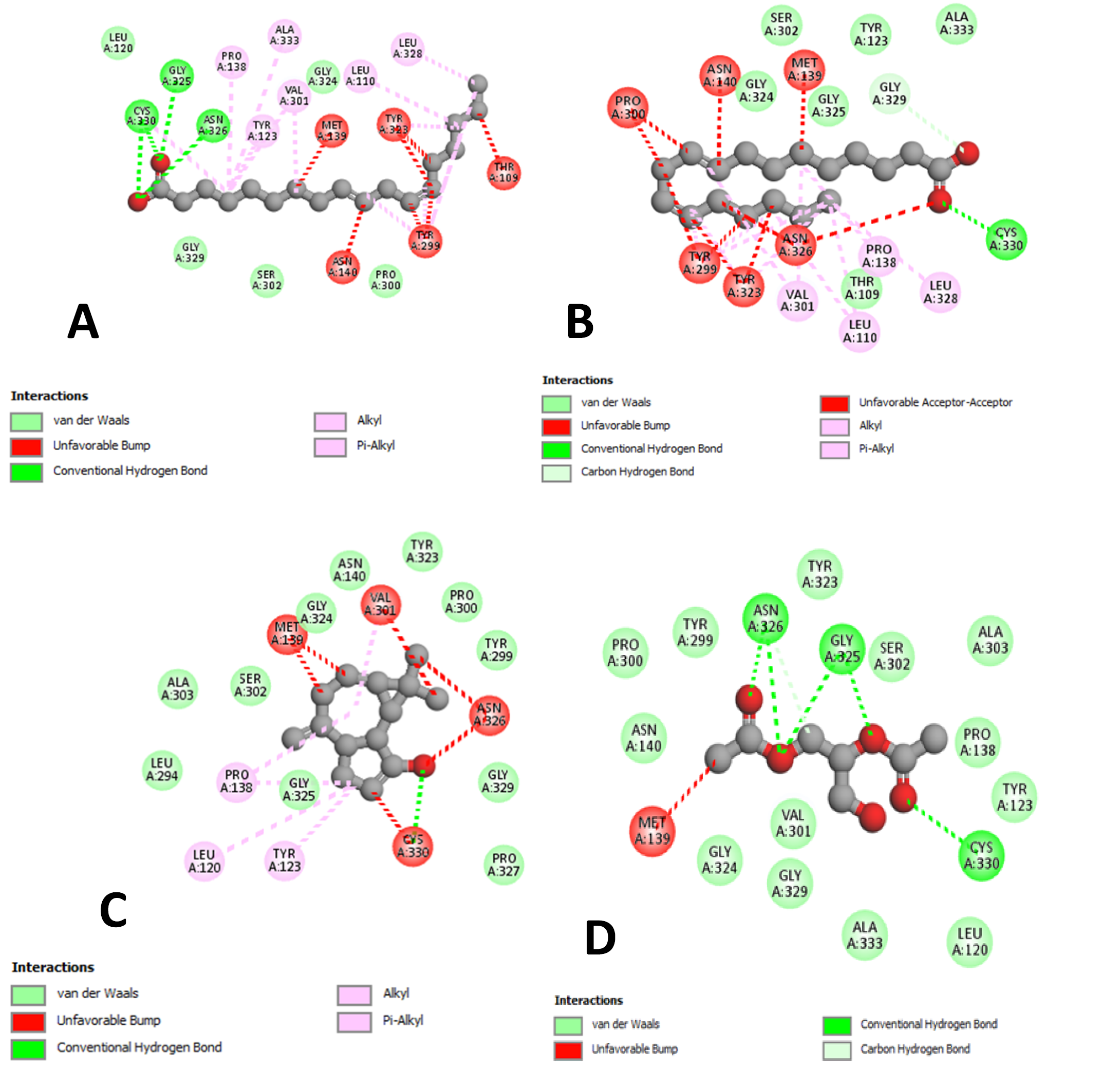
Molecular docking interactions between predicted compounds from the synergistic combination between the most potent polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) ingredinents and sorafenib drug against hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) protien. (A): Predicted compound from 9,12-Octadecadienoic acid (z,z) methyl ester and sorafenib druginteraction, (B): Predicted compound from Isopropyl linoleate and sorafenib drug interaction, (C): Predicted compound between Spathulenol and sorafenib drug interaction. (D): Predicted compound between Triacetin and sorafenib drug interaction.
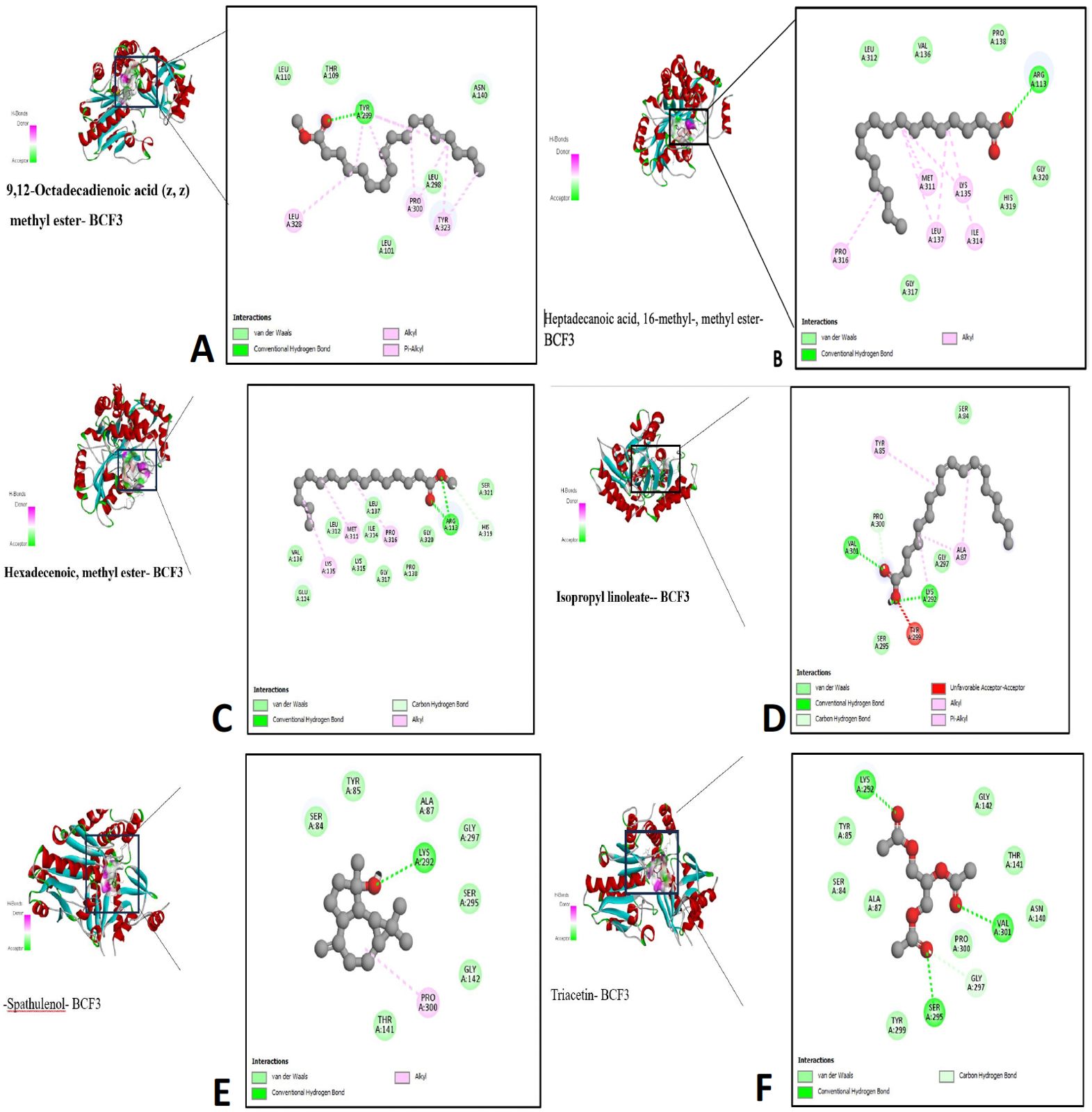
Interaction of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) compounds in active site with (1 S ,3 S)-3-Amino-4-(hexafluoropropan-2-ylidenyl)-cyclopentane-1-carboxylic acid (BCF3).