Prenatal and Histomorphological Development of Fungiform and Circumvallate Papillae in Local Awassi Sheep (Ovis aris)
Prenatal and Histomorphological Development of Fungiform and Circumvallate Papillae in Local Awassi Sheep (Ovis aris)
Rusul Thamer Ali*, Jafar Ghazi Abbas Al-Jebori
Photograph showing the method of measurement of sheep fetuses crown rump length by measure tape.
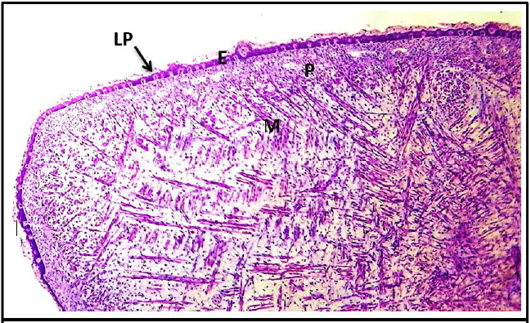
Cross histological section of apex at (50-55) day of tongue sheep fetuses showing: Epithelium (E), and Pluripotiantial tissue (PT) and tunica muscularis (M). (H & E stain 4X).
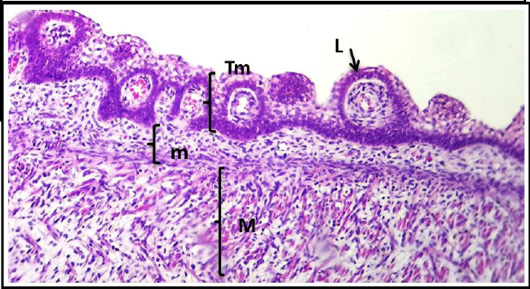
Cross histological section of the root tongue sheep fetuses at (50- 55) day showing: Epithelium (E), un-differential mesenchymal, layer (m), Muscularis (M) and primitive of lingual papillae (LP). (H & E, 10X).
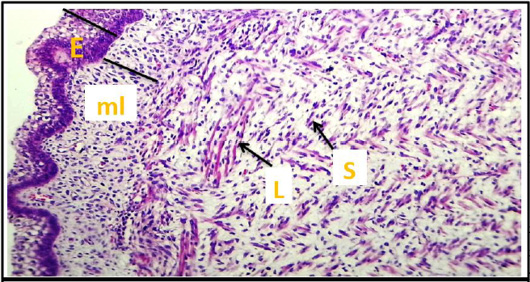
Cross histological section of apex of the tongue sheep fetuses at (50- 55) day showing: epithelium (E), mesenchymal layer (ml) and tunica muscularis (M) appear long (L) and short (S) of muscle fibers. (H & E stain, 10X).
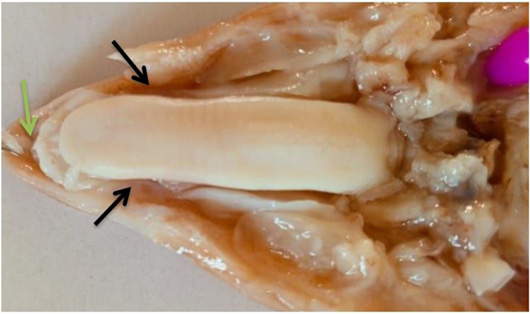
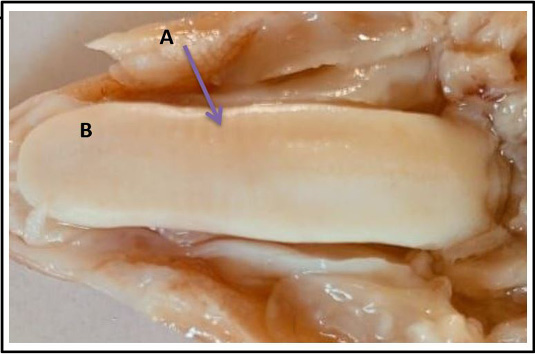
Photomacrograph of tongue sheep at (70-75) days show: A (purple arrow) impression of hard plate of dorsum. B: appear beginning of formation of lingual papillae scattered mostly at the tip and on the dorsal surface.
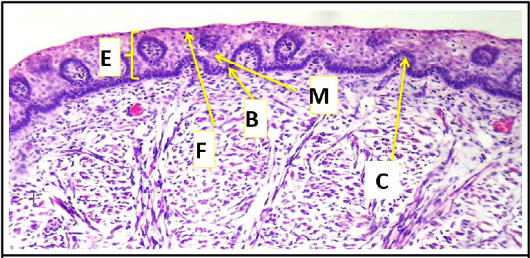
Cross histological section of body of the tongue sheep fetuses at (70-75) day showing: epithelial layer; a basal layer of cuboidal cells (B) which dark stain in color, middle layer of squamous cells (M) or hexagonal cells lighter in color with irregular or rounded centrally nuclei light in color and finally, superficial layer including flattened cells (F) may be keratin or non-keratin on dorsum and invagination of connective tissue core (C) (H & E stain, 10X).
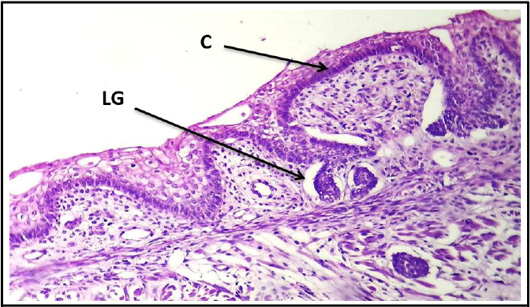
Cross histological section of the tongue sheep fetuses at (70-105) day showing: more development of circumvallate papillae and cluster of lingual gland (H & E stain, 10x).
Cross histological section of apex of the tongue sheep fetuses at (100-105) day showing: filiform and fungiform papillae. (H & E stain, 10X).
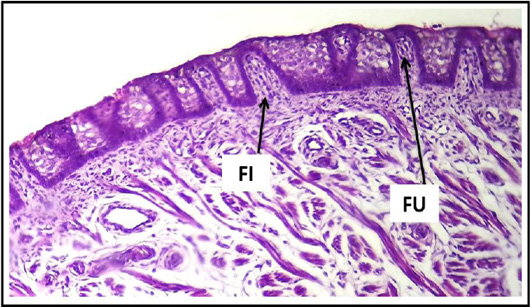
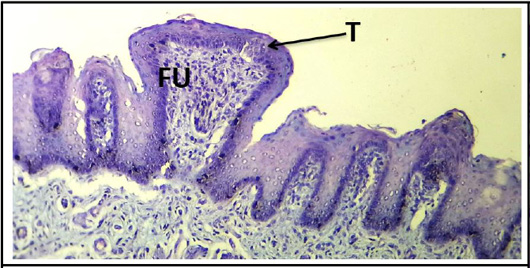
Cross histological section of apex of the tongue sheep fetuses at (130-140) days showing: Fungiform papillae (FU) and primitive of taste buds (T). (PAS stain, 10X).
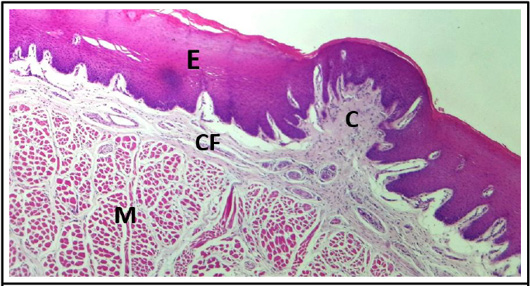
Cross histological section of body of the tongue sheep fetuses at (130-140) days showing: epithelium (E), connective tissue core of fungiform papillae (C), highly vascularized with blood vessels, bundles of collagen fibers (CF) of submucosa, and tunica muscularis (M). (H & E stain, 4X).
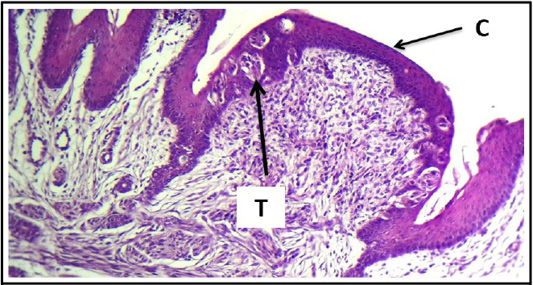
Cross histological section of tours linguae and root of the tongue sheep fetuses at(130-140) days showing: Circumvallate papillae (C) and taste buds (T). (H & E stain, 10X).
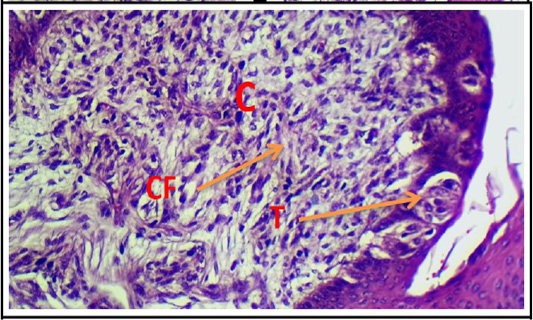
Cross histological section of tours linguae and root of the tongue sheep fetuses at(130-140) days showing: highly vascularize connective tissue core of circumvallate papillae, bundles of collagen fibers(CF) and taste buds (T). (H & E stain, 20X).
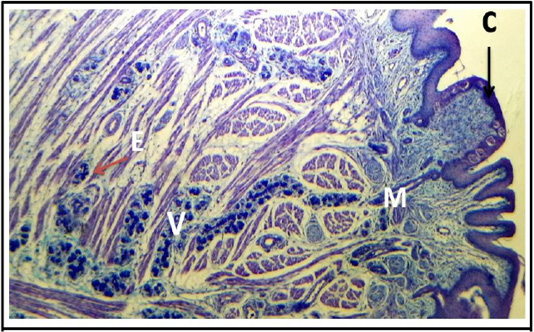
Cross histological section of tours linguae and root of the tongue sheep fetuses at(130-140) days showing: Von abners gland (V) that associated with circumvallate papillae (C), main duct (M), excitatory disc (E), intercalated duct and bundles f muscle fibers. (PAS stain, 4X).
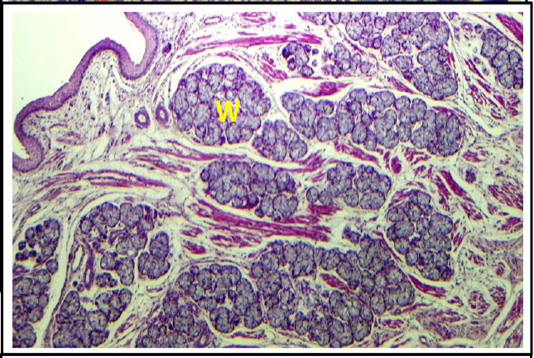
Cross histological section of root of the tongue sheep fetuses at (130-140) days showing: webers gland (W) in deep muscular tissue (H & E stain, 4X)
Cross histological section of tours linguae and root of the tongue sheep fetuses at (130-140) days showing: von abners gland (V) that associated with circumvallate papillae(C), main duct(M), excitatory disc (E), intercalated duct and bundles f muscle fibers. (PAS stain, 4X).
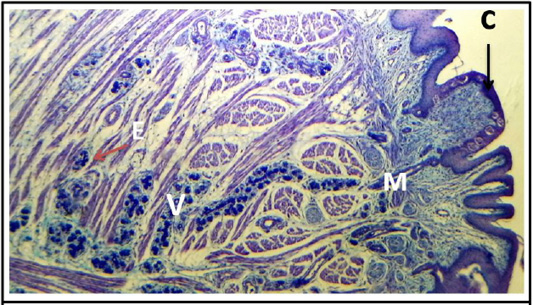
Cross histological section of tours linguae and root of the tongue sheep fetuses at (130-140) days showing: circumvallate papillae (C), taste buds (T), main duct (M), excretory disc (E) and intercalated duct (D). (PAS stain, 4X).
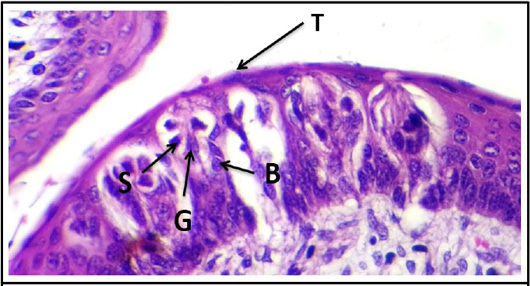
Cross histological section of tours linguae of the tongue sheep fetuses at (130-140) days showing: taste buds (T) of circumvallate papillae, basal cell (B), supporting cell (S) and gustatory cell (G). (H & E stain, 40X).