SOX9 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression through Targeted Regulation of HSPA1B
SOX9 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression through Targeted Regulation of HSPA1B
Jiangbo Shao1, Donglai Zhu2, Shengqiang Zou1, Guohong Ge1 and Ju Huang1*
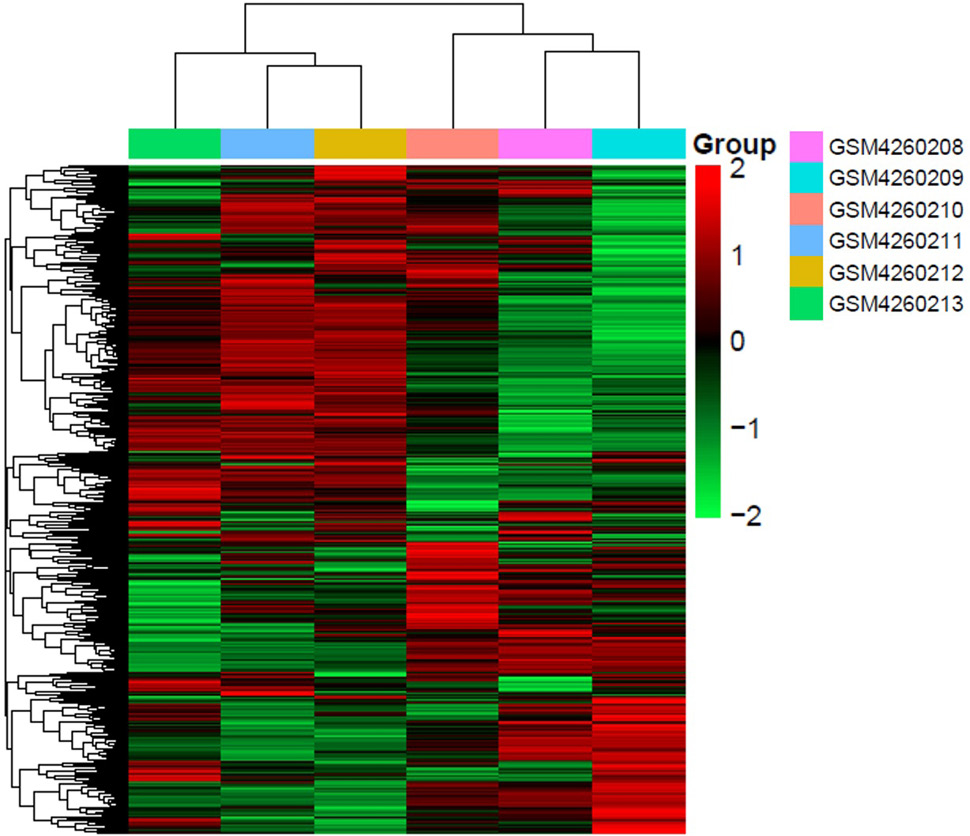
Identification differentially expressed genes correlated with SOX9 in HCC cell samples. Analysis differentially expressed genes correlated SOX9 from SOX9 knockdown (GSM4260211, GSM42602012, GSM4260213) and scrambled control (GSM4260208, GSM42602089, GSM4260210) HepG2 cell samples.
The PPI network and mCODE components of differently expressed genes. (A) PPI network and mCODE of up-regulated genes. (B) PPI network and mCODE of down-regulated genes.
Identification the binding sequence according to JASPAR. ATTGTT could be the core binding sequence for the SOX9 motif.
Expression and prognostic value of SOX9 and HSPA1B in HCC patients. (A) The transcriptional levels of SOX9 and HSPA1B in HCC and normal tissues. (B) The correlation between SOX9 and HSPA1B in HCC. (C) The overall survival of SOX9 and HSPA1B in HCC. The p value cut-off was set at 0.05. ***, p<0.001.