Severe Pitting Corrosion of Carbon Steel Caused by Sulfate Reducing Bacteria in Aqueous Medium
Severe Pitting Corrosion of Carbon Steel Caused by Sulfate Reducing Bacteria in Aqueous Medium
Sanaullah Sattar1, Ali Hussain2*, Javed Iqbal Qazi2, Arshad Javid1 and Shahid Mehmood1
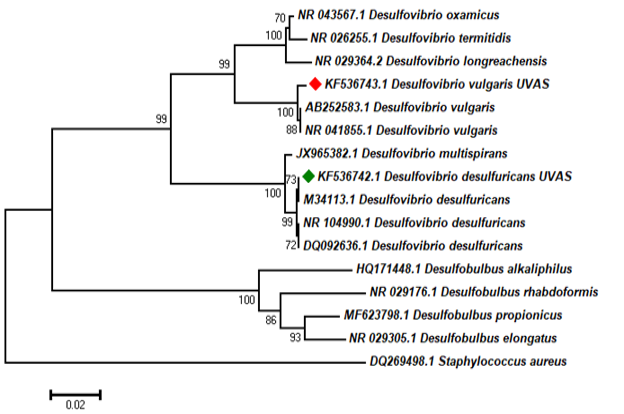
Neighbour-joining phylogenetic tree of Desulfovibrio vulgaris isolated from Hudiara Drain for the current study along with reference sequences recovered from the NCBI GenBank database. The phylogenetic tree was derived from 16S rRNA gene sequences. Bootstrap support values at each node are indicated by numbers (percentage of 1,000 replicates). Values above 70% are displayed only. The bar represents 0.02 substitutions per nucleotide position. The bacterial isolate for the present investigation is spotted in red colour. Staphylococcus aureus was used as an outgroup.
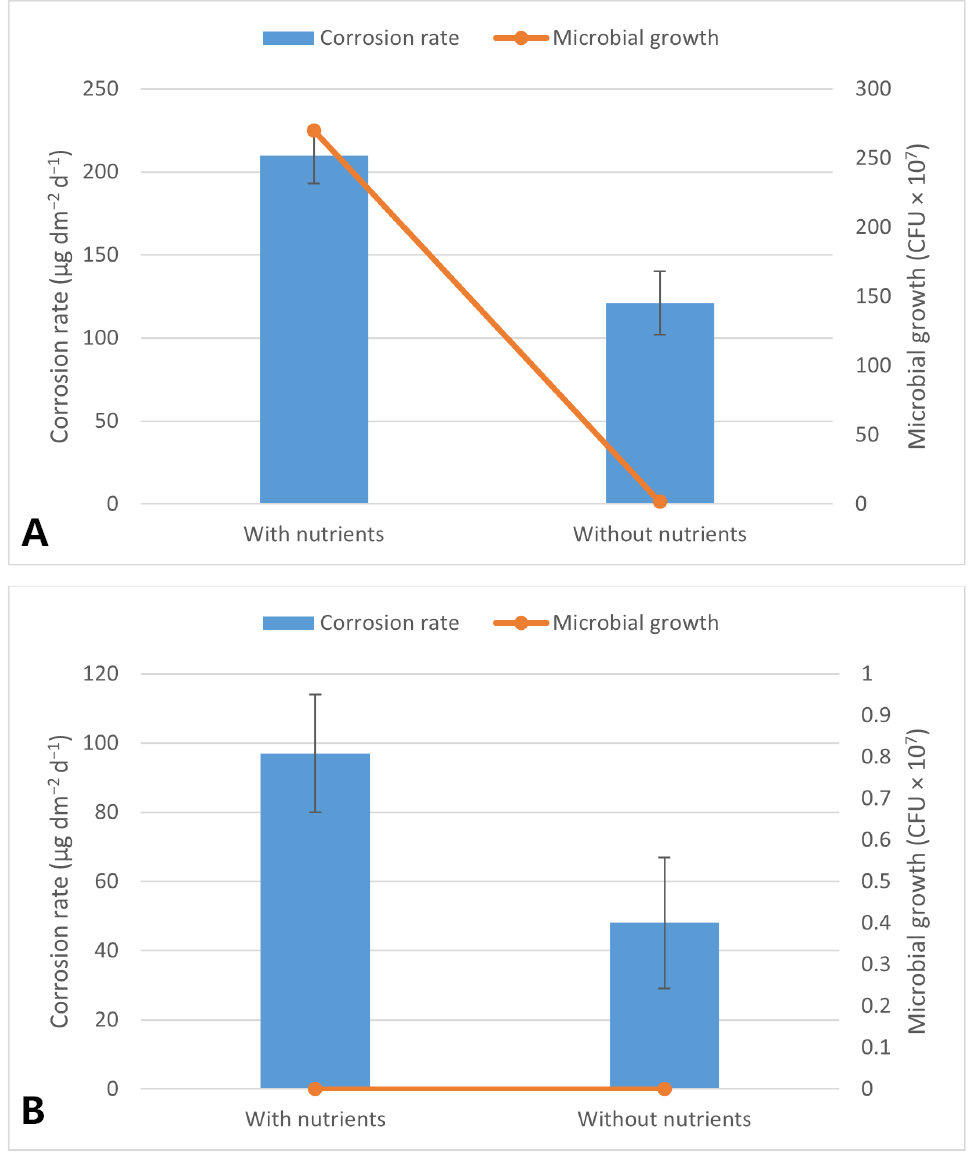
Corrosion rate and SRB growth pattern in inoculated (A) and un-inoculated (B) vials with and without nutrients after an incubation period of 60 days.
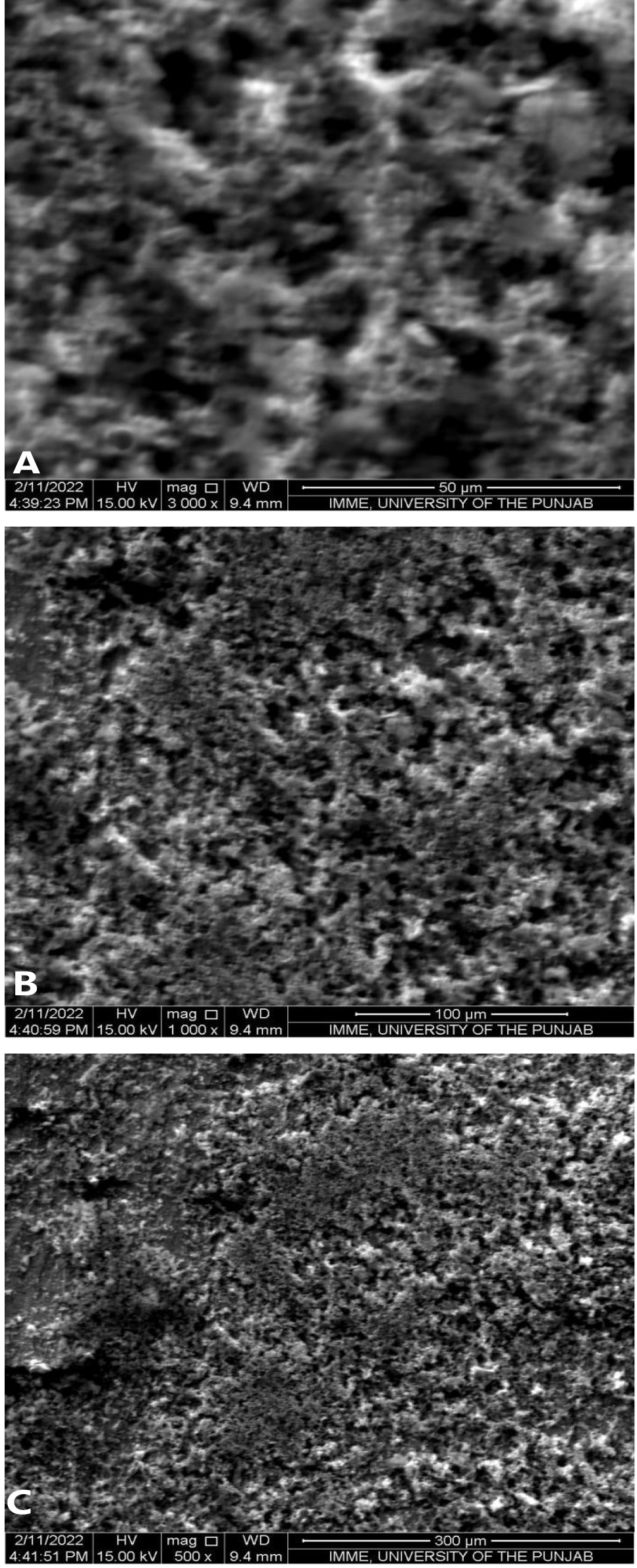
SEM analysis of the corroded metallic coupon showing severe pitting corrosion at different magnification powers, 50 µm (A), 100 µm (B) and 300 µm (C).