The Inhibitory Effect of Potassium Sorbate and Bifido-Bacterium on Shiga Toxin Producing E. coli in Kareish Cheese
The Inhibitory Effect of Potassium Sorbate and Bifido-Bacterium on Shiga Toxin Producing E. coli in Kareish Cheese
Gamilat A. Elsaid1, Weam Mohamed Baher1*, Eman Shukry1, Abeer E. Abd El. Ghafar2, Marwa Shalaby1
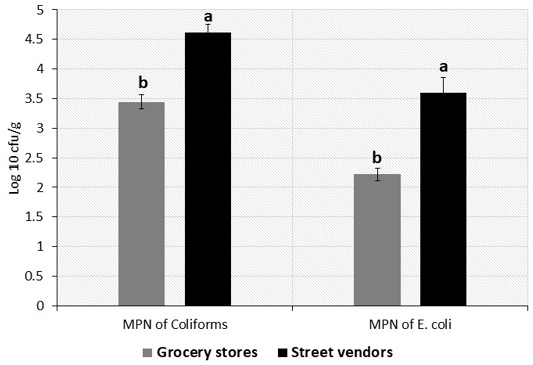
Most probable number of coliforms and E. coli in kareish cheese collected from grocery stores, and street vendors in Mansura city city, Egypt (n = 50). Values represent means ± SD (Log 10 cfu/g). Columns carrying different letter (a, b) are significantly different at p < 0.05.
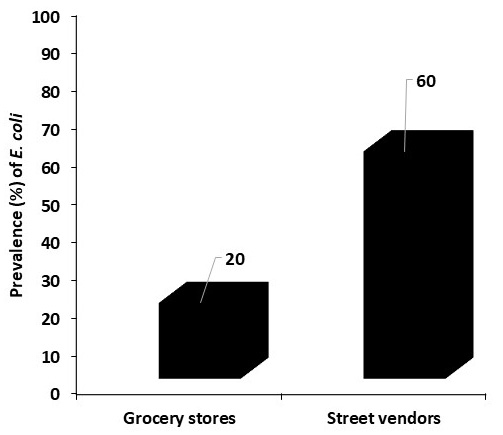
Prevalence rates (%) of E. coli in the examined kareish cheese in the present study.
Prevalence rates (%) of different E. coli serotypes.
DNA expression of 16S rRNA, and shiga toxins coding genes (stx1 and stx2) in the identified E. coli serotypes isolated from retailed Kareish cheese in the present study.