The Protective Effect of Ellagic Acid on Cyclophosphamide Induced Renal Damage in Rats
The Protective Effect of Ellagic Acid on Cyclophosphamide Induced Renal Damage in Rats
Muhammad Nasir Bhaya1,2* and Hikmet Keles2
Histopathological appearance of kidney tissues of all groups, HE staining, scale bar= 150 µm A, Control group: normal kidney morphology. B-C, CP group: hyperemia, epithelial degeneration, swelling, cystic dilatation, proteinaceous material in tubuli, congested and hypercellular glomeruli, inflammatory cells infiltration in cortical and medullary area. Arrows pointing events; h: hyperemia, c: congestion, d: degeneration, i: inflammation, p: proteinaceous material, cd: cystic dilatation. 1D, CP+EA50 group: significant decrease in pathological lesions. 1E, CP+EA75 group: more protective effect and normal architecture of kidney.
Bcl-2 positivity evaluation kidneys stained with Streptavidin biotin peroxidase complex method with AEC chromogen and Mayer’s Hematoxylin counterstain, scale bar=150 µm. A, Control group revealed specific cytoplasmic and luminal positivity of tubuli. B, CP group revealed less specific positivity. C. CP+EA50 group revealed mild positivity. D, CP+EA75 group revealed specific positivity like control group.
HIF-1α evaluation: kidneys stained with Streptavidin biotin peroxidase complex method with AEC chromogen and Mayer’s Hematoxylin counterstain, scale bar=150 µm. A, Control group revealed no positivity. B, CP group revealed specific positivity of tubuli. C, CP+EA50 group revealed mild positivity. D, CP+EA75 group revealed no positivity like control group.
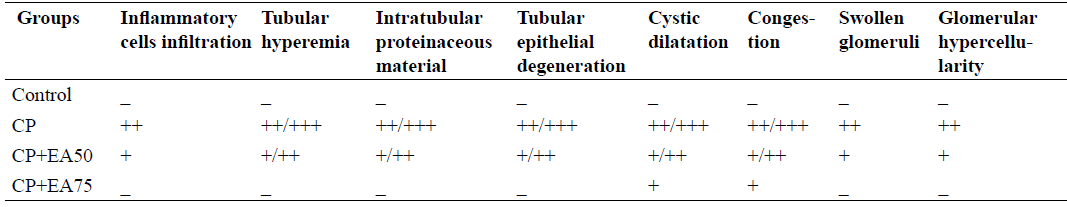
Grading of histopathological lesions in all groups.