Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus from Sore Throat Patients: Association Among Host Immune Evasion and Toxin Genes
Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus from Sore Throat Patients: Association Among Host Immune Evasion and Toxin Genes
Arifa Mehreen1, Iram Liaqat2,Muhammad Arshad3, Muzzamil Waheed4 and Najma Arshad1,*
Phylogenetic tree of 16s rRNA gene sequence of MRSA-42, showing genetic relatedness of different strains with each other.
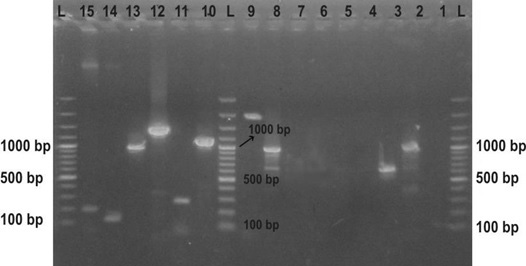
Electrophoretic profile of spa polymorphism product amplified through polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Lane L, molecular marker of 1Kb; Lanes 1, 2 and 3, isolates with 1100bp and 1300bp spa gene product and spa negative, respectively.
Electrophoresis profile in 2% agarose gel showing PCR amplification products for the S. aureus enterotoxins L., DNA ladder, 1-3 are sed, seb and sea.
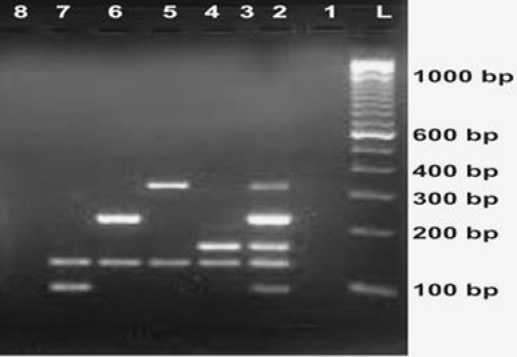
Electrophoresis profile in 2% agarose gel showing multiplex PCR amplification products for the S. aureus exo-foliative toxin tst toxin mec A and fem A genes. Lane L, DNA marker (100-bp ladder); Lanes 2 to 7, PCR amplicon; Lane 1 and 8, negative control; Lane 2, eta, etb, tst, mecA, and femA; Lane 3, mecA plus femA; Lane 4, tst and femA; Lane 5, eta and fem A; Lane 6, etb and femA; Lane 7, eta and femA.
Frequency of host immune evasion and mec A (A) and toxin genes (B) in S. aureus isolated from sore throat patients in Punjab.
Association among Coa and spa genes.