Chemical Compound Identification of Two Varieties Cat of Whiskers (Orthosiphon aristatus Blume Miq) from In Vitro Culture
Chemical Compound Identification of Two Varieties Cat of Whiskers (Orthosiphon aristatus Blume Miq) from In Vitro Culture
Fahrauk Faramayuda1,2*, Totik Sri Mariani3, Elfahmi1,4 and Sukrasno1
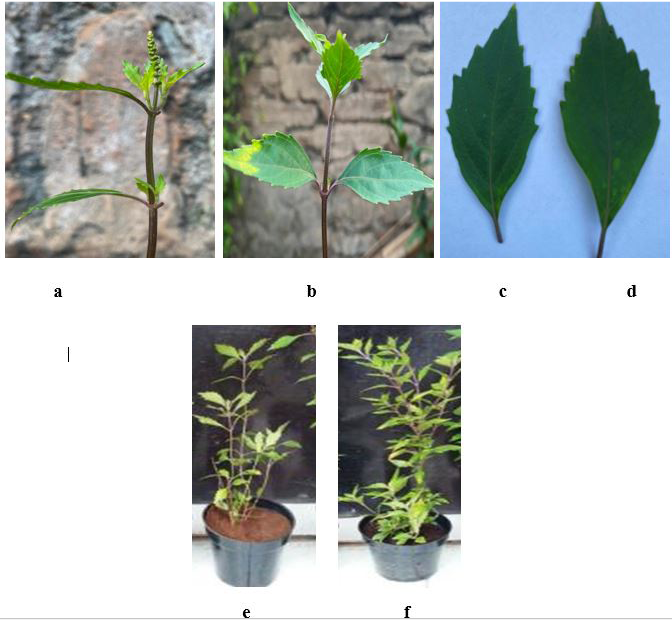
Morphology of leaves and stem of white-purple varieties of O. aristatus from in vitro cultures and wild type. a: white-purple stems (in vitro culture), b: white-purple stems (wild type), c: white-purple leaves (in vitro culture), d: white-purple leaves (wild type), e: white-purple varieties 5 months old (in vitro culture), f: white-purple varieties 5 months old (wild type)
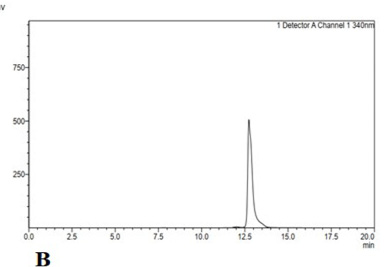
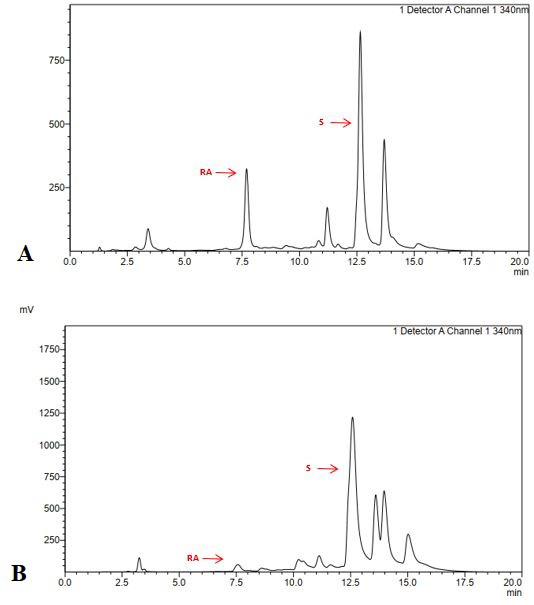
Chromatogram of rosmarinic acid and sinensetin standard at 340.60 nm. A, rosmarinic acid and B, sinensetin.
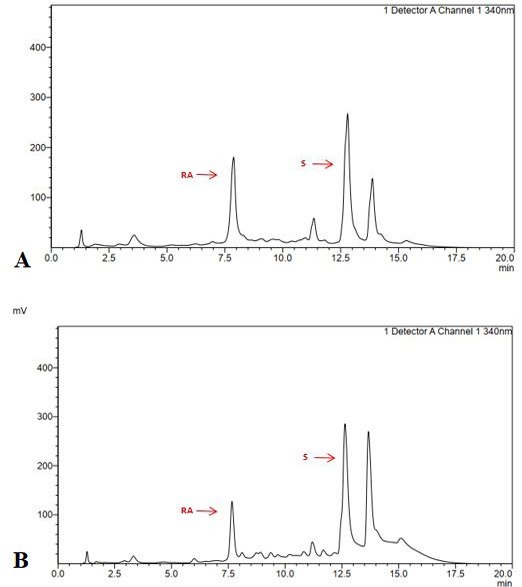
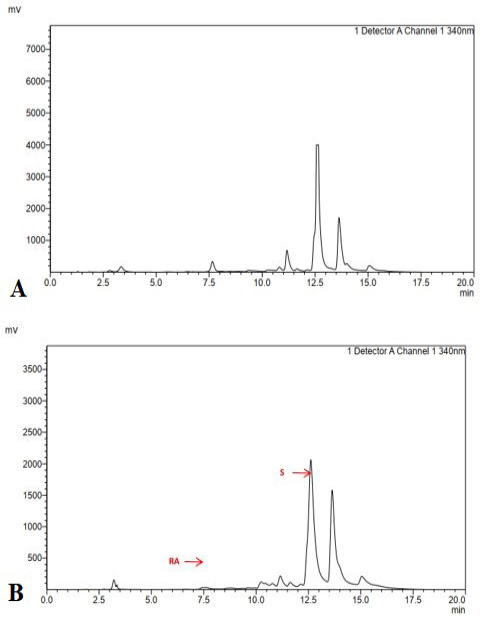
Chromatogram of ethanol extract of purple variety at 340.60 nm. a = in vitro culture b = wild type.
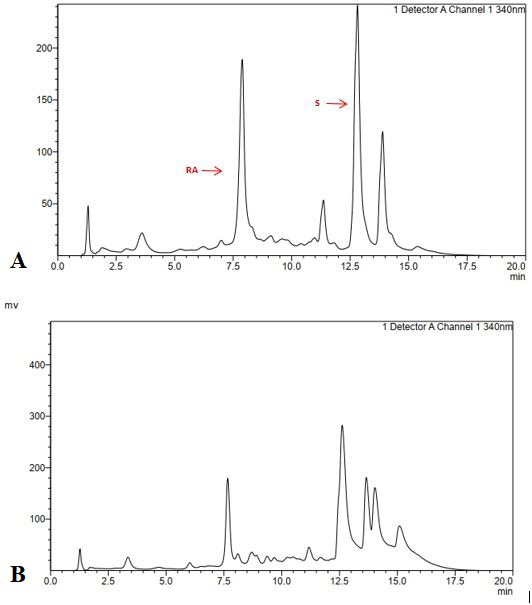
Chromatogram of ethyl acetate extract of white-purple variety at 340.60 nm. a = in vitro culture b = wild type.
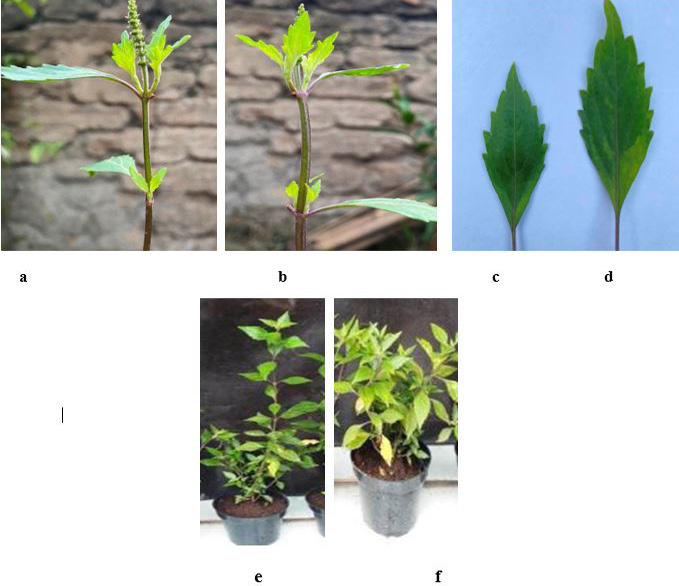
Morphology of leaves and stem of purple varieties of O. aristatus from in vitro cultures and wild type. a: purple stems (in vitro culture), b: purple stems (wild type), c: purple leaves (in vitro culture), d: purple leaves (wild type), e: purple varieties 5 months old (in vitro culture), f: purple varieties 5 months old (wild type).