ETV5 is a Putative Differentially Expressed Transcription Factor of Interleukin 1β Under Neuroinflammatory Conditions in Murine Cerebellum
ETV5 is a Putative Differentially Expressed Transcription Factor of Interleukin 1β Under Neuroinflammatory Conditions in Murine Cerebellum
Abeedha Tu-Allah Khan and Abdul Rauf Shakoori*
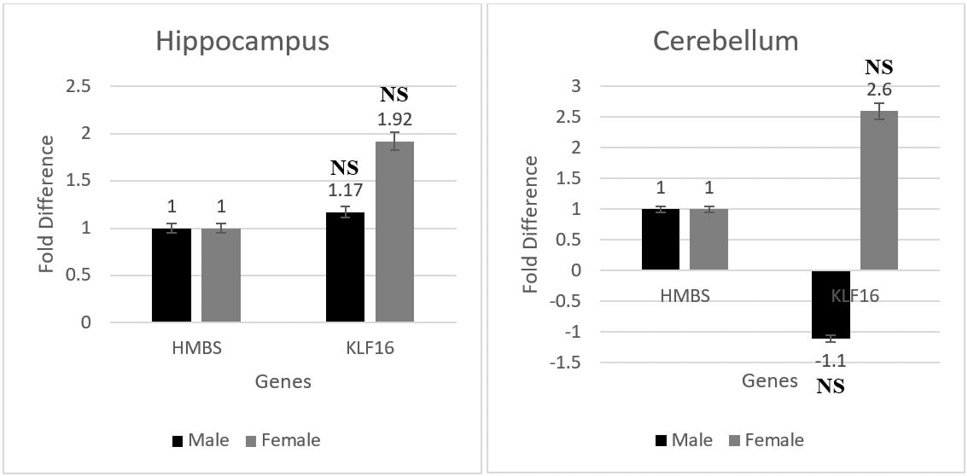
mRNA expression of the transcription factor Klf16 represented in terms of fold difference up/ down regulation in hippocampus and cerebellum. NS - (p > 0.05 = non-significant)
mRNA expression of the transcription factor Etv5 along with its interacting partners Cop1, GDNF, Det1, Bcl6b, and Dusp6, represented in terms of fold difference up/down regulation. A, male hippocampus; B, male cerebellum; C, female hippocampus; and D, female cerebellum. * (p < 0.05), ** (p < 0.005), *** (p < 0.0005), **** (p < 0.00005), and NS (p > 0.05 = non-significant).
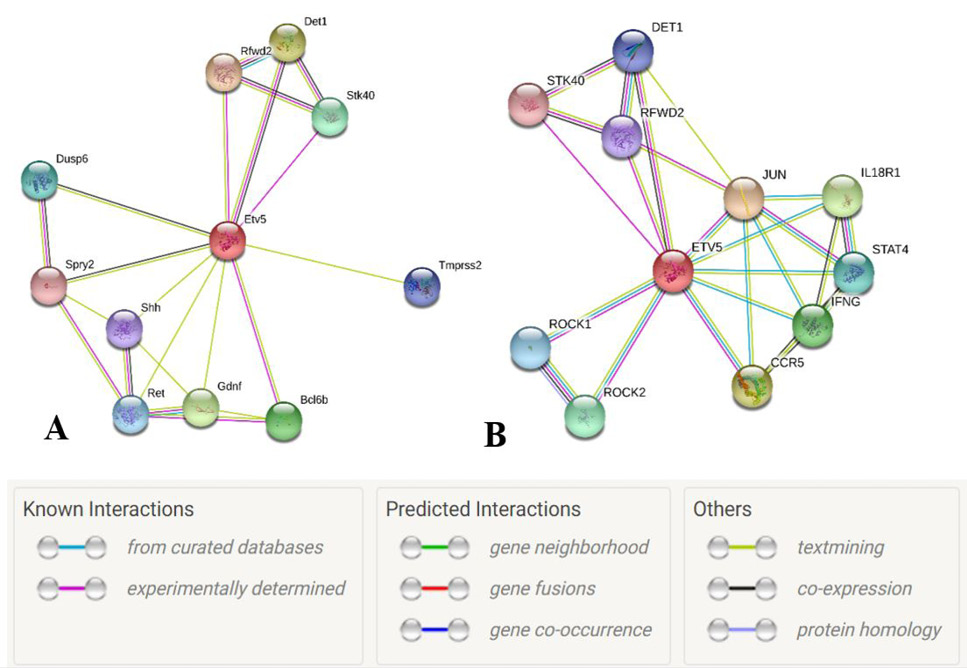
Node graph of the interacting partners of Etv5. A, Mus musculus and B, Homo sapiens, with proteins represented by network nodes. The node in red color is the query protein while other nodes are the proteins having first shell of interaction with the query protein (STRINGS, ETV5 Homo sapiens).
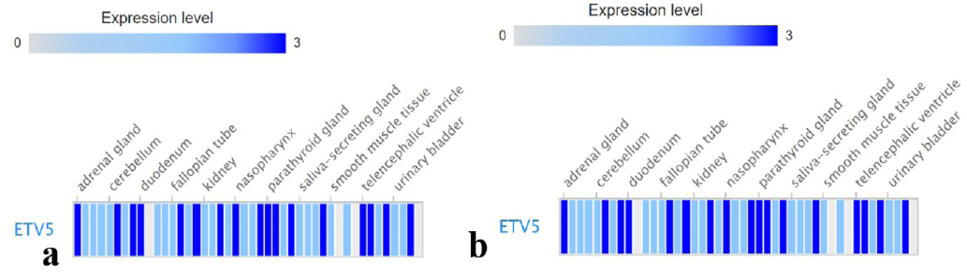
Protein expression levels of Etv5 in different tissues of human subjects. A, male; and B, female.
Dissection of murine brain to separate out hippocampus. A, Dorsal view of the mouse brain. On the lower side is the cerebellum and on the upper side are the cerebral cortices. Each cerebral cortex contains hippocampus embedded in its ventral inner side. B, right cerebral cortex is placed on its dorsal side with the crescent shaped hippocampus clearly visible. C, hippocampus flipped inside out; and D, hippocampus separated from the rest of the tissue.