Effect of Drying Methods on Physiochemical Characteristics and Mineral Composition of Mulberry Fruits
Effect of Drying Methods on Physiochemical Characteristics and Mineral Composition of Mulberry Fruits
Ishtiaq Ahmad1*, Muhammad Nafees1, Maryam2, Irfan Ashraf3, Ambreen Maqsood4 and Muhammad Saqib5
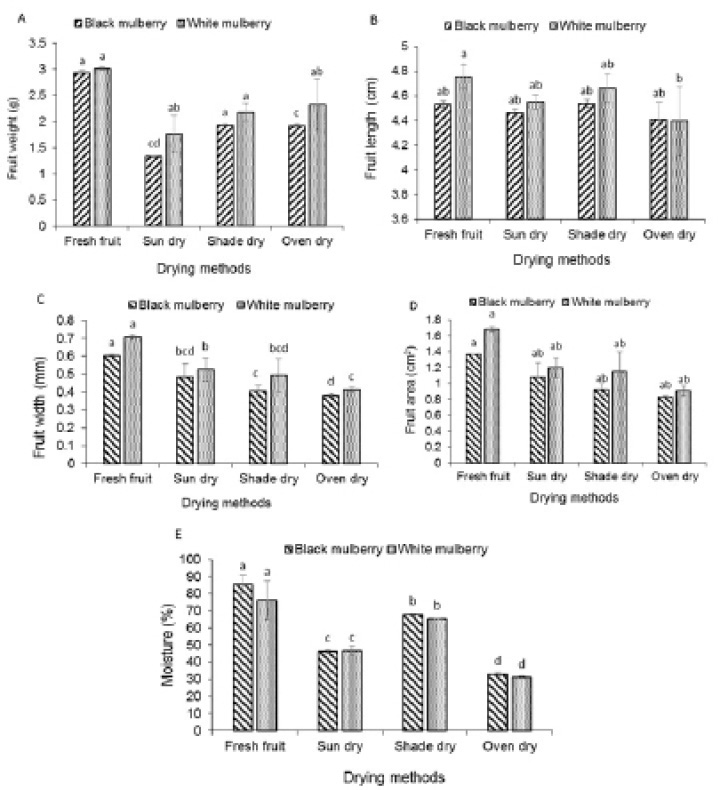
Effect of drying methods on, A) fresh and dry fruit weight, B) fruit length, C) width, and D) surface area, E) fruit moisture %age, on mulberry fruits. Similar letters indicate a non-significant difference (P ≤ 0.05) amongst the drying methods on two cultivars, the black and white mulberry.
Effect of drying methods on, A) Fe, B) Zn, C) Mn and D) Cu, contents in black and white mulberry fruits. Similar letters showed non-significant difference (P ≤ 0.05) among cultivars for different mineral contents affected by drying methods.