Effect of Blood Glucose Level of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Coronary Heart Disease on the Hypercoagulability and Thromboembolism
Effect of Blood Glucose Level of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Coronary Heart Disease on the Hypercoagulability and Thromboembolism
Qing Cao1, Wei Jiao2, Huihui Lu1, Jing Zhang2, Meiling Ren3, Yan Xu1* and Shuyang Hu1*
Effect of blood glucose level of patients on hypercoagulability. A, prothrombin time (PT); B, activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT); C, D-dimers (D-D); D, fibrinogen (Fb).
Effect of blood glucose level of patients on platelet functions. A, P-selectin (Ps); B, thrombus precursor protein (TpP); C, maximum platelet aggregation rate (MAR); D, mean platelet volume (MPV).
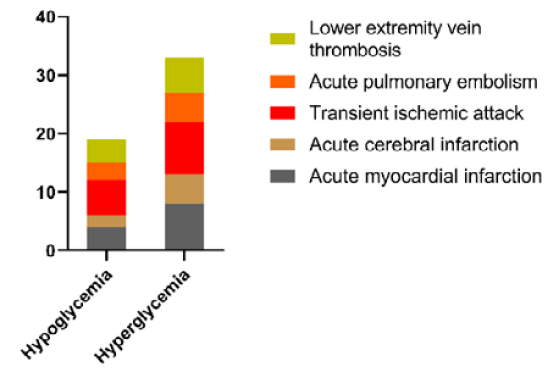
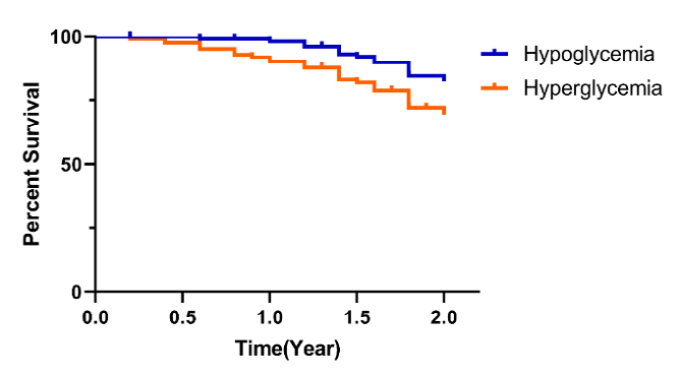
Effect of blood glucose level of patients on thromboembolism.
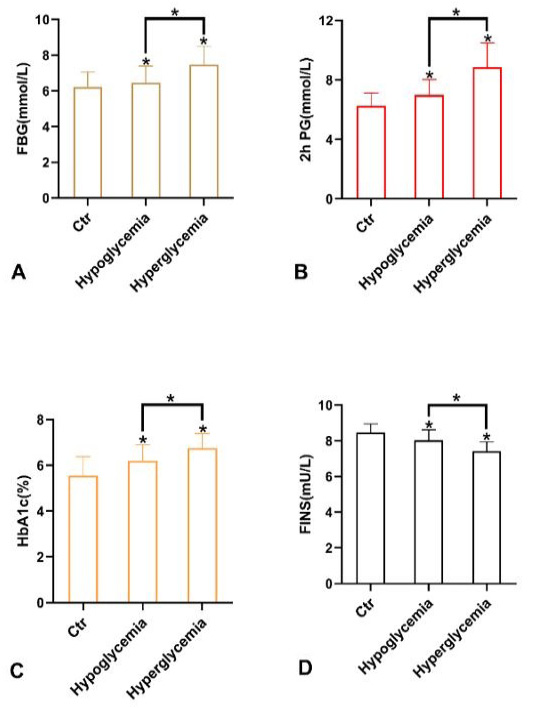
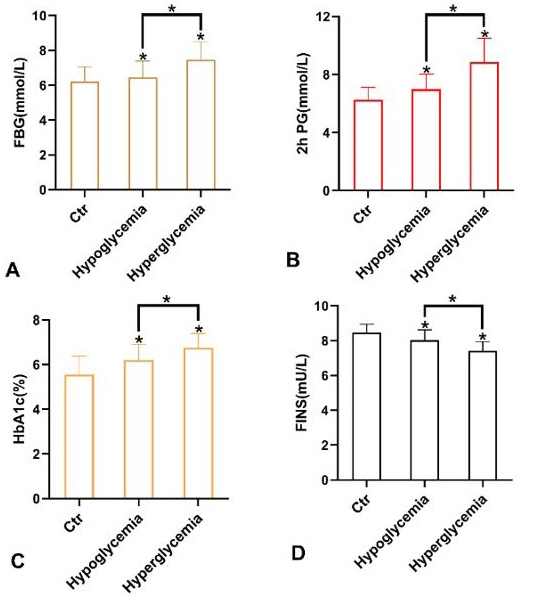
Effect of blood glucose level of patients on hypercoagulability. A, fasting blood glucose (FBG); B, 2 h postprandial glucose (2hPG); C, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c); D, fasting insulin (FINS).