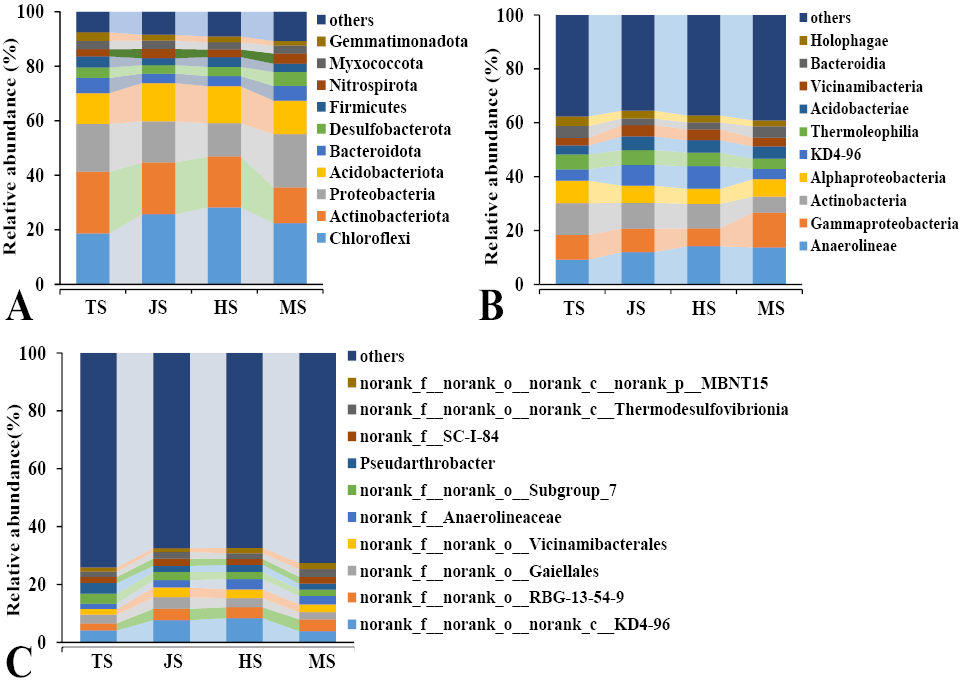
Effects of Rice Growth Stages on the Composition and Functional Potentialities of Rhizosphere Bacterial Community in Coupled Rice-Crab System
Effects of Rice Growth Stages on the Composition and Functional Potentialities of Rhizosphere Bacterial Community in Coupled Rice-Crab System
Yu Song1*, Yueping Wei2 and Peng Wang3
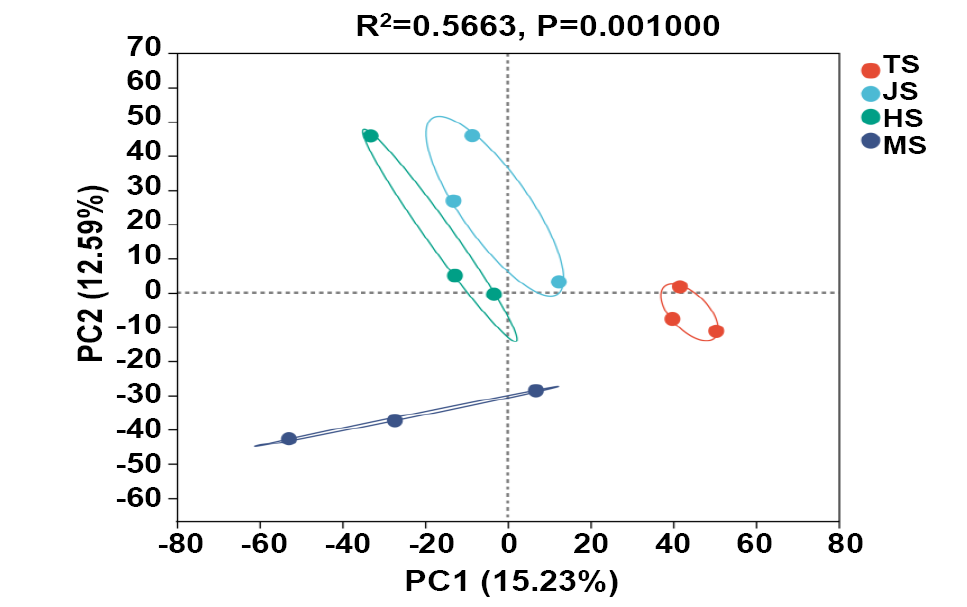
Principal component analysis (PCA) based on Bray-Curtis Distance Matrix for soil samples collected from the rhizosphere of the four different stages.
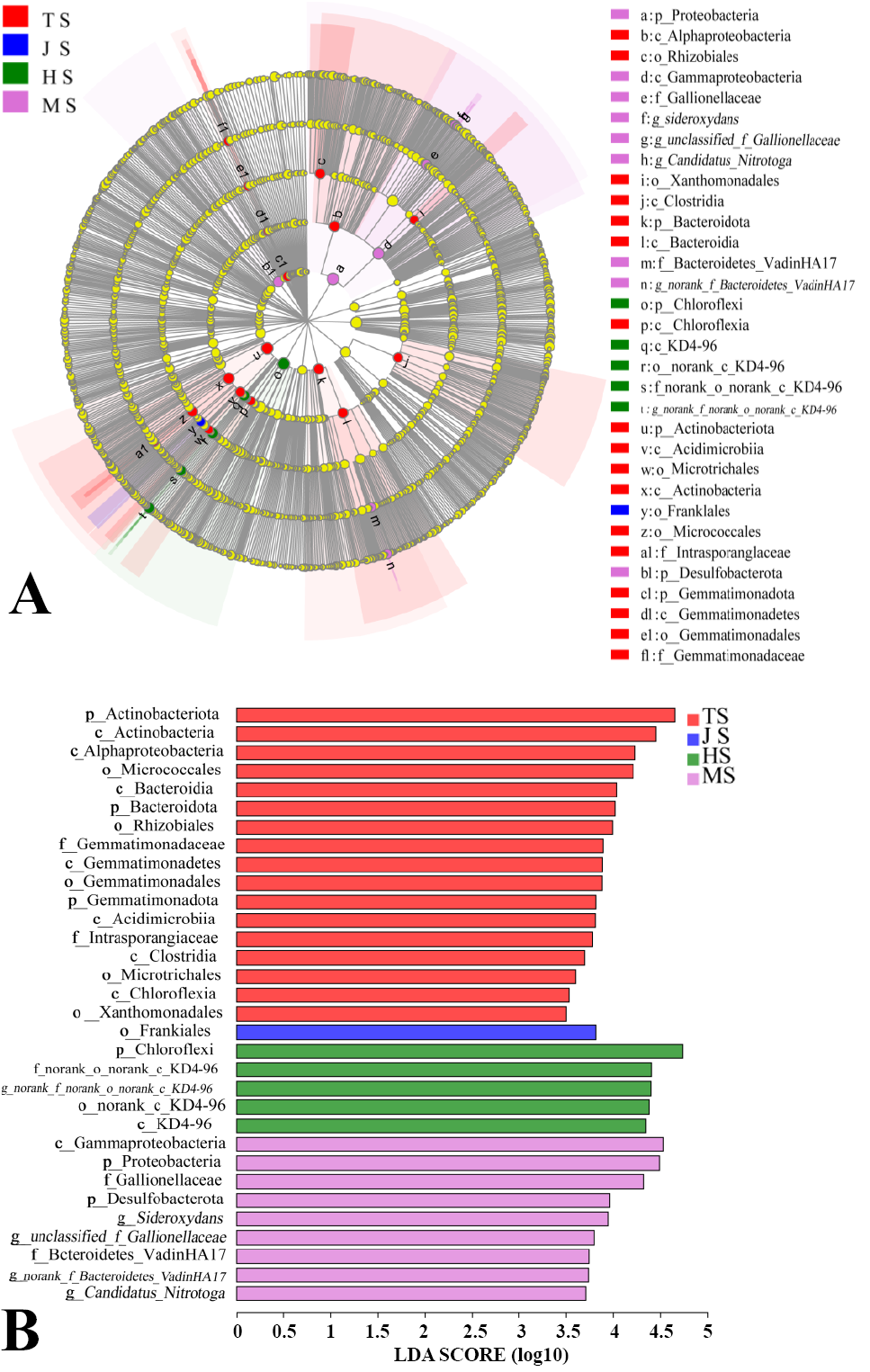
Cladogram showing the phylogenetic distribution of the bacterial lineages associated with rhizosphere soil from four growth stages in the rice-crab paddy field. (A) Indicator bacteria with LDA scores of 3.5 or greater in bacterial communities associated with soil from four stages in the coupled rice-crab paddy field. (B) Different coloured regions represent different constituents. Circles indicate phylogenetic levels from phylum to genus. The diameter of each circle is proportional to the abundance of the group.
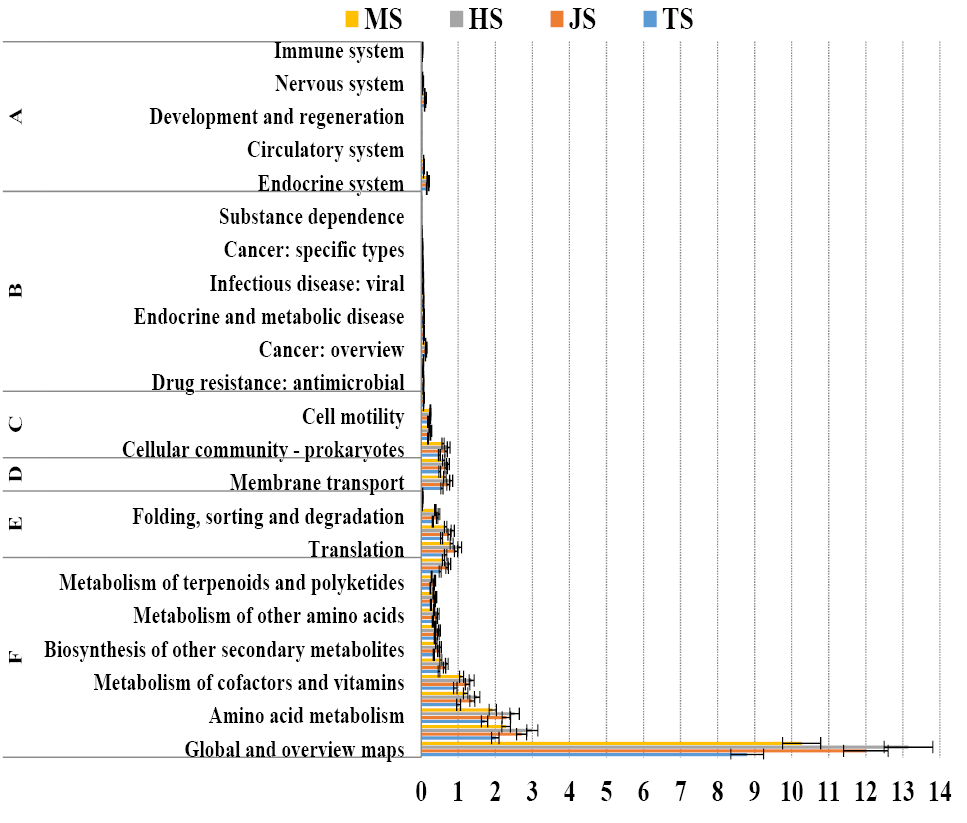
The relative abundance of rhizosphere soil bacterial community functions at four different stages in the coupled rice-crab system. A, organismal system; B, human diseases; C, cellular processes; D, environmental information; E, genetic information processing; F, metabolism.