Gross and Clinical Anatomy of the Skull of Adult Chinkara (Gazella bennettii)
Gross and Clinical Anatomy of the Skull of Adult Chinkara (Gazella bennettii)
Salahud Din1,*, Saima Masood1, Hafsa Zaneb1, Habib ur Rehman2, Saima Ashraf1, Imad Khan3, Muqader Shah4 and Syed Abdul Hadi1
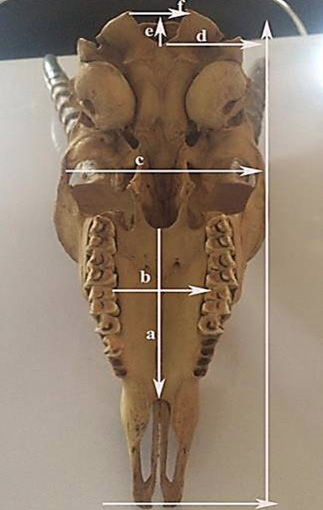
Orbit length (a), orbital width (b), maxilla length (c) and width (d), lacrimal bone length (e), lacrimal bone width (f), infra-orbital canal to the root of alveolar tooth (g), incisive bone Width (h) incisive bone length (i) and nasal bone length (j).
Length of palatine bone (a), width of palatine bone (b), skull width (c) height of the foramen Magnum (e) and width of the foramen magnum (f).
Width of the foramen magnum (a), width of the Intercondylar bones (b), height of occipiatal bone (c) and width of occipital bone (d).
Mandilbe of adult chinkara showing Interval from lateral alveolar root to the mental foramen (a), mental foramen (b) and space from mental foramen to the caudal mandibular border (c).
Mandilbe of adult chinkara showing mandibular length (a), mandibular foramen to the base of mandible (b), caudal border of mandible to below mandibular foramen(c), condyloid fossa to the base of the mandible (d), condyloid fossa to the height of the mandible (g) and maximum mandibular height (e).
Dorso-lateral view of the skull of male chinkara showing incisive bone (1), nasal process of incisive bone (2), maxilla bone (3), infraorbital foramen (4), parietal bone facial tuberosity (5), lacrimal (6), nasal process (7), nasal bone (8), orbital rim (9), cornual process of frontal bone (10), zygomatic bone (11), zygomatic arch (12), temporal fossa (13), tympanic bulle (14), paracondylar process (15) and orbit (16).
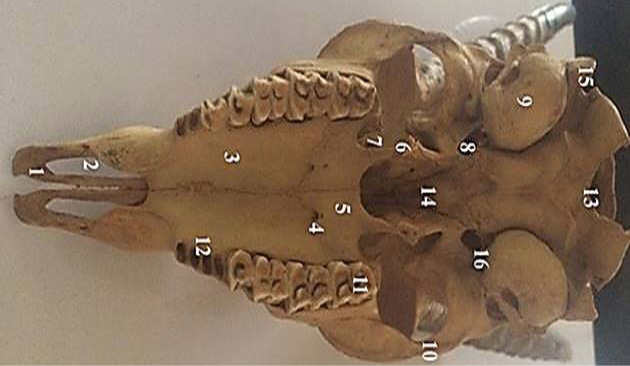
Ventral view of the chinkara skull showing incisive bone (1), palatine fissure (2), maxillary process of palatine bone (3), major palatine foramen(4), horizontal palate of palatine bone (5), hamalus of pteygoid bone (6), sphenoid of palatine bone (7), oval foramen (8), tympanic bulla (9), zygomatic arch (10), molar bone (11), alveoli (12) foramen magnum (13), vomar bone (14), paracondylar process(15) and muscular process (16).
Caudal view of the chinkara skull showing parietal bone (1), nuchal crest (2), external occipital protruberance (3), zig zag suture joint (4), paracondylar process (5), lateral part of the occipital bone (6), occipital crest (7), occipital condyle (8) and mastoid process (9).
Lateral view of the chinkara skull showing tympanic bulla (1), external acoustic meatus (2), temporal fossa (3), oval foramen (4), spheniod bone (5), orbit (7) and alveolar border (8).
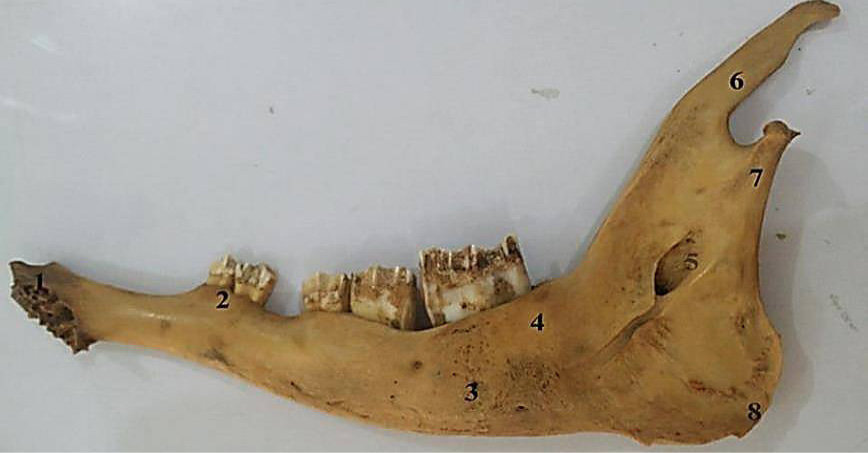
Medial view of the mandible of adult Chinkara showing alveolar sockets for incisors (1), first premolar (2), molar (4), mandibular foramen (5), coronoid process (6) and posterior border of ramus (7).
Lateral view of the mandible of adult Chinkara showing mental foramen (1), first premolar (2), premolar (3, 4), molar (5), mandibular tuberosity (6), mandibular angle (7), coronoid process (8) and condylar process (9).