Histopathological and PCNA-Based Immunohistochemical Assessment of Pumpkin and Grape Seed Extracts in Protecting Male Rat Accessory Glands Under Chemotherapeutic Stress
Histopathological and PCNA-Based Immunohistochemical Assessment of Pumpkin and Grape Seed Extracts in Protecting Male Rat Accessory Glands Under Chemotherapeutic Stress
Ibrahim Elmaghraby1, Zeinab Said2, Marwa Darweish1, Doaa Galal El-Sahra3 and Ahmed Ibrahim El-Nemr4*
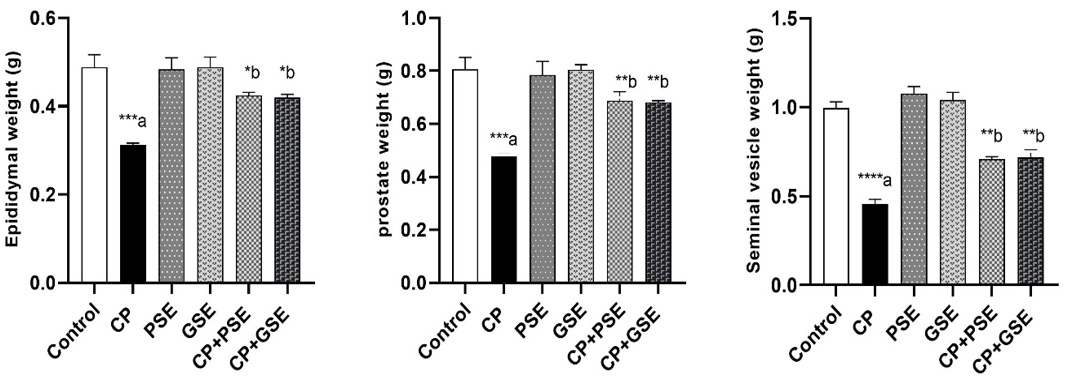
Effect of CP, PSE and GSE on epididymal, prostatic and seminal vesicle weight ****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, *p < 0.05. (a) versus the control group, while (b) versus the CP.
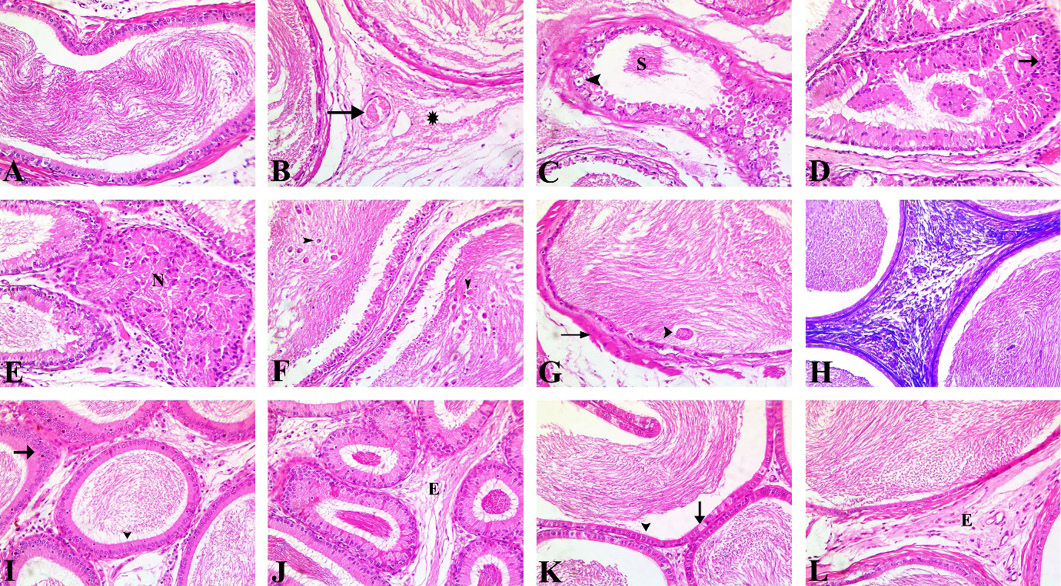
H & E-stained sections of epididymis of different experimental groups, x200. (A) The control group showed the normal histological structure of epididymal tissue. (B-H) The CP-intoxicated group, (B) showed wide interstitial spaces with congested blood vessels (arrow), edema and hemorrhage in between the epididymal tubules (asterisk), (C) Vacuolated epididymal epithelium (arrowhead) with necrotic sperm (S) in their lumen, (D) Some epididymal tubules displaying either hyperplasia (arrow), or (E) necrosis (N) in their lining epithelium, (F) Desquamated epithelial cells (arrowhead), (G) giant cell formation (arrowhead) and fibroplasia (arrow), (H) that stained blue with Masson Trichrome stain. (I, J) The epididymal tissue in pretreated with GSE showed (I) restored histoarchitecture of epididymal tubules lined with stereociliated columnar epithelium (arrowhead) with mild degree of hyperplasia (arrow), (J) some necrotic sperm inside the lumen and mild interstitial edema (E). (K, L) PSE pretreated group showed (K) nearly normal epididymal lining epithelium (arrowhead) with only mild vacuolation in lining epithelial cells (arrow), (L) mild oedema (E) in between the epididymal tubules.
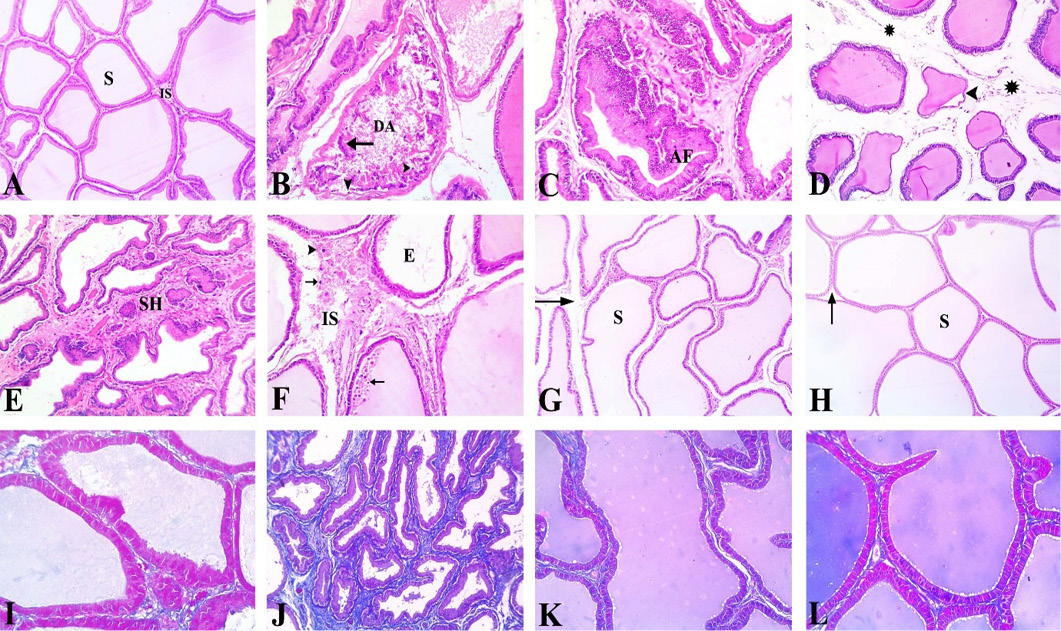
Photomicrograph of H&E-stained (A-H) and Masson Trichrome stained (I-L) prostate section of different experimental groups, x200. (A) Control group showing different sizes of acini lined with tall columnar cells with oval nuclei and occasional papillary infoldings. Homogenous acidophilic secretion (S) fills the lumen of acini. Narrow inter-acinar spaces (IS) occupied by fibro-muscular stroma separated the acini. (B-F) CP group, (B) Destructed acini (DA) filled with detached epithelial cells (small arrow) with small pyknotic nuclei (arrowhead), (C) Marked epithelial hyperplasia with arborization folds (AF) into the acinar lumen, (D) Atrophied prostatic acini with marked thinning of the epithelial lining (arrowhead) and increased stromal prominence (asterisk), (E) Fibromuscular stromal hyperplasia (SH) with hyaline plaques, (F) Wide inter-acinar spaces (IS) with noticeable hemorrhage (arrowhead), empty prostatic acini (E) and inflammatory cells (arrow) infiltration. (CP+GSE) and (CP+PSE) groups (G, H) respectively show the normal appearance of prostatic folding and secretion (S) with some stromal widening (arrow). (I) Control group showing little collagen in interstitial tissue. (J) CP group shows excessive bluish stained collagen. (K, L) CP+GSE and CP+PSE groups showing decreased collagen in the interstitial tissue.
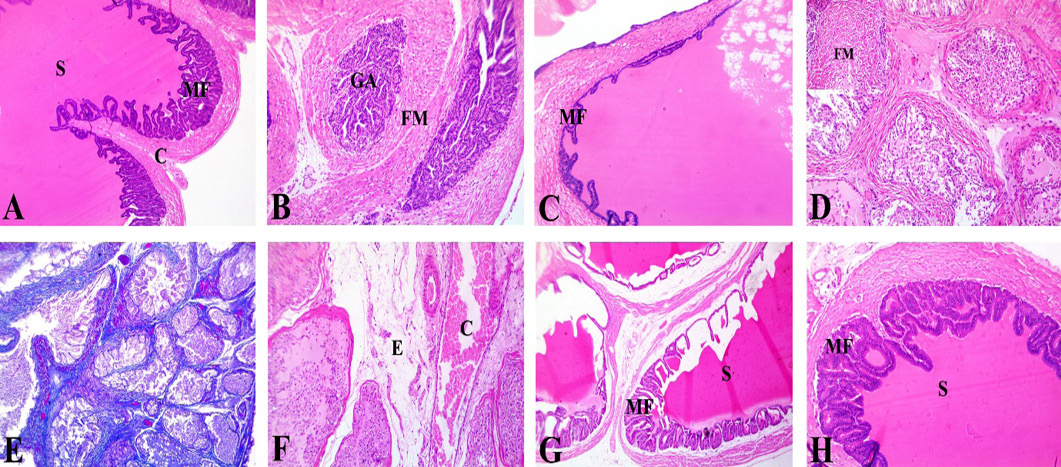
Photomicrograph of H&E-stained seminal vesicle section of different experimental groups, x200. (A) Control group showing normal histological structure with acidophilic secretion (S) in the lumen supported by a well-developed fibromuscular capsule (C). The parenchyma showed anastomosing mucosal folds (MF). (B- F) CP group, (B) Glandular atrophy (GA), with a reduction in glandular components, and prominent fibromuscular stroma (FM), (C) Alveoli showing a reduction in mucosal fold height (MF), with flattened papillary folds, (D) Necrosis of the lining epithelium with detached epithelial cells and little acidophilic secretion, Inset showing prominent fibromuscular stroma (FM) and monocellular inflammatory cell infiltrations, (E) Fibromuscular stroma showing positive color for Masson trichrome stain, (F) widespread congestion (C) and edema (E) between the degenerated acini. (G, H) CP+GSE and CP+PSE group respectively, showing normal epithelium, mucosal folds (MF), and secretion (S) with restoration of most of the normal architecture of seminal vesicle.
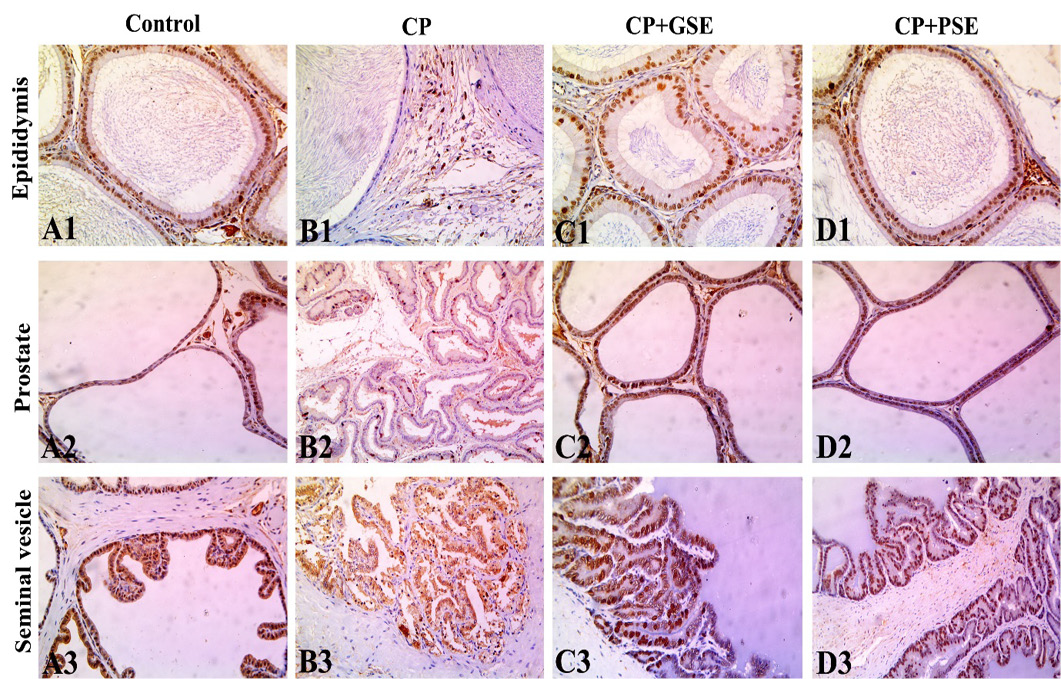
Photomicrographs of PCNA expression in the epididymal, prostatic and seminal vesicle tissues, showing an intensive brown positive reaction in the nuclei of epithelial cells in the control group (A1, A2, A3), weak positive reaction in an intoxicated group with CP (B1, B2, B3), While rats given CP and pretreated with GSE (C1, C2, C3) or PSE (D1, D2, D3) had a greater increase in PCNA expression in the nuclei of epithelial cells. All magnifications were x200.