Identification of Myomaker in Yellowfin Seabream (Acanthopagrus latus) (Hottuyn, 1782) and its Transcriptional Regulation by Two MyoDs
Identification of Myomaker in Yellowfin Seabream (Acanthopagrus latus) (Hottuyn, 1782) and its Transcriptional Regulation by Two MyoDs
Kecheng Zhu1,2,3, Peiying He1, Baosuo Liu1,2,3, Huayang Guo1,2,3, Nan Zhang1,2,3, Liang Guo1,2,3, Shigui Jiang1,2,3 and Dianchang Zhang1,2,3,*
Sequence characterization of the Myomaker gene in Acanthopagrus latus. A, the nucleotide sequence of the Myomaker gene and the deduced amino acid sequence of T. ovatus. Initiation and termination codons are marked by green. Six transmembrane domains are shown in red; B, hydrophobicity profile of Myomaker; C, TMHMM posterior probabilities of Myomaker.
Amino acid sequences of Myomaker homologues in vertebrates. A, amino acid alignment of Myomaker proteins from A. latus (Al), Oreochromis niloticus (On), Xiphophorus maculatus (Xm), Oryzias latipes (Ol), Poecilia formosa (Pf), Danio rerio (Dr), Tetraodon nigroviridis (Tn), Gallus gallus (Gg), Latimeria chalumnae (Lc), Pelodiscus sinensis (Ps), Homo sapiens (Hs), and Mus musculus (Mm). Conserved sequences are marked with asterisks. B, Percent identities of Myomaker amino acids compared to the above 12 Myomaker amino acids, and the accession numbers of the Myomaker sequences used are also listed.
Phylogenetic relationship and structure of the Almyomaker gene with other vertebrates. Genome structure analysis of Almyomaker genes according to their phylogenetic relationship. Lengths of exons and introns of each Myomaker gene are displayed proportionally. Different colour boxes and lines represent exons and introns, respectively. The identical colour boxes represent homologous sequences.
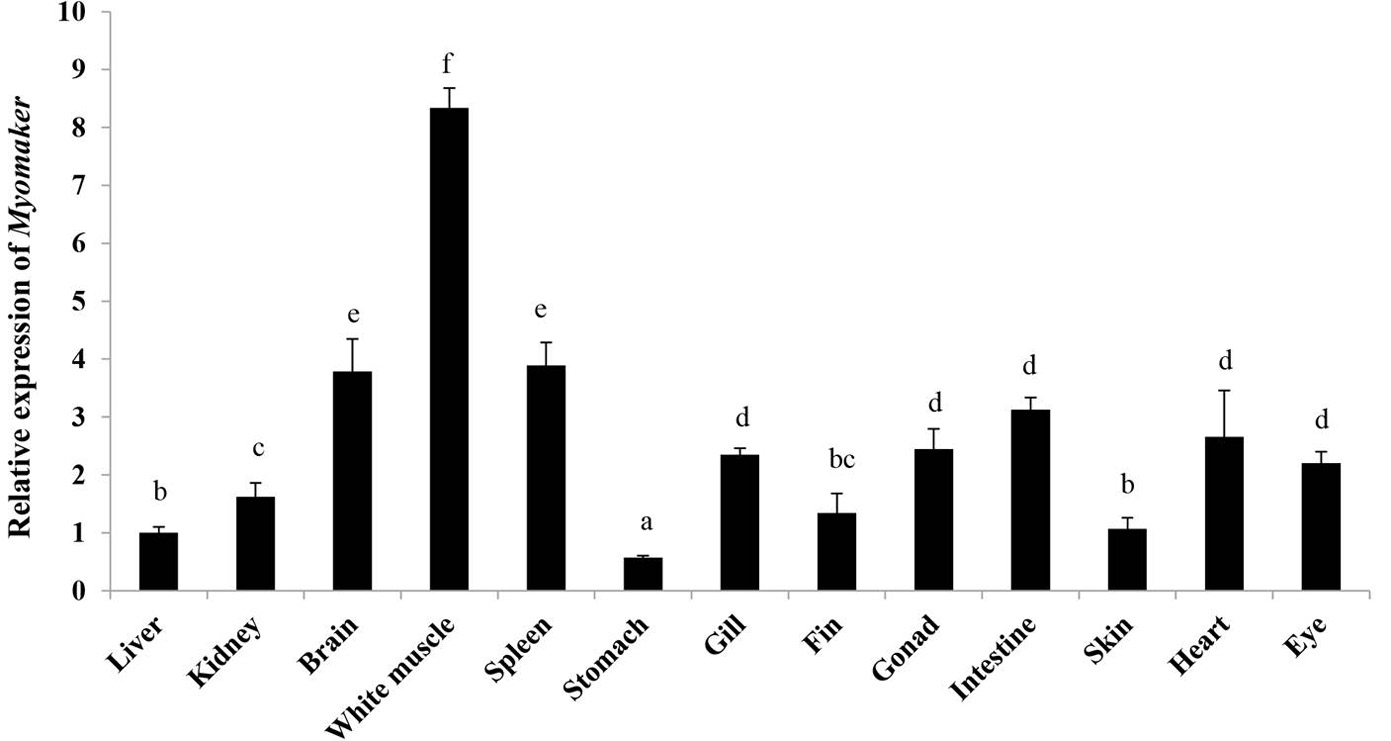
Relative expression levels of Almyomaker in different tissues. The twelve tissues are heart, gonad, eye, skin, brain, fin, spleen, small intestine, gill, white muscle, kidney, liver, and stomach. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
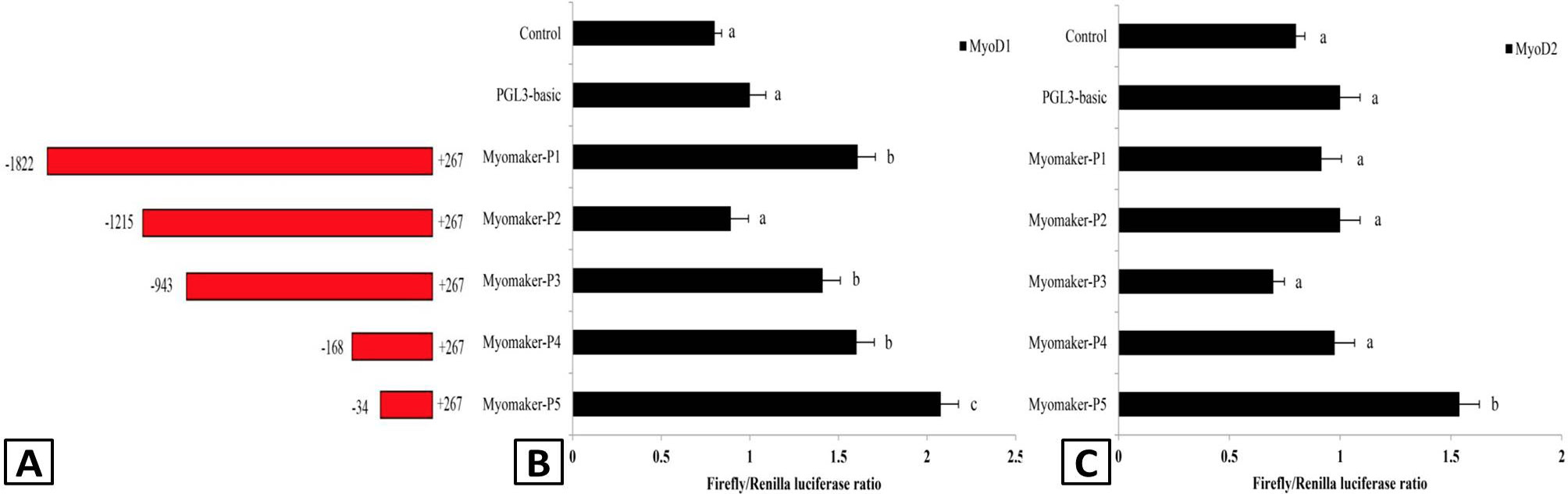
Promoter activity analysis of the Almyomaker gene. A, the structure of the Almyomaker promoter and 5’UTR region. Five recombinant plasmids were denoted myomaker-p1 (-1822 to +267), myomaker-p2 (-1215 to +267), myomaker-p3 (-943 to +267), myomaker-p4 (-168 to +267) and myomaker-p5 (-34 to +267). B and C, Transcriptional activity of the Almyomaker promoter. These plasmids were transfected along with the transcription factors MyoD1 (B) and MyoD2 (C) into HEK 293T cells. Dual-luciferase activity was driven by the Almyomaker promoter upon the transfection of pcDNA3.1-MyoD1, pcDNA3.1-MyoD2 or pcDNA3.1 into HEK 293T cells. Data are presented as the means of three replicates ± SE. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
Construction of truncated mutants for the identification of predicted transcription factor (TF) binding sites in the Almyomaker candidate sequence. A, the nucleotide sequence and predicted binding sites in the core region of the Almyomaker-p5. TSS indicates the transcription start site. Effects of three mutants on Almyomaker-p5 promoter activity transfected with pcDNA3.1-MyoD1 (B) or pcDNA3.1-MyoD2 (C) or pcDNA3.1. Binding sites are shown with boxes. Data are presented as the means of three replicates ± SE. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).